Telecommunications, the
Internet, Intranets, and Extranets
CSC101 SECTIONS 01 & 02
1
Telecommunication Systems
Telecommunication Medium is anything that
carries an electronic signal and interfaces
between a sending device and a receiving
device.
2
Media Types
Twisted-pair wire cable (Telephone)
Coaxial cable (Cable and Telephone)
Fiber-optic cable (Higher Speed, Smaller)
Microwave transmission (No cable, High spd)
Cellular transmission (Mobile users)
Infrared transmission (Unobstructed line of
sight, Move and reinstalled)
3
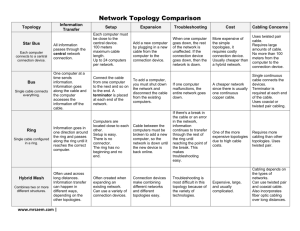
Wiring and Cabling Types
4
Telecommunication Devices
5
DSL versus Cable Modems
6
Compare Line and Service Types
7
Computer Network
The communications media, devices,
and software needed to connect two or
more computer systems and/or devices
8
Data Processing Strategies
Centralized Processing: all processing
occurs in a single location or facility
Decentralized Processing: processing
devices are placed at various remote
locations
Distributed Processing: computers are
placed at remote locations and
connected via telecommunication
devices
9
Terminal-to-Host Connection
10
File Server Connection
11
Client/Server Connection
12
Client/Server
Advantages
Reduce cost (potential)
Improve performance
Increase security
Disadvantages
Increase Cost of managing network
Loss of control Administration can be difficult
Complex systems (Internal and External users)
13
Local Area Network (LAN)
14
Wide Area Network (WAN)
15
Home Computer Network
16
Terminology
NOS (Network Operating System)
NMS (Network Management Software)
Allows all computers on the Network to
communicate with each other
Allows the network administrator to scan for
viruses and manage users facilities
Communication Protocols
Rules and standards that make communication
possible
17
The Internet
ARPANET – Advanced
Research Project Agency,
Now is called DARPA
UCAID –
University Corporation for
Advanced Internet
Development
Internet add hoc linkage of
many networks
18
Internet Protocols
Internet Protocol (IP): standard that enables
traffic to be routed from one network to
another as needed
Transport Control Protocol (TCP): rules that
computers on a network use to establish and
break connections
Uniform Resource Locater (URL): an assigned
address on the Internet for each computer
Backbone High-speed, long distance links
19
U.S. Top-Level Domains
20
Accessing the Internet
LAN
SLIP
AOL
ISP
21
Internet Service Providers
22
Internet Services
Voice Mail, Electronic Mail, and Instant
Messaging
Telecommuting, Videoconferencing, and
Internet Phone Service
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Public Network and Specialized Services
Distance Learning
23
Internet Services (con’t.)
On-line Music, Radio, and Video
Telnet, FTP, and Content Streaming
Chat Rooms
24
Videoconferencing
25
Electronic Data Interchange
26
Public Network Services
27
The World Wide Web (WWW)
An Internet service compromising tens
of thousands of independently owned
computers that work together as one.
28
Interesting Web Sites
29
Interesting Web Sites
Monster.com
Askme.com
WebMD
30
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
<!-- Header -->
<HTML>
<head>
<meta name="generator" content="Microsoft FrontPage 4.0">
<BASE href="http://www.askmecorp.com/" />
<!-- BEGIN WEBSIDESTORY CODE v6.1 -->
<!-- COPYRIGHT 1997-2000 WEBSIDESTORY, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
U.S.PATENT PENDING. Privacy notice at: http://websidestory.com/privacy ->
<META name="description" content="Askme Corporation is a knowledge
sharing Company"></META>
31
Search Engines
32
Intranets and Extranets
Intranet
An internal corporate network built using Internet
and World Wide Web standards and products;
used by the employees of the organization to
access corporate information.
Extranet
A network that links selected resources of the
intranet of a company with its customers,
suppliers, or other business partners; based on
Web technologies.
33
Internet, Intranet, and
Extranet
34
Virtual Private Network
Tunneling – encapsulating IP’s to send over the Internet.
Firewall – sits between the intranet and the outside internet
35
Net Issues
Management Issues
Managed at the local level
IAB Internet Activities Board (TCP/IP)
Service Bottlenecks
Corporate intranet traffic is growing faster
then internet traffic
Recapturing missing packets
Privacy and Security (Next Lecture)
36
Cryptography
37