i. male reproductive system
advertisement

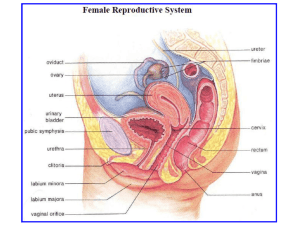
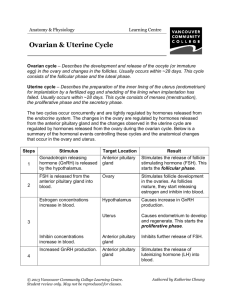
THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM I. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A. Introduction 1. Testes outside the abdominal cavity within the scrotum a) Sterility results if testes fail to descend due to higher temperature of the abdominal cavity b) Suspended by the spermatic cord (1) Composed of connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels (2) Descends out of the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal (a) This is a weak portion of the abdominal wall subject to hernias 2. Includes seminiferous tubules and interstitial tissue a) Sperm is produced in seminiferous tubules b) Testosterone is produced in the interstitial tissue (1) Male sex hormone B. Seminiferous tubules 1. One to 3 seminiferous tubules are found in each testes a) Total length ~ 250 cm b) Each undergoing spermatogenesis 2. Spermatogenesis a) Spermatogonia (1) Located next to the outer wall (2) Undergo meiosis to form spermatocytes b) Spermatozoa (1) Male gametes 3. Sertoli cells a) Nurse degenerate sperm cells C. Sperm 1. Head a) Contains 23 chromosomes within a nucleus b) Covered by the acrosome (1) Contains enzymes that facilitate penetration of the egg 2. Middle-piece a) Contains mitochondria to produce energy for sperm motility 3. Tail a) Provides motility D. Genital tract 1. Epididymis a) Coiled tube lies outside each testis b) Used for maturation and storage of sperm. 2. Vas deferens a) First part stores sperm b) Duct passes through inguinal canal into the abdomen and empties into the urethra 3. Urethra a) Duct within the penis that passes to the outside of the body b) Also carries urine from the urinary system E. Seminal fluid 1. Seminal vesicles a) Fructose (1) Energy for sperm b) Prostaglandins (1) Causes uterus to contract to propel sperm toward the egg 2. Prostate gland a) Slightly basic (1) Neutralizes the acidity of the females reproductive tract b) May enlarge in males over 40 (1) Makes urination difficult and painful 3. Cowper's glands a) Lubrication (1) Helps penis penetrate vagina b) Contains some sperm (1) Makes withdrawal method of contraception unreliable II. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A. Ovaries 1. Contain follicles a) Oocyte plus surrounding follicle cells b) Females are born with about 2 million follicles (1) Reduced to about 350,000 at puberty (2) Only about 400 ever reach maturity in her lifetime (a) One a month from puberty to menopause 2. Follicle development a) Primary follicle's oocyte divides meiotically to form the secondary oocyte and a polar body (1) Primary oocyte contains largest amount of cytoplasm (a) Contains23 chromosomes (2) Polar bodies has small amount of cytoplasm and disintegrates b) Graafian follicle (1) Larger in size due to accumulation of fluid (2) Oocyte eventually ruptures out during ovulation c) Corpus luteum (1) Remaining follicular cells after ovulation (2) Degenerates if pregnancy does not occur (3) If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum persists and secretes estrogen and progesterone B. Genital tract 1. Oviducts (fallopian tubes) a) Tubes from the ovary to the uterus b) Not directly attached to ovary (1) Fimbrae (a) Finger like projections that collect eggs toward the oviduct (2) If egg does not enter oviduct and is fertilized, this results in an ectopic pregnancy (a) Pregnancy that begins outside the uterus c) Cilia (1) Move egg towards uterus d) Sexually transmitted diseases may cause scarring of oviduct (1) This prevents eggs from going through resulting in sterility 2. The Uterus a) Gross anatomy (1) Oviducts join anteriorly while the cervix enters vagina posteriorly at right angles (a) Cancer of the cervix is detected by the Pap smear (b) If cancerous, hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or ovariohysterectomy (removal of uterus and ovaries) may be recommended b) Endometrium (1) Outer lining (2) Participates in the formation of the placenta (3) Shed during the uterine cycle each month in the non-pregnant female C. Vagina 1. Receives the penis 2. Serves as the birth canal III. FEMALE HORMONE LEVELS A. Regulation of cycle 1. Hypothalamus secretes gonadotropic-releasing hormone a) Gonadotropic-releasing hormone triggers anterior pituitary to produce two hormones (1) Follicle-stimulating hormone (a) Stimulates follicles in ovary to produce eggs (b) Causes follicles to secrete estrogen (i) Negatively feedbacks the production of follicle stimulating hormone by the pituitary (ii) Causes development of the endometrium (2) Luteinizing hormone (a) Causes the development of the corpus luteum (b) Corpus luteum secretes progesterone (i) Negatively feedbacks the production of luteinizing hormone by the pituitary (ii) Causes development of the endometrium B. Ovarian Cycle 1. Follicular phase a) First half of 28-day cycle (days 1 to 13) b) Follicle stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary stimulates follicular development in ovary (1) Follicle produces estrogen c) Ovulation on 14th day 2. Luteal phase a) Second half of 28-day cycle (days 15 to 28) b) Luteinizing hormone from anterior pituitary promotes development of the corpus luteum (1) Secretes progesterone (2) High progesterone inhibits (negative feedback) LH secretion from anterior pituitary so that corpus luteum begins to degenerate. As luteal phase ends, menstruation occurs. 3. Uterine Cycle a) Menstrual period (1) Days 1 to 5 (2) Low levels of estrogen and progesterone cause endometrium to disintegrate b) Proliferative phase (1) Days 6 to 13 (2) Endometrium becomes thicker and more vascular due to increased amounts of estrogen c) Secretory phase (1) Days 15 to 28 (2) Endometrium doubles further in thickness and uterine glands mature and secrete mucus due to production of progesterone by the corpus luteum (a) Ready to receive the developing embryo (3) If not pregnant, corpus luteum degenerates and less hormones cause uterine lining to break down C. Pregnancy 1. Definition a) When embryo embeds in the endometrial lining (implantation) 2. Menstruation does not occur a) Production of estrogen and progesterone by the corpus luteum and later the placenta maintains the endometrium 3. Ovulation does not occur a) High levels of estrogen and progesterone prevent the pituitary from producing follicle stimulating hormone 4. During implantation, the outer layer of cells surrounding the embryo produce human chorionic gonadotropic hormone a) Pregnancy test is based on the presence of human chorionic gonadotropic hormone in the blood and urine as early as 10 days after conception b) Prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum 5. Placenta a) Produces human chorionic gonadotropic hormone, estrogen and progesterone (1) Maintains the endometrium lining of the uterus IV. Shuts down the anterior pituitary so that no new follicles mature