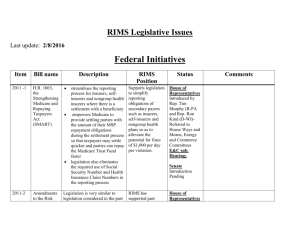
LINKING ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT TO STRATEGY
November 27, 2014
Presented by:
Carolyn M. Snow
RIMS President
Director, Risk Management, Humana Inc.
Mary Roth
RIMS Executive Director
87%
Companies surveyed
with revenue above
$1 billion say
expectations of the
risk management
department have
increased.
2
Enterprise
Risk
Wheel
Source: Zurich
INVESTING IN STRATEGIC & ENTERPRISE
RISK MANAGEMENT
63% HAVE FULLY OR
PARTIALLY IMPLEMENTED
ERM
Increases risk awareness
Contributes significantly to risk
avoidance and mitigation strategies
Assurance that the organization will
reach strategic & operational
objectives
4
A RIMS
ERM COMMITTEE
REPORT:
COMPARING TRADITIONAL RM WITH ERM
1. Traditional RM focuses on
hazard risk.
1. ERM encompasses both hazard
risk and business risk.
2. Traditional RM seeks to restore
an organization to former preloss condition.
3. Traditional RM focuses on the
value of the accidental loss.
4. Therefore traditional RM is
both its own discipline & part
of the broader ERM discipline.
2. ERM seeks to enable an
organization to fulfill its
greatest productive potential.
3. ERM focuses on the value of
the organization.
4. ERM focuses on the
organization as a whole.
Excerpt from ARM textbook: Risk Financing by Berthelsen, Elliot and Harrison page 1.14.
THE VALUE OF ERM
The Valuation Implications of Enterprise Risk Management
Maturity Study
Organizations exhibiting mature risk management
practices realize a value growth potential of up to 25%
Federation of European Risk Management Associations Survey
Firms with a more mature approach to Risk Management
have better financial results.
75% more firms with advanced risk management practices
had Earning Before Interest Taxes Depreciation and
Amortization (EBITDA) growth of over 10%
62% more firms with advanced risk management practices
attained annual revenue growth of 10%.
Source: 2012 study by Federation of European Risk Management Associations
5 STEPS TO TRANSITION TO
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT
FIVE STEPS FOR TRANSITIONING TO ERM
Determine
what
value
your organization
will gain
5
STEPS
TO
TRANSITION
TO
ERM
from ERM.
Scan the internal environment for what is
already being done.
Find a champion.
Adapt processes to the organization’s needs.
Strive for continuous improvement.
Source: RIMS Executive Report Transitioning to Enterprise Risk Management. All Rights Reserved.
MANAGEMENT’S EXPECTATIONS
Source: 2013 RIMS ERM Survey. All rights reserved.
HOW EFFECTIVE ARE WE?
Source: 2013 RIMS ERM Survey. All rights reserved.
RISK TOLERANCE DEFINITION
Source: RIMS Strategic Risk Management Implementation Guide 2012. All rights reserved.
• Risk Tolerance is the amount of uncertainty an
organization is willing to accept in the aggregate
(or occasionally within a certain business unit or
for a specific risk category), expressed in
quantitative terms that can be monitored and
may be expressed in acceptable/unacceptable
outcomes or as limited levels of risk.
RISK APPETITE DEFINITION
Source: RIMS Strategic Risk Management Implementation Guide 2012. All rights reserved.
• Risk Appetite is the amount of total risk
exposure that an organization wishes to
undertake on the basis of risk-return
trade-offs. Reflective of the company’s
business strategy, risk strategies and
stakeholder expectations, risk appetite is
generally set and/or endorsed by the
board of directors through discussions
with management.
WHAT IS STRATEGIC RISK MANAGEMENT?
Strategic risk
management (“SRM”)
is a business discipline
that drives deliberation
and action regarding
uncertainties and
untapped
opportunities that
affect an
organization’s strategy
and strategy
execution.
Source: RIMS Strategic Risk Management Implementation Guide. All rights reserved.
Not just another framework – another way to think
Strategic risks
Risks arising
from the
strategic plan
Source: RIMS Strategic Risk Management Implementation Guide. All rights reserved.
Strategic Risk Management in Action…
HOW DOES STRATEGIC RISK MANAGEMENT
WORK AT HUMANA?
Fortune 100 Company
52,000 Employees
$13 Billion Market Cap
$40 Billion in Revenue
Humana’s
Journey
Where are
we along the
journey?
Ad-hoc
Initial
Build the Base
Mature the Process
Link to Performance
Set risk strategy, policy and
framework
Consistent enterprise risk
identification and assessment
Embedded in strategic planning
and other business processes
Set optimal risk management
structure
Business unit risk profiles
Management has risk and
control performance objectives
Build resource pool
Aggregate risks across the
enterprise
Systematic risk reporting
Defined appetite / tolerances
Risk owners defined and
accountable
Detection of emerging risks
Defined materiality
Provide risk reports to Executive
Committee Audit Committee
Identify and monitor key risk
indicators
Technology solution in place
Risk linked to business
performance measurement
Enterprise-wide risk awareness
and education
Initiate technology solution
Optimize resource pool
Copyright 2009-2014 Risk and Insurance Management Society, Inc.
Humana’s
Program
Identify
Strategic
Operational
Financial
Compliance
Analyze
Planning Risks
Execution Risks
How Well Managed
Report
By Business Area and
Initiative
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
Input
Sources
Consider
Potential
“Black
Swans”
10-K
Identified
Risks
Internal Audit /
Oversight
Groups
Identified Risks
Deconstruct
Risks from
Corporate
Strategy
Process
Leader Risk
Workshops /
Executive
Leader Input
Deconstruct
Risks from
Cash Flow
and Earnings
Assess
Surprise Risk
Events and
Near Misses
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
Engagement at Humana
What’s the purpose?
Who is involved?
Workshop Methodology
Stage 1
Process
discussion with
business area
leader
Interview session
with leader
Survey of
leadership team
Stage 2
Workshop
session with
leadership team
for collaboration
and key risk
prioritization
Stage 3
Optional second
workshop
regarding
mitigation plans
Link to detailed information in Journal of Accountancy 2013 article
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
Stage 4
Key risk list,
business area
consideration,
and Internal
Audit planning
Interview (structured
and unstructured)
Stages 1 & 2
Identify
Questionnaire
Business Area
Leader
(face-to-face,
e-quiz)
Individual
(observation,
storytelling)
Facilitator
Analyze
Collective (round
table, brainstorming)
IT
Troubleshooter
Challenger
Evaluate
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
Scenarios,
war games
Potential risks
placed in
appropriate
quadrants, after
assessing
potential impact
to business
objectives and
current mitigation
activities. Aids
the business in
prioritization,
mitigation and
strategic
planning.
How Well Managed?
Stage 3 Workshop
Consider
Improvement
Urgently
Assess
Confirm
Adequacy
Avoid Further
Exposure
How Impactful?
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
Illustrative Purposes Only
Stage 4 Reporting
Prioritized Risks
High
Impact
Well
Managed
Moderate
Impact
Moderately
Managed
Not
Managed
Well
Low
Impact
Risk 2 Risk 7 Risk 9 Risk 4 Risk 3 Risk 1 Risk 5 Risk 8 Risk 6
How Impactful?
Copyright Humana Inc., 2014
How Well Managed?
THANK YOU!!!!
Our Website:
WWW.RIMS.ORG
RIMS Risk Knowledge Library
WWW.RIMS.ORG/RISKKNOWLEDGE
Thank You