Lecture Outline
advertisement

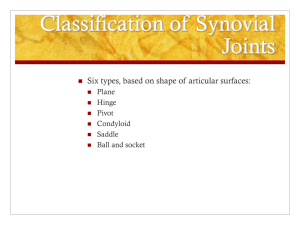
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System ARTICULATIONS and MUSCULAR SYSTEM PART #1 – ARTICULATIONS 1. Introduction A. Articulation B. 2. Arthrology C. Kinesiology D. Rheumatology Structural Classifications for Joints A. Fibrous Joints • i. Suture ii. Gomphosis a. iii. B. Periodontal ligament Ligament Cartilaginous Joints i. ii. C. Dense Regular Connective Tissue Symphysis a. Symphesis pubis b. Annulus fibrosis of Intervertebral disk Synchondroses a. Costal Cartilages b. Epiphyseal plates (Growth plates) Synovial Joints i. Anatomical Characteristics a. Synovial Cavity b. Articular Capsule • Synovial Membrane * • Synovial Fluid (SF) Fibrous Capsule Page 1 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System iv. c. Articular Cartilage d. Accessory Ligaments • Extracapsular Ligaments • Intracapsular Ligaments e. Menisci f. Bursae g. Fat Pad Synovial Joint Movements Note: Know all examples given in class in preparation for the lab practical. See your text as well for support) a. Gliding b. Angular • Flexion • Extension • Hyperextension * Examples: antebrachium, lower leg, vertebral column, cervical vertebrae • Abduction • Adduction * c. Examples: arm, leg Rotation (example: rotation of arm) • Medial Rotation • Lateral Rotation d. Circumduction (example: glenohumeral joint, coxal joint e. Special •. Inversion (Example: feet) • Eversion (Example: feet) • Dorsiflexion (Example: feet) Page 2 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System 4. • Plantar Flexion (Example: feet) • Protraction (Example: mandible, pectoral girdle, head) • Retraction (Example: mandible, pectoral girdle, head) • Supination (Example: palms of hand) • Pronation (Example: palms of hand) • Elevation (Example: mandible, pectoral girdle) • Depression (Example: mandible, pectoral girdle) Major Body Articulations A. Humeroscapular (Shoulder) Joint i. ii. iii. iv. B. Coxal (Hip) Joint i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. C. Articular Capsule Coracohumeral Ligament Glenohumeral Ligaments Transverse Humeral Ligament a. Subscapular bursa b. Subdeltoid bursa c. Subacromial bursa d. Subcoracoid bursa e. subacromial bursa. Articular Capsule Iliofemoral Ligament Pubofemoral Ligament Ischiofemoral Ligament Capitate Ligament Acetabular Labrum Tibiofemoral (Knee) Joint i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. “Sub-Joints” a. Intermediate Patellofemoral b. Lateral Tibiofemoral Joint c. Medial Tibiofemoral Joint Articular Discs a. Medial Meniscus b. Lateral Meniscus • Transverse Ligament • Coronary Ligaments Intraarticular Ligaments a. Tibial Collateral Ligament b. Fibular Collateral Ligament c. Anterior Cruciate Ligament d. Posterior Cruciate Ligaments Articular Capsule Anterior Accessory Ligaments a. Medial and Lateral Patellar Retinacula b. Patellar Ligament Posterior Accessory Ligaments a. Oblique Popliteal Ligament b. Arcuate Popliteal Ligament Page 3 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System vii. Bursae a. b. c. Anterior Bursae • Prepatellar Bursa • Infrapatellar Bursa • Suprapatellar Bursa Medial bursae Lateral Bursae PART #2 – MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction A. Muscle Tissue B. Muscular System Muscular Orientation A. Origin B. Insertion C. Belly (Gaster) Group Actions A. Agonists B. Antagonists C. Synergists D. Fixators Naming of Skeletal Muscles - (Memorization of these examples in not encouraged. But when you see a muscle name, you are expected to be able to identify what information is inherent within the name) A. Direction of Fibers i. Terminology • • Rectus Page 4 Transverse Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System • ii. B. Examples (What is the direction of the fascicles for each muscle?) • Rectus abdominis • External Oblique • Transverse abdominis • Orbicularis oculi Examples (The name communicates what location?) • Temporalis • Frontalis • Occipitalis • Pectoralis Minor • External Intercostals • Internal Intercostals • Iliacus • Orbicularis oris Number of Origins i. Examples (The name communicates how many origins?) • D. Triceps Brachii Examples (The following muscles will have what shapes?) • Deltoid • Rhomboideus Major • Serratus Anterior • Trapezius Origin and Insertion i. F. • Biceps Brachii Shape i. E. Orbicularis Location i. C. • Oblique Examples (Identify the origin and/or insertion of each) • Sternocleidomastoid • Supraspinatus • Choracobrachialis • Infraspinatus Action i. Examples (What are the actions for each muscle below?) • Massater (Mastication = chewing) • Levator Scapulae • Page 5 Depressor Labii Inferioris Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline – Articulations and Muscular System • • Adductor Magnus Pronator teres PART #3 – Muscles and Groups - Pull out Muscle Groups Handout Page 6