heart structure edited ANSWERS
Answers
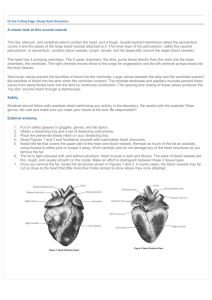
1. Structures of heart and related blood vessels all labelled.
Valve Open
1
2
3
4
Atriums contracting
Ventricles contracting
Atriums contracting
Ventricles contracting
Closed
Ventricles contracting
Atriums contracting
Ventricles contracting
Atriums contracting
2. (a) (i) Region around coronary arteries below clot is shaded;
(shading does not take in areas served by other blood vessels) 1
(b) (i) Risk increases 3 times;
Evidence of correct working (e.g. 7.5/2.5); 2
(ii) Increasing cholesterol levels carries greater risk;
Starting smoking increases risk from 2.5% to 3% ;
Increasing cholesterol levels from 5 to 7 increases risk from 2.5% to 5% ;
3. (a) Pressure reaches highest value / greatest range of pressure in ventricle / description of sequence of changes;
(b) (i) Pressure in ventricle / B is higher than pressure in atrium / A ; 1
(ii) 0.2s;
Time when pressure in ventricle / B is higher than pressure in aorta / C ;
(c) (i) Higher;
(ii) Thicker muscle in (wall of) left ventricle;
1
1
4. (a) (i) because there are big differences; any correct named example e.g. lung cancer/bronchitis much lower in women than in men; 2
(ii) easier to compare if sample size effectively the same; different numbers of people in each group;
(b) ANY TWO: more stress / more saturated fats in diet / less time to exercise / reliance on cars;
2
2
5.
(b) (i) average number of admissions on ordinary day; when no football match being played;
3
2
[6]
(2)
Trinity School 1
similar time of year / conditions;
(ii) large / significant difference for three days; then small difference;
(c) increases heart rate; raises blood pressure / causes hypertension; blood supply to heart / oxygen use by heart increased; atheroma restricts blood / oxygen supply to heart muscle;
(d) reduces heart rate; beta-blocker fits receptor sites; on walls of heart / blood vessel;
(receptor sites for) adrenaline / moradrenaline / stops adrenaline / noradrenaline binding; max 2
2 max 2 max 3
6.
(a) (i) C and D ; 1
(ii) left ventricle with thicker wall/more muscle / (muscle in) left ventricle contracts more forcefully/beats more strongly; 1
(b) higher in atria/lower in ventricles; atrioventricular valves/valves between atria and ventricles open;
(position of valves must be identified. Do not accept an unqualified reference to valves. Assume pronouns refer to atria.)
2
(c) (i) allows blood to pass into ventricles/from atria/so that atria can empty; before ventricles contract; 2
(ii) ventricle contracts from base /upwards; blood pushed through B and C /arteries/all blood ejected; 2
7.
(a) (i) all parts labelled
(ii) (valves close) due to high blood pressure / when ventricles contract;
Y prevent valve from being inverted / restricts/stops valve movement;2
(allow AV valve, disqualify tricuspid)
(b) (i) B;
(ii)
5
60 x 60
37 .
5 s correct method 1 correct answer 2
[15]
[8]
[6]
Trinity School 2