B. Heart
advertisement

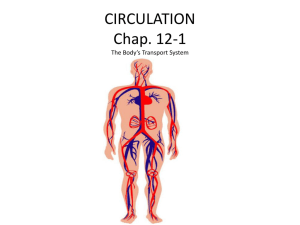
Lesson 14- The Pumping Heart A. Functions of the Circulatory System: 1. Carries oxygen to body 2. Carries nutrients to body B. Heart: 4 chambers in human heart (2 on top, 2 on bottom) Top 2 chambers called Atria Bottom 2 chambers called Ventricles C. Parts of the Heart: 1. Atria Receives blood Right Atria- carries blood without oxygen (deoxygenated) Left Atria- carries blood without oxygen (deoxygenated) 2. Ventricles Pump blood Right Ventricle- caries blood with oxygen (oxygenated) Left Ventricle- carries blood with oxygen (oxygenated) Left Ventricle septum wall around this chamber is very thick because the blood has to go through the entire body, the thickness allows for the heart to pump the blood strong enough to go to entire body 3. Septum (Intra Ventricular Septum) divides heart into right and left side 4. Valves found between atria and ventricles, and allow blood to flow in 1 direction only Tricuspid valve Pulmonary valve Mitral (bicuspid) valve Aortic valve 5. Arteries carry blood away from heart, carries oxygenated blood (**exception below) **Pulmonary Artery takes blood away from the heart to the lungs but it carries deoxygenated blood in it. This is the only artery that carries blood without oxygen 6. Veins bring blood to the heart, usually deoxygenated blood (without blood) (**exception below) **pulrnonary Vein takes blood from the lungs back to the heart, but are the only veins that carry oxygenated blood 7. Capillaries smallest blood vessels in body, connects arteries to veins 8. Superior (upper) Vena Cava large blood vessel which brings blood from upper part body back to the right atria (heart) of 9. Inferior (lower) Vena Cava large blood vessel which brings blood from the lower the body back to the right atria (heart) part of 10. Aorta carries blood from left ventricle to the upper and lower parts of the body to get oxygen and nutrients to body D System Definitions 1. Pulmonary Circulation - when deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle, goes to the lungs, picks up oxygen, drops off Carbon dioxide, travels to the left atria 2. Systemic Circulation - Oxygenated blood leaves the left ventricle, goes to the whole body, drops off oxygen, picks up carbon dioxide and returns to the right atria 3. Closed Circulatory System a system in which blood travels through a system of blood vessels * Capillaries are the thinnest walled vessels along the line of vessels * The human heart pumps 7200 liters of blood daily * It only takes the body 60 seconds to pump blood through the body and back to the heart LESSON 15 (pp 130-137) Factors affecting Heart Rate • 2 main factors are weight and exercise • Measure your resting heart rate by feeling your pulse • Vital signs= heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and respiratory rate • Heart rate and blood pressure are indicators of how well your circulatory system is doing • Your pulse is an indication of your heart rate • Pulse: When blood travels from your heart through the arteries by the contractions of the ventricles • To check your pulse you count how many beats per minute Pulse- The rhythmic expansion and recoil of arteries that is caused by the contractions of the heart. Heart rate- This can be determined by measuring the pulse • Heart rate can be influenced by a variety of factors, including exercise and weight. • Emotional, mental, or psychological stress can also affect your heart rate. (Being scared etc.) • To determine the average resting heart rate for all the students in the class, you would total the heart rates and divide by the number of students in the class. • Blood is made up of plasma (pale yellow fluid=95% water) The rest of your blood is made up of sugar, protein, minerals, and wastes. The solid parts of blood are red cells, white cells, and platelets. • Red cells- Transport oxygen • White cells- Warriors to help your immune system • Platelets- Patch holes in blood vessel walls so blood doesn’t leak out. LESSON 16 (pp138-143) The Heart Meets Resistance Blood pressure — The force exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries. Expressed as a fraction. Ex) 110/60 Systolic Pressure — Peak pressure created when the left ventricle of the heart contracts and forces blood to the aorta. The first part of the fraction. Ex) 110/60 the 110 is the systolic pressure Diastolic Pressure — The pressure that is the denominator of the fraction is this. Ex) 110/60 the 60 is the diastolic pressure Average Blood Pressure — 110/60 and 140/90 mm Hg. Hypotension — Low blood pressure. Hypertension -- high blood pressure. Atherosclerosis — Plaque begins to form on the artery walls. Ateriosclerosis – thickening of arterial walls Stroke — Caused by a ruptured vessel or by a clot that blocks the passage of blood through the artery of the brain.