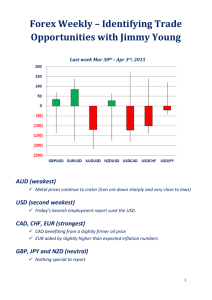
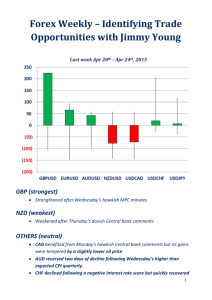
Bullish gap up - NUS Investment Society
advertisement

NUSInvest Workshop Series Session One Introduction to FA/TA DISCLOSURES & DISCLAIMERS This research material has been prepared by NUS Invest. NUS Invest specifically prohibits the redistribution of this material in whole or in part without the written permission of NUS Invest. The research officer(s) primarily responsible for the content of this research material, in whole or in part, certifies that their views are accurately expressed and they will not receive direct or indirect compensation in exchange for expressing specific recommendations or views in this research material. Nothing in this research material constitutes a representation that any investment strategy or recommendation contained herein is suitable or appropriate to a recipient’s individual circumstances or otherwise constitutes a personal recommendation. It is published solely for information purposes, it does not constitute an advertisement and is not to be construed as a solicitation or an offer to buy or sell any securities or related financial instruments. No representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is provided in relation to the accuracy, completeness or reliability of the information contained herein. The research material should not be regarded by recipients as a substitute for the exercise of their own judgement. Any opinions expressed in this research material are subject to change without notice. FA vs TA FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS Fundamental analysis of a business involves analyzing its financial statements and health, its management and competitive advantages, and its competitors and markets. Economic Analysis Industry Analysis Company Analysis TECHNICAL ANALYSIS The study of market action, primarily through the use of charts, for the purpose of forecasting future price trends. • All information is reflected in price (responses & sentiments) • History repeats itself • Technical Analysis can be applied to different trading mediums/markets/assets FA vs TA FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS • Focuses on the economic forces of Demand & Supply that causes prices to move • Finding the intrinsic value of the market/asset • Characteristics of a company is employed in the analysis • Effects of economic factors on a stock such as earning reports, cash flow, etc are concerned TECHNICAL ANALYSIS • Analysis using past data of Demand & Supply • Study of historical graphs is stressed • Identify a trend at a relatively early stage & ride on that trend until the weight of the evidence shows or proves that the trend has reversed • Deals in probabilities, never certainties Efficient Market Hypothesis Criticisms of FA and TA 3 Versions: Weak / Semi-strong / Strong Impossible to "beat the market" because stock market efficiency causes existing share prices to always incorporate and reflect all relevant information EMH: stocks always trade at their fair value (impossible to purchase undervalued stocks or sell at inflated prices) Intro to TA Charts • Candlesticks stresses relationship between open and close prices Candle Anatomy • Body: Distance between open and closing • Tip of upper wick/shadow: Highest price of that period • Bottom of lower wick/shadow/hair: Lowest price of that period • Range (length) of candle stick indicates volatility • Upward candlestick usually or green or blue • Downward candlestick usually black or red Bearish Candle Bullish Candle Gaps • Gap: Current open is not the same as prior closing price • No price and no volume transacted hands between the gap (area on price chart where there is no trades) • Effect of news after stock market closed for the day (e.g. earnings report) • Psychology: Can act as resistance/ support (news that sparked the gap is still in play) Daily Chart – Wal-Mart (WMT) 1 Price-Bar Pattern Hammer • • • • Found in downtrend Short body at the top of price range Little to no upper shadow Lower shadow must be at least twice the length of real-body • Signals: Reversal pattern when found in a downtrend • Short-term outlook indication • Real body can be black or white (white: stronger signal) Hammer • Low reliability, requires confirmation – Bullish gap for next session – Subsequent session shows white real body above that of the hammer’s real body Buyers drive prices back up to close near the highs • Significance/ Strength: – Length of Lower Shadow – Colour Long lower wick indicates initial selling prices BACKGROUND 1-BAR PATTERN 2-BARS PATTERN 3-BARS PATTERN PRICE TRADING STRATEGIES Hanging Man • • • • Found in uptrend Short body at the top of price range Little to no upper shadow Lower shadow must be at least twice the length of real-body • Warning of a potential downward • Short-term outlook indication • Also requires confirmation Hanging Man Greater gap: Higher likelihood of reversal 1. Uptrend 2. Gap Up 3. Lower Shadow at least twice as big as Real Body 4. Real Body Bullish or Bearish; better if Bearish 5. Confirmation Candle Shooting Star • Found in uptrend • Short body at the bottom of price range • Little to no lower shadow • Upper shadow must be at least twice the length of real-body • Signals: Reversal pattern • Short-term outlook indication • Real body can be black or white (black: stronger signal) Shooting Star • Low reliability, requires confirmation – Bearish gap for next session – Subsequent session shows black real body below that of the shooting star’s real body • Significance/ Strength: – Length of Upper Shadow – Colour Long upper wick indicates initial buying prices Open Bears were able to reject bulls completely (or push prices even lower by closing below open) Shooting Star 1. Uptrend 2. Upper shadow at least twice as big as real body 3. Real body bullish or bearish (bearish: stronger indication) Inverted Hammer • Found in downtrend • Short body at the bottom of price range • Little to no lower shadow • Upper shadow must be at least twice the length of real-body • Signals: Reversal pattern • Short-term outlook indication • Real body can be black or white (white: stronger signal) Inverted Hammer Spinning Top & Doji • Short body in the middle of two long wicks • Market closed relatively unchanged • Indicates indecision (‘standoff’ after significant price movement) • Trend losing momentum; possible turning point • Doji/ Long-legged Doji: stronger signal • Open and close are the same • Insignificant in sideway markets Buyers in control Sellers in control More Doji Patterns Dragonfly Doji • Long lower, no upper Gravestone Doji • Long upper, no lower Four Price Doji • Same upper, lower, open & close • Very rare • Low volume situations 2 Price-Bars Pattern Bullish Engulfing Candle When found in a downtrend: • Bullish candle opens lower than previous candle’s close, closes higher than previous candle’s open • Potential sign that trend is reversing • Indicates control has shifted from sellers to buyers Gap down Bearish Engulfing Candle When found in a uptrend: Gap Up • Gap up: Bullish sign • But: Bulls only push prices up slightly before bears take over and push prices much lower • Potential sign that trend is reversing • Indicates control has shifted from buyers to sellers Bullish Engulfing 1. Downtrend 2. Bearish Candle 3. Gap Down 4. Bullish Candle 5. Close above previous Bearish Candle 3 Price-Bars Pattern Morning Star • Consists of 3 candlesticks • Bearish Gap: Bears are in control during opening • Day 2: Prices are not pushed much lower (small / neutral candlestick) – Bullish: stronger sign • Day 3: Bullish gap up • Prices pushed further upward, sometimes eliminating all Day 1 losses Evening Star • Consists of 3 candlesticks: - Bullish, Small/ Neutral, Bearish • Presence of bullish gap, bearish gap • Day 2: Prices are not pushed much higher – Bearish: stronger sign • Day 3: Large bearish candlestick • Prices pushed further downward, sometimes eliminating all of Day 1’s gains Evening Star 1. Uptrend 2. Bullish Candle 3. Gap Up 4. Small Bullish/ Bearish Candle 5. Gap Down 6. Bullish Candle Morning Star Pattern Many other chart and price patterns, indicators, theories… CHART CONSTRUCTION SUPPORT & RESISTANCE Reversal Patterns CHART CONSTRUCTION SUPPORT & RESISTANCE Others • • • • • • • • Fibonacci Continuation Patterns Moving averages Oscillators and momentum indicators Pivot Points Trading Divergences Elliott Wave Theory … Resources • Babypips.com • Forexfactory.com Intro to FA Basics of FA Buy and Hold Latch onto a good business and allow investor’s assets to grow with the business Value Investing Seek under-valued companies Dividend Investing Seek blue chip stocks that generate dividends consistently Basics of FA Top-Down Approach Starts with analysis of global economics • E.g. GDP, Interest Rates Narrows down to regional/industry analysis • Total sales, trends, Growing/Sunset Basics of FA Bottom-Up Approach Starts with specific businesses, regardless of industry/region Basics of FA Qualitative & Quantitative Intrinsic Value (true value, not necessarily market price) Find opportunities to buy at a discount Wait for investment to pay off when market catches up Industry Factors • Industry life cycle – Emerging, Growth, Maturity, Decline • Key Trends – E.g. Airlines: Fuel Cost; Jewellery: Gold Price; REITs: Interest rates Company Factors • Business Model • Competitive Advantage • Management (ownership - founder? Insider shareholdings?) • Market Share – Competitors’ Performance Financial Ratios • 5 types of financial ratios Liquidity Solvency Profitability Efficiency Market value Price Earning Ratio (P/E) • Price of Share divided by Earnings per share (EPS) • Values the share based on earnings • The lower the PE compared to similar companies the better the value • However, more research the reason behind low valuations EBIT • Earnings Before Interest and Taxes • Adds Interest and Tax Expense to NI • Gives a clearer picture of company’s ability to generate profits • By taking away distortions from financing cost and tax structure EBITDA • Earnings Before Interest Tax Depreciation Amortization • A PROXY of Operating cash Flow • Important in determining firm’s ability to generate cash Price to Book Ratio (P/B) • Compares stock’s market value to its book value • A low P/B ratio could mean that the stock is undervalued • Also gives some idea of whether you’re paying too much for what would be left if the company goes bankrupt Earnings per Share (EPS) • The only financial indicator companies are mandated to provide in their annual report • One of the most important indicators of profitability • Shows the ability of each share in generating accounting profits • Trend is important in analyzing EPS Debt to Equity • Most common leverage ratio • Shows us the capital structure of the firm • Can indicate financing expenditure, solvency of the firm Profit margin • Net Profits/Net Sales • Shows efficiency of revenue in generating profits • Important in evaluating efficiency within the industry Return on Equity • Net Income / Total Equity • Shows how much of income is attributable to equity holders • Also shows how efficient company is generating profits with given capital Other Ratios • Current Ratio • only measures short term liquidity status • Current Assets / Current Liabilities • Return on Assets (ROA) • More… Resources • • • • • Bloomberg terminal Bloomberg.com Investopedia.com SGX.com Equity Research Reports Thank You! CHART CONSTRUCTION SUPPORT & RESISTANCE