Sports Injuries – using the correct equipment
advertisement
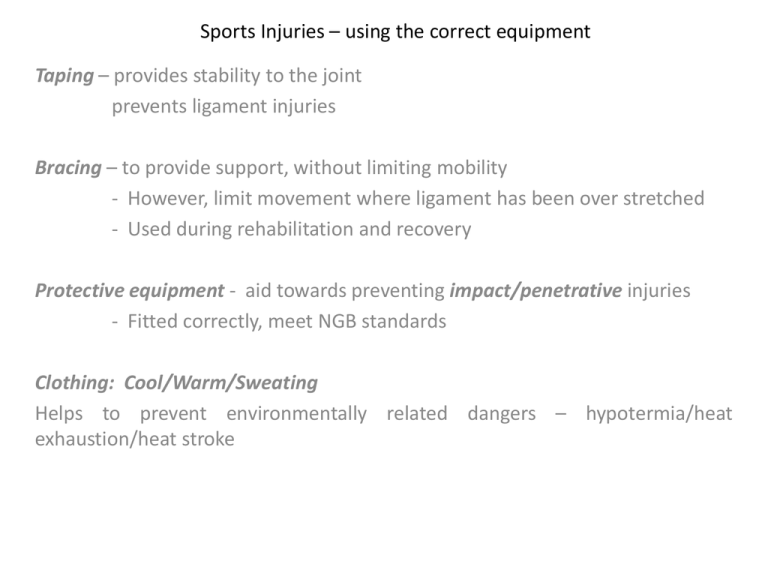
Sports Injuries – using the correct equipment Taping – provides stability to the joint prevents ligament injuries Bracing – to provide support, without limiting mobility - However, limit movement where ligament has been over stretched - Used during rehabilitation and recovery Protective equipment - aid towards preventing impact/penetrative injuries - Fitted correctly, meet NGB standards Clothing: Cool/Warm/Sweating Helps to prevent environmentally related dangers – hypotermia/heat exhaustion/heat stroke • Marathon De Sables Importance of Warm up/Warm Down • Post exercise warm downs are of benefit on performance/injury prevention and recovery • W/D should be designed to decrease injurious effects of the performance/training session • To prepare performer for next session • • • • • HOW? Prevents; blood from pooling in the limbs Lactic acid building up in the muscles Helps muscles and tendons to relax/loosen Stiffness/tightness of muscles/joints Delayed Onset of Muscle Soreness • Condition caused by damage to the muscle fibre and connective tissue • Inflammation and increased local muscle temperature • Caused by intense muscular activity and eccentric muscle contraction • Possible research may suggest Lactic Acid may also be a cause • Avoiding DOMS/recovering: • Carry out an active/dynamic warm up • When beginning an exercise programme, avoid strenuous eccentric muscle action (plyometrics) • Gradually increase intensity/duration • Carry out extra eccentric contraction exercises • Active warm down/Theraputic warm down Exam Question Prevention and Rehabilitation • Sports science and technological research are essential to the provision of rehabilitative processes. • • • • • • Cyrogenic chambers Computerised axial tomograhpy (CAT/CT) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Electrotherapy Ultrasound Acupuncture • Hyperbaric chambers • Oxygen tents • Ice baths Hyperbaric Chamber Therapy • Hyperbaric Chambers • Inhalation of Oxygen under high pressure – in pressure chambers • Boosts white blood cell activity in damaged parts of the body: – Controls infection – Constricts blood vessels – diminishing blood flow to injured region – Reduces pressure and swelling Not proven to be effective in all sports, although football clubs and athletes have used the procedure. Oxygen Tents • Canopy placed over the head and shoulders, or over the entire body • Provides an oxygen rich environment • Endurance athletes use oxygen tents to try and improve VO2 max • Or to aid recovery from injury more quickly • Hypoxic Tents (however) – stimulates high altitude by maintaining a lower oxygen concentration • Used to stimulate the body’s natural adaptations to altitude – facilitating the production of more oxygen-carrying red blood cells and haemoglobin Ice Baths • Ice – (RICE) reduces internal bleeding (due to vasoconstriction) and flow of fluids from damaged cells • Controls inflammation and swelling • Cryotherapy – cooling therapy to treat chronic/acute injuries • Ice baths used as post-match recovery in contact sports – as ice is used to treat strains and sprains • A Cryogenic chamber is cooled with liquid nitrogen, to a temp of -110 C. • Treatment for muscle and joint pain – where athlete is placed in a chamber for only a few minutes • Pain relief can last up to 6-8 hours after treatment