Chapter 19-Persian Gulf and Interior
advertisement

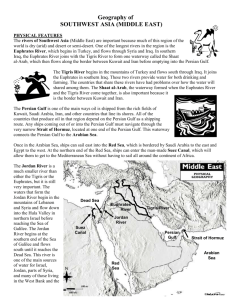
The Persian Gulf and Interior. ●Identify the landforms and rivers of the Persian Gulf area and interior Southwest Asia. ●Explain the effect the region’s geography has on its climates and biomes. ●Identify the region’s natural resources. Mesopotamia Greek for “between the rivers” ◦ Tigris and Euphrates, flow into one channel known as the Shatt al Arab. Location : Northeastern Afghanistan Name: Hindu Kush This is where bin Laden was hiding. Picture of Hindu Kush Elburz Mountains & Caspian Sea Zagros Mountains Location Due to the orographic effect areas on the windward sides of mountains get more moisture allowing more plants to grow. Why In the day it can climb as high as 114F & the night time temperature can be as low as 30F. This is due to a lack of moisture in the air Grasses Shrubs Trees in dry river bends ◦ Usually are small and thin Plants have had to adapt to limited amounts of water, by storing water. Gazelles Wild goats Wild Camels Wild Donkeys Hyenas Leopards Lions Tigers Name 3 more reptiles. Lions having lunch! Domesticated Camels Domesticated Donkeys Lizards Poisonous Snakes What are the 2 most important resources in this area? Oil and Water. Why are these so important to the region? Rivers (Tigris & Euphrates) Canals Rain Oasis Wells( ground & fossil water) Saltwater (Desalinization) ◦ This is expensive ●Describe how peoples, empires, and Islam have affected the history of the Persian Gulf area and interior Southwest Asia. ●Identify the major features of the region’s cultures. Persian Empire ◦ 550BC Marked the beginning of their occupation ◦ Conquered Mesopotamia & Asia Minor with the use of troops and advanced weapons ◦ Located the center of their empire in Persia or what is now present day Iran. Founded by Muhammad ◦ At the age of 40, while in Mecca, the Angel Gabriel to him to preach the word of Allah (God) Wrote down the message in a book known as the Koran (Qur’an) He was forced from Mecca & would later settle in Medina After his death, Islam would spread to Spain in less that 100 years 1200’s Mongols control Central Asia, Afghanistan, Iraq, & Iran 1500’s Safavids control Iran & Afghanistan, this was know as the golden age of Persian Culture and lasted until the 1700’s. Ottoman Turks controlled Mesopotamia & the East and West coasts of the Arabian Peninsula until the early 1900’s 1800’s British & Russian empires tried to control Iran & Afghanistan 1900’s Iran & Afghanistan become independent ◦ Britain takes over the area formerly controlled by the Ottoman Turks. 1932 Iraq and Saudi Arabia emerge as independent countries 1960-1970 Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirate, & Yemen become independent Group Location Language Arabs Persian Gulf and Interior SW Asia Arabic Kurds Iran, Iraq, Syria, Turkey Kurdish Persian Iran Farsi Baloch, Bakhtiari, & Hazara Iran Language similar to Farsi Turkmen Northeastern Iran Turkic Group Location Language Azeri Northwestern Iran Turkic Qashqai Southern Zagro Mnts Turkic Pashtun Scattered across the region Pashtu Tajiks Northern Afghanistan & Eastern Iran Pashtu ●Identify the activities on which the region’s economies depend. ●Describe the region’s cities. ●Explain some important issues in the region today. Petroleum Agriculture Nomadic Herding Manufacturing Main source of income for the area. Saudi Arabia produces 8.25 million barrels a day. Some subsistence farming, but mainly specialized farms (flowers shipped to Europe) “Bedouins” Trade animal products and hand crafts. Many are leaving to take jobs on farms and in the city Building materials, food products, & household supplies Life is much like centuries ago 1 & 2 story buildings Narrow twisting streets, not for cars Bazaars for shopping Crafts sold in markets Neighborhoods centered around churches or mosques Old Modern buildings Air Conditioning in buildings Shopping malls Wide streets and highways Traffic jams People live in high rise apartments Fast food and gas stations on most streets New Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries ◦ Influences oil prices by controlling supply Increase or decrease can affect economies around the world by causing the price and value of oil to rise and fall based on supply. Conservative Monarchy defends Arab traditions and economic success have kept them in power. Rebellion against monarchy to a theocracy (ruled by religion) ◦ Now controlled by the ayatollahs religious leaders of high authority What type of government did Iraq have? Dictatorship controlled by Saddam Hussein. After his capture and death was changed to a democracy, with a freely elected president 1980 Invaded Iran to take over is rich oil fields. 10 years later no one had won. 1990 Iraq invades Kuwait to control oil fields 1991 group of countries led by the US drove Iraq back out or Kuwait 2000’s US over took and helped the new government with training a new military and improving the infrastructure. Ethnic rivalries & competing political factions have fought each other since the 1970’s 1990 Taliban came to power till now. Destroyed Buddhist statues because their were seen as an affront to Islam, most Muslims disagree Use their interpretation of Islam to limit the role of women in society Limit access to education for women & banned them from the workplace Education for everyone Influence of foreign cultures Oil becoming an increasingly valuable resource Communication technology expanding making information more widely available