Development of Transmission System in India
advertisement

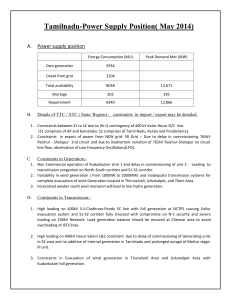
India - Present Power Scenario • Generation Total Installed Capacity – 228.7 GW (As on 30.09.13) NR NER ER WR : 132 GW • Growth Rate : 9 – 10 % (per annum) KS HA DW EE AN & ANDAM AR N IC O B SR LA • Peak Demand P Evolution of National Grid State Grids by SEBs National Grid Interconnecting Regional Grids with HVDC Regional Grids with ATS of Central Generation 2000 onwards 1990s 1970-80s (Paradigm Shift from self sufficiency at Regional level concept to National level) 1950-60’s IR Capacity (MW) Local 100000 1950’s 50000 5100 14100 27750 66400 0 IX Plan X Plan XI Plan XII Plan Five Regional Grids Two Frequencies August 2006 North synchronized With Central Grid March 2003 West synchronized With East & Northeast NEW Grid October 1991 East and Northeast synchronized South Grid Central Grid MERGING OF MARKETS North West South East Northeast Five Regional Grids Five Frequencies Installed Capacity 229 GW 4 Transmission Network - Present Transmission network The ‘Electrical’ Regions NORTHE RN REGION 1 spread geographically over 3.3million sq km : Inter-State and Intra-State level Transmission line : 2,80,571 ckm (POWERGRID : 1,020,000 ckm) NORTHEASTER N REGION EASTER N REGION WESTE RNREGI ON 765kV : 7910 ckm 400kV : 1,20,693 ckm 220kV : 1,42,536 ckm HVDC Bipole (±500kV) : 9,432 ckms Transformation capacity (MVA/MW) HVAC :474,091 MVA (POWERGRID : 170,000MVA, 171 S/s) 2 SOUTH ERN REGION − 765kV : 56,500 MVA − 400kV : 170,397 MVA − 220kV : 247,194 MVA HVDC : 13,500 MW FSC – 33nos., TCSC – 6 nos. Inter-Regional Capacity - Existing Present IR Capacity – 31,850 MW NR 6,220 MW NER 14,230 MW WR WR 4,390 MW 1,520 MW ER 1,260 MW 3,630 MW SR 6 Players in the Power Sector Generators Central/State GENCO, IPP, Captive CTU Inter-State Trans. system, Open Access STU Intra-State Tr./Sub-tr. system DISCOMS Consumers Industries, household, agriculture System Operator Power Exchange Traders Role of POWERGRID as CTU • To undertake transmission of electricity through ISTS • To discharge all functions of planning and co-ordination relating to ISTS with Central Govt, CEA, RPC, STU, Trans Licensees. • To ensure development of an efficient, co-ordinated and economical system of ISTS lines for smooth flow of electricity from generating stations to the load centres • To provide non-discriminatory access to its transmission system for use by any licensee or generating company on payment of the transmission charges; or any consumer as and when such open access is provided by the State Commission Grid Management - Hierarchy NLDC: Ensure integrated operation of National Grid 5 31 RLDC: Ensure integrated operation of Regional Grid SLDC: Ensure integrated operation of State Grid NATIONAL GRID - FUTURE Projected Power Scenario NEED OF NEW INITIATIVES IN TRANSMISSION # Considering 9% GDP growth rate 205GW Present Generation Capacity & Demand - 228 GW & 132 GW ** Source- Planning commission report on IEP Demand Pattern in India Ahmedabad Mumbai & Pune Hyderabad Bangalore & Chennai Source: NASA Satellite Snapshot Energy Resource Map Energy resources (coal, water etc.) unevenly distributed E x p e c te d G e n e ra tin g S ta tio n s - 2 0 2 5 Hydro E x p e c te d In s ta lle d C a p a c ity (2 0 2 5 ) : 6 ,0 0 ,0 0 0 M W Jam m u L u d h ia n a S IK K IM D e lh i NEPAL BHUTAN P a rta b p u r G u w a h a ti J a ip u r Lucknow DESH G a n d h in a g a r AN ER V in d h y a c h a l K o lk a ta In d o re P ip a v a v K o d e rm a B A N G L A MY P a tn a S asan M u d ra NER C H IC K E N NECK AR RAPP MM NR Bhopal K o rb a A k a lta ra WR R a ip u r T a lc h e r/Ib V a lle y L a ra D a rlip a li B h u b a n e s w a r M um bai V iz a g H y d e ra b a d M a n g a lo re S im h a d ri SR T a d ri K a ig a LEG END K ris h n a p a tn a m B a n g a lo re E n n o re C hennai S o u th M a d ra s K o z h ik o d e C o a l B a s e d g e n e ra tio n H y d ro B a s e d G e n e ra tio n C o a s ta l G e n e ra tio n N u c le a r g e n e ra tio n C u d d a lo re U ltra -M e g a G e n e ra tio n L o a d C e n tre B a s e d G e n e ra tio n K a y a m k u la m T h iru v a n a n th a p u ra m L o a d -C e n tre K u d a n k u la m Hydro – In North Eastern & Northern Himalayan region Coal T a ra p u r G iry e Coal – In Central India - Chhattisgarh : 58000 MW - Orissa : 30000 MW - Jharkhand : 15000 MW - Madhya Pradesh:16000 MW Coastal based - Andhra Pradesh: 24000 MW - Tamil Nadu : 10000 MW - Gujarat : 11000 MW Future Generation Scenario (5-6 Years) 12th Plan (2012-17) Capacity Addition : 88 GW • • • Thermal Hydro Nuclear – 72 GW – 11 GW – 6 GW Renewable Capacity Addition - 12th Plan(2012-17) : 42 GW • • • Wind Solar Small Hydro – 30 GW – 10 GW – 2 GW Expansion Programme – 12th Plan Transmission Line : 1,10,000 ckm (POWERGRID – 40,000ckm) 765kV – 27,000 ckm 400kV – 38,000 ckm 220kV/132kV – 35,000 ckm HVDC – 9,500 ckm Substations : about 270,000 MVA (POWERGRID – 100,000 MVA) Emerging National Grid National Grid comprises of Inter-State, Intra-State and Inter-regional transmission system Cummulative Growth of Inter-regional capacity in MW 66000 80000 60000 40000 27750 20000 0 2011-12 By 2016-17 National Grid – A Continuing Process Augmentation of IR Capacity in XII Plan 6000 MW NR 10200 MW NER 5800 MW WR 8400 MW ER 1600 MW 6400 MW SR National Grid - XII Plan addition – 38,400 MW National Grid - Total by XII Plan – 66,000 MW 17 TECHNOLOGY Pursuing Higher Voltage Levels World’s Highest Voltage level – Test station Charged in Oct.’12 World’s longest multi-terminal HVDC to harness renewable Hydro Power from North-east Voltage (kV) 765kV D/C - AC 1200kV 765kV 800kV HVDC 500kV HVDC 400kV 220kV 1977 1990 2000 2002 Year 2012 2017-18 Technology being Adopted High Voltage line EHVAC : 400kV 765kV 1200kV HVDC : 500kV 800kV Increase the capacity of trans. corridor through HSIL/reconductoring with HTLS /Upgradation Utilisation of existing transmission lines upto full thermal capacity – Series capacitors, SVC, FACTS Optimization of Tower design – tall tower, multi-ckt. tower GIS substation High Power Intensity Corridor ROAD MAP FOR INDIAN POWER SYSTEM RoW Capacity MW/m (m) (MW) RoW 400kV S/c 52 500 9.6 400kV D/c 46 1000 21.8 765kV S/c 64 2500 39 765kV D/c 67 4000 60 800kV HVDC 69 6000 87 176 m 69 m Implementing +800kV HVDC Bipole Link World’s longest multi-terminal ±800 kV HVDC under implementation from Biswanath Chariali, NorthEastern Region to Agra, Northern Region. Shall transmit power to the tune of 6000-8000 MW. Biswanath Chariali Agra 2000 km Indigenous Development of 1200kV UHVAC World’s highest voltage, 1200kV UHV AC, test charged at Bina, Madhya Pradesh in October 2012. Has been Developed Indigenously through Public Private Partnership (PPP) with 35 Indian manufacturers in open collaboration. DEVELOPMENT PLAN Change in Generation Profile Central Sector State Sector Private Sector Total XI 15220 (30%) 16732(30%) 23012(42%) 54964 XII 26181 (30%) 15530(17%) 46825(53%) 88537 Long Term Open Access / Connectivity Long-term Open Access – Application Received : 218no. , 132,000MW – Granted : 148 No., 83,000 MW Connectivity – Application Received : 188no. , 176,300MW – Granted : 84 No., 74,400 MW Short Term Open Access – 2012-13 : 32,000 transactions, 74BU energy : High Capacity Corridors S.No Corridor Ins. Capacity (MW) LTOA granted (MW) 1 HCPTC –I ( for IPP projects in Orissa) 10090 6080 2 HCPTC –II ( for IPP projects in Jharkhand) 3820 3510 3 HCPTC-III (for IPP projects in Sikkim) 2162 2162 4 HCTPC-IV ( for IPP projects in M.P & Chhattisgarh) 4370 3554 5 HCTPC –V ( for IPP projects in Chhattisgarh) 18270 16289 6 HCTPC –VI ( for IPP projects in Krishnapatnam) 4240 3516 7 HCTPC –VII ( for IPP projects in Tuticorin) 2520 2000 8 HCTPC –VIII ( for IPP projects in Srikakulam) 1320 1240.8 9 HCTPC –IX ( for IPP projects in SR, for transfer of power to WR/NR) 8446 7026 10 HCTPC –X ( for IPP projects in Vemagiri) 4568 4325 11 HCTPC –XI ( for IPP projects in Nagapattinam/ Cuddalore ) 2250 2137 62,000 52,000 Total HIGH CAPACITY CORRIDORS 28 CROSS-COUNTRY INTERCONNECTION Linkages with Neighboring Countries IN T E R C O N N E C T IO N B E T W E E N IN D IA A N D B A N G L A D E S H G R ID S B A R A P U K U R IA JAYPU R H AT M ALDA K H E JU R IA KAH ALG AO N BOGRA FARRAKA NAOGAON BOGRA SOUTH N IA M A T P U R CH. NAW ABGANJ BANG LADESH D H U L IA N R AJSH AH I MADHOPUR RAGHUNATHGANJ NATORE S IR A J G A N J S A G A R D IG H I BAHARAMPUR IS H U R D I DURGAPUR GOKARNA PABNA S H A H JA D PUR BAHARAMPUR (4 0 0 K V ) BAGHABARI 4 0 0 k V D /c GHORASAL BHERAMARA IN D IA B O T T A IL KATW A BAKRESHW AR F A R ID P U R LEG END T H E P R O JE C T KO LAG HAT SUBHASGRAM JEER AT KH U LN A (S O U T H ) 4 0 0 kV 2 3 0 kV 1 3 2 kV 31 E xistin g U n d e r C o n s tr. / F u tu re India - Bhutan : Interconnection 32 India - Nepal : Interconnection 33 India – Sri Lanka Interconnection Madurai Madurai-New 48 Kms 130 Kms 120 Kms Panaikulam Thirukketiswaram * Taliamannar 110 Kms Proposed Route for Interconnection New Anuradhapura Issues & Challenges ROAD MAP FOR INDIAN POWER SYSTEM Issues concerning availability of RoW and same are becoming critical – Resistance of people, terrains in areas of mountains and forest Sector to grow from 228 GW to 600 GW in next 20 years – Even 765kV system may not be good enough. New methods have to be found out Challenges to develop Transmission system to meet the requirement of power flow from anywhere to anywhere. With increasing magnitude of power transmission, create new challenges of proper O&M Thank you