The Essential Parts of a Narrative
advertisement

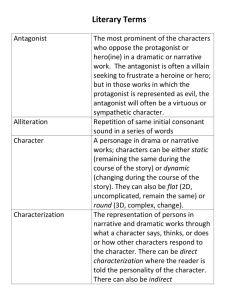
The Essential Parts of a Narrative Narratives are also known as stories. “The Three Little Pigs” is an example of a narrative. Essential Parts of a Narrative Narrative Character Setting Plot Character: A character can be a person, animal, or imaginary creature There are usually 1 or 2 main characters in a narrative There can be many secondary characters in a narrative Characterization: the technique an author uses to present and develop a character Indirect Characterization Direct Characterization The reader draws conclusions based on words and actions of all characters The author makes straight forward comments describing the characters Example: “She grabbed me by the hair and yanked me from the chair. She punched me in the side of the head and threw me to the floor.” (page 45) Example: “Oh Martha’s wonderful. She would even hum to you.” (page 207) Protagonist Antagonist The central character in a literary work The character or force that opposes the protagonist in a work of literature Example: Jennings is the protagonist in They Cage the Animals at Night. Example: The “system” is the antagonist in They Cage the Animals at Night. Setting: Setting refers to where the story takes place. The time (ex. future, past, present) The place (ex. outer space, Jones Beach, Julie’s house Plot: the series of related events in a literary work; often follows a pattern The plot must: have a beginning, middle, and end tell events in a logical order Contain EXPOSITION, RISING ACTION, a PROBLEM or CONFLICT, a CLIMAX, FALLING ACTION, and a RESOLUTION Plot Diagram: Climax Conflict Falling Action Rising Action Exposition BEGINNING Resolution MIDDLE END Definitions: EXPOSITION: A fancy word for the beginning of the story. This is where the characters and setting are introduced. RISING ACTION: In this part of the story the conflict(s) occur, tension builds, and the story moves toward the climax. CONFLICT: The problem or struggle between opposing forces. There can be many conflicts leading up to the climax CLIMAX: The pivotal moment in a story when the protagonist is faced with a choice which will effect the outcome of the story. FALLING ACTION: The events that happen after the climax which usually wrap up the action and lead to the resolution. RESOLUTION: The conclusion of the story in which we see the outcome of the main conflict. Congratulations! You have successfully completed your introduction to the essential elements of a narrative.