Network Topologies & Extranet/Intranet Overview
advertisement
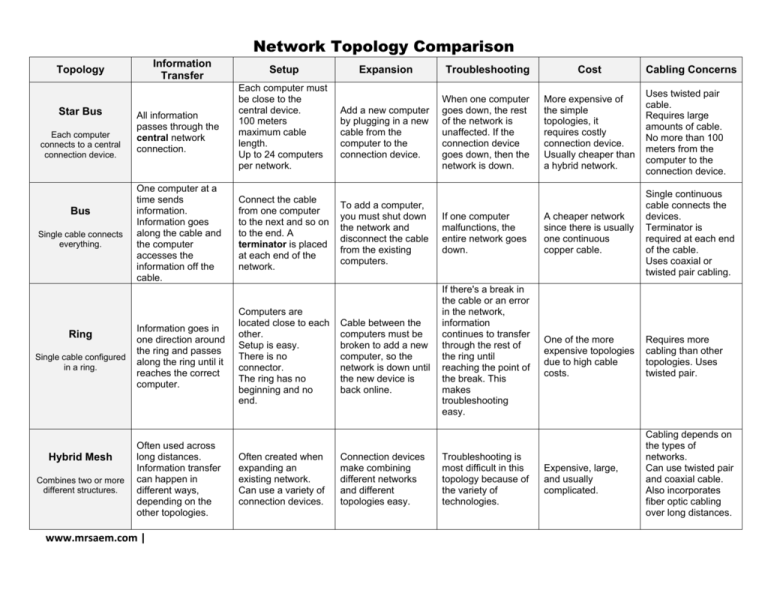
Network Topology Comparison Information Transfer Topology Star Bus Each computer connects to a central connection device. Bus Single cable connects everything. Ring Single cable configured in a ring. Hybrid Mesh Combines two or more different structures. All information passes through the central network connection. One computer at a time sends information. Information goes along the cable and the computer accesses the information off the cable. Information goes in one direction around the ring and passes along the ring until it reaches the correct computer. Often used across long distances. Information transfer can happen in different ways, depending on the other topologies. www.mrsaem.com | Setup Each computer must be close to the central device. 100 meters maximum cable length. Up to 24 computers per network. Connect the cable from one computer to the next and so on to the end. A terminator is placed at each end of the network. Computers are located close to each other. Setup is easy. There is no connector. The ring has no beginning and no end. Often created when expanding an existing network. Can use a variety of connection devices. Expansion Troubleshooting Cost Add a new computer by plugging in a new cable from the computer to the connection device. When one computer goes down, the rest of the network is unaffected. If the connection device goes down, then the network is down. More expensive of the simple topologies, it requires costly connection device. Usually cheaper than a hybrid network. Uses twisted pair cable. Requires large amounts of cable. No more than 100 meters from the computer to the connection device. A cheaper network since there is usually one continuous copper cable. Single continuous cable connects the devices. Terminator is required at each end of the cable. Uses coaxial or twisted pair cabling. One of the more expensive topologies due to high cable costs. Requires more cabling than other topologies. Uses twisted pair. To add a computer, you must shut down the network and disconnect the cable from the existing computers. Cable between the computers must be broken to add a new computer, so the network is down until the new device is back online. Connection devices make combining different networks and different topologies easy. If one computer malfunctions, the entire network goes down. If there's a break in the cable or an error in the network, information continues to transfer through the rest of the ring until reaching the point of the break. This makes troubleshooting easy. Troubleshooting is most difficult in this topology because of the variety of technologies. Expensive, large, and usually complicated. Cabling Concerns Cabling depends on the types of networks. Can use twisted pair and coaxial cable. Also incorporates fiber optic cabling over long distances. Ring Network Topology Bus Network Topology Star Network Topology Mesh Network Topology www.mrsaem.com | Tree Network Topology Extranet An intranet that allows customers, vendors or other partners to access resources or information is called an extranet. Most companies extend their intranets into extranets when they see the benefits of giving customers and vendors quick access to current information. For example, companies that once relied on regular mail-outs can now make the same information available via an extranet to save printing and postage costs. What is Extranet? is an intranet for outside authorized users using same internet technologies. The outside users are trusted partners of the organization who have access to information of their interest & concern. It extends the intranet concept to provide a network that connects a company‟s network to the networks of its business partners, selected customers, or suppliers. www.mrsaem.com | How it is different from Intranets? Intranets differ from extranet in that the former are generally restricted to employees of the organization while extranets may also be accessed by customers, suppliers, or other approved parties. Extranets extend a private network onto the Internet with special provisions for access, authorization and authentication. Types of Extranet Public Network Extranet Exists when an organization allows the public to access its intranet from any public network. Security is an issue in this configuration, because a public network does not provide any security protection. Private Network Extranet Is a private, leased-line connection bet. Two companies that physically connects their intranets to one another. The single advantage of this is Security. The single largest drawback is Cost. Virtual Private Network (VPN) [Will shortly discuss this is detail] Is a network that uses public networks and their protocols to send sensitive data to partners, customers, suppliers, and employees by using system called “tunneling”. Tunnels are private passage ways through the public internet that provide secure Companies can use an extranet to: Exchange large volumes of data using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Share product catalogs exclusively with wholesalers or those "in the trade" Collaborate with other companies on joint development efforts. Jointly develop and use training programs with other companies. Provide or access services provided by one company to a group of other companies, such as an online banking application managed by one company on behalf of affiliated banks Share news of common interest exclusively with partner companies www.mrsaem.com | Virtual Private Network (VPN) Some example uses for a VPN network include: Access your computers, servers and files in your office from your home Connect 2 or more remote offices together to make it appear they are all on the same computer network. You'll have access to all files stored on a server, access to all printers, etc.. It will seem like all remote offices are in the same building. Employees will have access to all resources on the computer networks of all offices setup in your VPN. Work from a public hotspot, like at an internet cafe, and still have access to your files, computers and servers in your office. While on vacation or off-island you can have access to your files, computers and servers from anywhere in the world If you have a dialup internet account, you can use your computer/laptop from a remote location to connect to your office using the public telephone network. Work from home using your DSL or broadband connection while still having access to your office computer network. A well-designed VPN can greatly benefit a company. For example, it can: www.mrsaem.com | Extend geographic connectivity Improve security Reduce operational costs versus traditional WAN Reduce transit time and transportation costs for remote users Improve productivity Simplify network topology Provide global networking opportunities Provide telecommuter support Provide broadband networking compatibility Provide faster ROI (return on investment) than traditional WAN www.mrsaem.com | What is Intranet? The term Intranet is derived from two words: „Intra‟ which means within and „net‟ which means group of interconnected computers. is a private computer network that uses Internet protocols and network connectivity to securely share any part of an organization's information or operational systems with its employees. In short, an intranet is private network, similar to the Internet and using the same protocols and technology, contained within an enterprise or not-for-profit organization. How it is different from Internet? The technologies used in Intranet and Internet may be same but the main difference between them is that the information shared in intranet can be access only by authorized persons especially members or employees of the organization or company where as in internet the information is shared world wide with any public user to explain in simple terms, intranet is private, within the organization while internet is public available for global access requirement. Thus, Intranet is like a private Internet. www.mrsaem.com | Benefits of intranets Workforce productivity: Intranets can help users to locate and view information faster and use app. relevant to their roles and responsibilities. With the help of a web browser interface, users can access data held in any database the organization wants to make available, anytime and - subject to security provisions – from anywhere within the company workstations, increasing employees' ability to perform their jobs faster, more accurately, and with confidence that they have the right information. It also helps to improve the services provided to the users. Time: With intranets, organizations can make more information available to employees on a "pull" basis (i.e., employees can link to relevant information at a time which suits them) rather than being deluged indiscriminately by emails. Communication: Intranets can serve as powerful tools for communication within an organization, vertically and horizontally. From a communications standpoint, intranets are useful to communicate strategic initiatives that have a global reach throughout the organization. The type of information that can easily be conveyed is the purpose of the initiative and what the initiative is aiming to achieve, who is driving the initiative, results achieved to date, and who to speak to for more information. By providing this information on the intranet, staff has the opportunity to keep up-to-date with the strategic focus of the organization. Cost-effective: Most organizations have already established TCP/IP networks, and the incremental infrastructure cost of adding Web servers to the network is well within even departmental-level budgets. Users can view information and data via web-browser rather than maintaining physical documents such as procedure manuals, internal phone list and requisition forms. Low maintenance With information residing in only one place - the Web server - it is relatively easy and affordable to add new information or to update existing information and make it instantly available. WLANs (Wireless local area networks) using spread spectrum transmission Spread spectrum is a form of wireless communications in which the frequency of the transmitted signal is deliberately varied. This results in a much greater bandwidth than the signal would have if its frequency were not varied. Wireless Networking: What is it? To loosely define the term wireless networking is to say that it is any connection between two points for the purpose of transmitting information without any physical connection, i.e. fiber optics, copper wires, phone lines, etc. www.mrsaem.com |







