Short Holding Presentation
advertisement

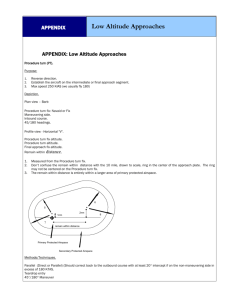
Advanced Holding Patterns Christian Pezalla ATP, CFII www.3pointaviation.com What is holding a pattern? • Racetrack Shaped Pattern • Used to: • Hold aircraft during delays • Hold aircraft during inclement weather • Provide course reversal (procedure turn) • Provide default actions at clearance limit • Climb aircraft to required altitude • Handle aircraft in non-radar environment Hold Segments Inbound Leg Outbound Turn Outbound Leg Inbound Turn No-Wind Pattern (1 Min Legs) 1 Minute Inbound Leg • 1 Minute Outbound Turn • 180 Degrees of heading Change 1 Minute Outbound Leg • 1 Minute Inbound Turn • 180 Degrees of heading Change Lateral Wind Correction Wind affects the path of the aircraft at all times, even while turning turns A 1 minute pattern with no adjustment for wind requires 4 minutes to complete. 4 Minutes equals 1/15 of an hour A 15kt wind will push the aircraft off course by an entire mile in the time required to complete one circuit A 30kt wind will push the aircraft 2 miles off course unless correction are made for wind Lateral Wind Correction (Wrong) Example 1 • No outbound wind correction • Entire inbound leg used to correct • Aircraft is pushed during both turns and outbound leg Lateral Wind Correction (Wrong) Example 1 Example 2 • No outbound wind correction • Outbound wind correction insufficient • Entire inbound leg used to correct • Inbound leg correcting for wind but not returning to inbound course • Aircraft is pushed during both turns and outbound leg • Aircraft is pushed during both turns Lateral Wind Correction (Correct) Example 3 Same as Example 3 • Outbound wind correction (Triple Method) • Outbound wind correction towards wind • Inbound leg properly aligned after turn • Inbound leg properly aligned after turn • Aircraft is pushed during both turns • Aircraft is pushed during both turns Timing Points Complete Timing at the Fix and Turn Outbound Start Inbound Timing 1. Crossing the Inbound Course 2. Rolling Wings Level -Whichever occurs first Start Outbound Timing 1. Abeam the Holding Fix 2. Wings Level (If Abeam Point Cannot be Determined) Complete Timing and Turn Inbound Timing for Wind Outbound Timing Too Long Correct Timing Correct Timing Outbound Timing (b) Outbound leg timing begins over/abeam the fix, whichever occurs later. If the abeam position cannot be determined, start timing when turn to outbound is completed. (FAA AIM, February 2013) Abeam Point What to Write Down • All of the Instructions • Write down and readback all parts of the ATC clearance • If too busy for readback, say “standby for readback” • Inbound Course • Determine and write down the inbound course • May be the same as the number in the clearance or reverse • Outbound Heading • Determine and write down the nowind outbound heading • Will always be the opposite of the inbound course • Time or Distances • Determine distances or timing to be used and write down What to Write Down • All of the Instructions • Write down and readback all parts of the ATC clearance • If too busy for readback, say “standby for readback” • Inbound Course • Determine and write down the inbound course • May be the same as the number in the clearance or reverse • Outbound Heading • Determine and write down the nowind outbound heading • Will always be the opposite of the inbound course • Time or Distances • Determine distances or timing to be used and write down Navigation Sources • VOR • • • • VOR Only VOR/VOR VOR/DME VOR Area Nav (RNAV) • NDB • NDB Only • NDB/VOR • NDB/DME • GPS • OBS Mode • Database Mode • ILS • • • • • ILS/Marker Beacon ILS/LOM ILS/DME ILS/GS ILS/VOR VOR Holding (Always Timed) Cessna 1234, Hold south of the Ranger VOR on the 180 radial, make right hand turns, and expect further clearance 1400Z Cessna 1234, Hold northeast of the Volunteer VOR on the 030 radial, make left hand turns, and expect further clearance 1200Z ATC Instructions: Direction Holding Fix Inbound Course Direction of Turns Expect Further Clearance Time Write Down: All of the Instructions Inbound Course Outbound Heading Time or Distances VOR/DME Holding (with Timing) ATC Instructions: Direction Holding Fix Inbound Course Direction of Turns Expect Further Clearance Time Write Down: All of the Instructions Inbound Course Outbound Heading Time or Distances GPS Holding • Satellite Based • Ground Speed read accurately at all positions • Distance is measured from the selected fix (not the NAVAID) • Three Types of GPS Holds • GPS OBS Holding • GPS Database holding • GPS FMS Holding GPS OBS Holding • Functions like a VOR Hold • Fix, NAVAID, intersection or airport • Works with user defined waypoints • Provides distance to fix information • Inbound course must be manually set • GPS will not provide entry guidance User Defined Waypoint Simplifying the Hold with GPS OBS (Mode) • Replacing Ground Based Navigation • • • • Allowed when not part of an approach More stable and consistent than ground based systems Constant CDI Scale Normally requires OBD mode GPS Database Holding • GPS driven CDI • Provides distance to fix information • Inbound course is automatically set • GPS may provide entry guidance Holding (Protected) Airspace • Outlined in FAA Order 7130.3A • Determined by ATC • Not Readily Available to Pilots • Not Pilots’ Responsibility • Depends on • Altitude • Speed • Navigation Aid Diagram Courtesy of the FAA Flight on the Non-Holding Side is Normal Diagram from FAA Order 7130.3A Flying the Parallel Entry Wrong (Attempting to Track Radial) Correct (Flying Outbound Heading) Diagrams from FAA Order 7130.3A Dealing with High Winds • Consider the wind before entering the hold • Be aggressive with wind correction angles • Extend length of the hold legs • Increasing your speed in the hold • Do not make the outbound leg too short • Request a different hold Advanced Holding Concepts • Knowing the Wind on Entry • • • • Winds Aloft Report (FD) Pilot Reports (PIREPs) Tracking prior to the hold On board systems (GPS based) • GPS wind vector • GPS track indicator Disorientation • When does it happen? • Before and during entry • How does it happen? • Failure to understand hold orientation • How do we prevent disorientation? • Clarify ATC instructions and write down headings • What to do when it happens? • Fly 20 sec in any direction then turn back to fix and redo entry • Or fly outbound for 30 sec and reverse course Key Points • Always refer to the FAR/AIM for correct information • Write down and readback air traffic control instructions • Always confirm the navigation source in use • Use large correction angles during high wind How to Best Utilize Technology • Learn the functions and limits of your equipment • Monitor navigation systems to ensure proper function and cross check against paper charts (or ipad) • Use the most appropriate techniques, not necessarily the most automated method Direct Entry Procedure • Fly directly to the fix and turn to the outbound heading • Apply wind correction to first outbound if possible • Start timing at abeam point (or wings level if abeam can not be determined) • Consider disregarding timing from first circuit Teardrop Entry Procedure • After crossing fix turn to a heading 30 degrees towards the outbound leg (15 degrees for distance legs) • LARS (Left Add, Right Subtract) • Start timing over the fix • Turn over the fix could be either direction • Turn inbound will be same as direction of the hold Parallel Entry Procedure • Cross the fix and turn to the outbound heading • Do not track the radial, bearing or course • Start timing while crossing the fix • Fly specified time or distance then turn opposite the direction of the hold ATC Instructions Holding instructions will always include: The direction of the hold from the fix (orientation) The holding fix to be used (May or may not be a NAVAID) The course that defines in the inbound leg (radial, bearing or track to) The direction of the turns Expect Further Clearance time (EFC) Holding instructions are “instructions” not a clearance VOR/DME Holding (with Distance Legs) Cessna 1234, Hold south of the Orlando VOR 10 mile DME on the 360 radial, make right hand turns, with 4 mile legs and expect further clearance 2100Z ATC Instructions: Direction Holding Fix Inbound Course Direction of Turns *Leg Length* Expect Further Clearance Time Write Down: All of the Instructions Inbound Course Outbound Heading Time or Distances Advanced Cockpits • Electronic Wind Information • • • • Compares actual ground path against projected path Inaccurate while turning Inaccurate without correct airspeed, pressure, temp, heading and GPS data Bad data when changing aircraft direction causes large changes in wind • Building a User Defined GNSS Waypoint • May be used for points not defined in the GPS database • Not all fixes are included in GPS databases • Out of date databases may be missing critical fixes • Useful for training G1000 Holding with MFD (Moving Map) • MFD only displays a hold if it is in the database • Holds in the database may not be changed or reprogrammed • Size determined by groundspeed • Invalid airspeed data does not affect hold size • Shaped determined by groundspeed and wind • Assumes no wind when wind data is not available • Course deviation indicator does not track the MFD hold image • CDI functions are the same in database and OBS mode • Flight director follows MFD holding pattern • Only works with database holds, not OBS What is the Distance to KROME? Distance to KROME • • • • • • I-MFA DHP KROME COPRA MAP RW 15.1NM 10.6NM 00.0NM 04.0NM 12.0NM 13.2NM Examples • NBD App with GPS Overlay • One Minute Hold on GPS App • MADKS Fix • Crossing Altitude Examples Holding Pattern Lateral Guidance: LOM AG Fix Identification: • LOM (NDB) • Marker Beacons • DME from IRQ Pencil Method • Write down ATC instructions • Point aircraft towards fix • Determine outbound heading • Find that heading on gyro • Horizontal line is always offset 20 degrees with high set in the direction of turns • Second line is always vertical Parallel/Teardrop Split