CHAPTER 6 THE X-RAY BEAM SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES NOTED IN
advertisement

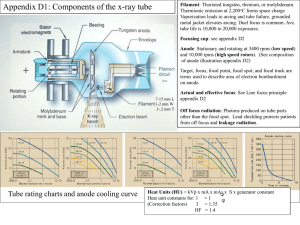
CHAPTER 6 THE X-RAY BEAM SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES NOTED IN THIS POWER POINT BEGIN ON PAGE 110-117. Four timers • 1) Synchronous-min time is 1/60. Increase in equal multiples • 2) Electronic-most accurate/controlled by microprocessor • Where are 1 and 2 located in the circuit? • mAs time and falling load generator-let’s discuss this! • AEC AEC • WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF AN AEC? • HOW DO YOU USE THEM WHEN POSITIONING? • CHAMBERS VS. PHOTOMULTIPLIERS • Can they produce the same density of radiograph for any size patient? Ion chamber • Waits for a charge • Sequence – – – – X-ray Patient Ion chamber IR vs photomultiplier or photodiode • Collects a charge via light • Sequence – – – – X-ray Patient Special cassette photodiode High Voltage Transformer • What do you remember? RECTIFICATION • Unrectified • Half wave rectified • Fully rectified Phases Voltage Ripple page 30 Fauber figure 2-12 • Single • 100% • Three phase • Three phase/6 pulse • 13 or 14% • Three phase/12 pulse • 3 or 4% • High Frequency • How do these phases impact technique?? • Less than 1% POWER RATING • • • • • UNIT OF MEASUREMENT OF POWER IS WATTS AMPS MEASURES THE QUANTITY OR QUALITY? Volts measures the ________________________ Amps=current Volts = potential • Try this problem: If your kitchen is on a 25 amp circuit breaker and 110 volts is the available voltage what is the maximum watts this circuit can handle? • ON TO CHAPTER SEVEN!! CHAPTER SEVEN • • • • REVIEW THE PROTECTIVE HOUSING Let’s dissect the cathode What happens at the cathode? Focusing cup – Imbedded in cathode – Two (page 15 in fauber, figure 2-1) – Confines the electron beam • Grid controlled tubes • Allows for tube to be turned off and on quickly • Space charge and space charge effect – High mAs and low kVp can be space charge limited..why? The Anode • Three functions of the anode -What do you know already about the anode • The target • What does the rotor do? • Note: please skip induction motors at this time Focal spot, line focus principle and anode heel effect • Focal spot and target angle (Fauber pg 16 figure 2-2) • The smaller focal spot – More concentration of heat – Better detail – Usually located in the smaller angle • Large focal spot – – – – Less concentration of heat Less detail Larger angle Page 25 Fauber, figure 2-10 Line Focus Principle • Effective focal spot size is always smaller than the actual focal spot size • Fauber-pg 34 figure 2-13 and pg 35 figure 2-14 Anode Heel effect • • • • Bushong pg 130, pg 7-20 The heel effect is more or less with a greater angle? Which side has greatest intensity? Off Focus radiation How is heat dissipated in the tube? • Tube rating charts • Heat units • Anode cooling charts