6.2_H.5 HL Opening Question
advertisement

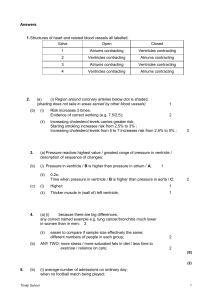
• The pumping of blood is a vital process. Explain the roles of the atria and ventricles in the pumping of blood. • (4) • Atria collect blood from veins (vena cava/pulmonary); • Atria collect blood while ventricles are contracting; • Atria pump blood into ventricles/ensure ventricles are full; • Ventricles pump blood into arteries/out of the heart (pulmonary artery / aorta); • Ventricles pump blood at high pressure because of their thicker, muscular walls; • Heart valves (semilunar/ AV) work with atria and ventricles to keep blood moving; • Left ventricle pumps blood to body systems and right ventricle pumps blood to lungs; (b) Outline the control of the heartbeat. (6) • • • • • • • • • • Heart muscle cells are myogenic; The pacemaker / SA node /is located in the right atria; The pacemaker / SA node stimulates atria to contract; The contraction of the atria leads to contraction of ventricles; Autonomic nerves in the medulla oblongata can alter the pace of the heart; The pace of the heart can be altered by secretion of epinephrine/adrenaline norepinephrine/noradrenaline increase the pace; The pace of the heart can be altered by secretion of acetylcholine which reduces the pace; The adrenal glands release epinephrine/adrenaline which alters the pace of the heart ; Epinephrine is carried by blood to heart; Epinephrine and acetylcholine change the pace of heart rate;6 max • Describe the relationship between the structure and function of blood vessels. [6] Describe the relationship between the structure and function of blood vessels. [6] • arteries carry blood under high pressure; • Arteries have a thicker elastic wall and a narrower lumen; • Arteries have muscles that control pressure and help move the blood; • Veins carry blood under lower pressure; • Veins have thinner walls with less elastic tissue, muscle and a wider lumen; • Veins have valves to prevent back flow; • Capillaries have walls which are one cell thick; • The one cell thick walls of capillaries allow easy diffusion across their wall / ultrafiltration; • Outline the events that occur within the heart, which cause blood to move around the body. [6] • • Outline the events that occur within the heart, which cause blood to move around the body. [6] • • (b) blood is collected in the atria; • blood is pumped from the atria to the ventricles; • opened atrio-ventricular valves allow flow from the atria to the ventricles; • closed semi-lunar valves prevent backflow from the arteries to the ventricles; • blood is pumped out from the ventricles to the arteries; • open semi-lunar valves allow flow from ventricles to arteries; • closed atrio-ventricular valves prevent backflow to the atria; • pressure generated by the heart causes blood to move around the body; • pacemaker (SAN) initiates each heartbeat; [6 max] •