Chapter 9 - The Politics of Territory and Space

Chapter 9
Political Geography
09.01 The European Union (EU) would be best described as what kind of organization?
1. territorial
2. national
3. supranational
4. global
5. sectional
09.01 The European Union (EU) would be best described as what kind of organization?
1. territorial
2. national
3. supranational
4. global
5. sectional
Explanation: A supranational organization is a collection of individual states with a common goal.
09.02 Which of these is one of Friedrich Ratzel’s seven laws of state growth?
1. the space of the state grows with the expansion of the population
2. a state grows by absorbing smaller units
3. states seek to absorb politically valuable territory
4. the impetus for growth comes to a primitive state from a more highly developed civilization
5. all of the above
09.02 Which of these is one of Friedrich Ratzel’s seven laws of state growth?
1. the space of the state grows with the expansion of the population
2. a state grows by absorbing smaller units
3. states seek to absorb politically valuable territory
4. the impetus for growth comes to a primitive state from a more highly developed civilization
5. all of the above
Explanation: Ratzel was the German founder of
Geopolitics. He used biological and organic metaphors to explain the growth of states.
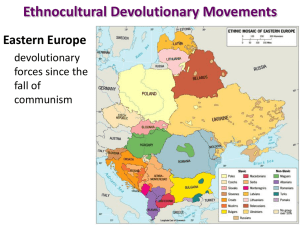
09.03 Which of these countries did not exist as an independent state in 1989?
1. Sweden
2. Yugoslavia
3. Lithuania
4. Hungary
5. Bulgaria
09.03 Which of these countries did not exist as an independent state in 1989?
1. Sweden
2. Yugoslavia
3. Lithuania
4. Hungary
5. Bulgaria
Explanation: Lithuania, along with two other Baltic states, was absorbed into the USSR. Today they are independent states once again.
09.04 Which of these places is the best example of a frontier region today?
1. Australia
2. American West
3. Canadian North
4. Sub-Saharan Africa
5. Antarctica
09.04 Which of these places is the best example of a frontier region today?
1. Australia
2. American West
3. Canadian North
4. Sub-Saharan Africa
5. Antarctica
Explanation: Antarctica is still undeveloped, virtually unsettled, and is not subject to local or national government jurisdiction.
09.05 Spain is not considered to be a nationstate because:
1. Spain is not a Western nation
2. Spain is a republic
3. Spain is a monarchy
4. nation-states are comprised of more than one nation
5. Spain contains more than one ethnic group
09.05 Spain is not considered to be a nation-state because:
1. Spain is not a Western nation
2. Spain is a republic
3. Spain is a monarchy
4. nation-states are comprised of more than one nation
5. Spain contains more than one ethnic group
Explanation: A nation-state is an ideal form consisting of a homogeneous group governed by their own state.
Spain is a multinational state, with more than one ethnic group, or nation.
09.06 The early Russian state was centered on, and expanded from, the city of:
1. St. Petersburg
2. Moscow
3. Vladivostok
4. Astrakhan
5. Bokhara
09.06 The early Russian state was centered on, and expanded from, the city of:
1. St. Petersburg
2. Moscow
3. Vladivostok
4. Astrakhan
5. Bokhara
09.07 An outcome of the dissolution of the
Soviet Union was:
1. war in the Baltic states
2. a new Soviet Union
3. breaking of diplomatic relations with the USA
4. Kazakhstan’s refusal to leave the Soviet
Union
5. the establishment of the Commonwealth of
Independent States (CIS)
09.07 An outcome of the dissolution of the Soviet Union was:
1. war in the Baltic states
2. a new Soviet Union
3. breaking of diplomatic relations with the USA
4. Kazakhstan’s refusal to leave the Soviet Union
5. the establishment of the Commonwealth of
Independent States (CIS)
Explanation: The CIS is a confederation, a group of states loosely united for a common purpose.
09.08 Which of these countries did not have any colonies in Africa in 1912?
1. Belgium
2. Portugal
3. Germany
4. Italy
5. they all had colonies at this time
09.08 Which of these countries did not have any colonies in Africa in
1912?
1. Belgium
2. Portugal
3. Germany
4. Italy
5. they all had colonies at this time
09.09 The Heartland Theory of Geopolitics was developed by which person?
1. Halford Mackinder
2. Theodore Roosevelt
3. Alexander von Humboldt
4. Elbridge Gerry
5. Osama bin Laden
09.09 The Heartland Theory of Geopolitics was developed by which person?
1. Halford Mackinder
2. Theodore Roosevelt
3. Alexander von Humboldt
4. Elbridge Gerry
5. Osama bin Laden
Explanation: Mackinder, a British geographer in the early twentieth century, developed this theory to explain and support British imperialism and the containment of
Russia, Germany, and Japan.
09.10 The theory that held that if one country in a region accepted a communist political and economic system, neighboring countries would fall to communism as well, is known as:
1. Heartland Theory
2. Domino Theory
3. Nationalism
4. Supranationalism
5. Gerrymandering
09.10 The theory that held that if one country in a region accepted a communist political and economic system, neighboring countries would fall to communism as well, is known as:
1. Heartland Theory
2. Domino Theory
3. Nationalism
4. Supranationalism
5. Gerrymandering
Explanation: This theory was an important influence on American foreign policy in the latter half of the twentieth century, and helped inspire the American policy of containment as well as American involvement in Vietnam.
09.11 Which of these countries has experienced one or more terrorist attacks in the past ten years?
1. Sri Lanka
2. United Kingdom
3. Russia
4. Indonesia
5. all of the above
09.11 Which of these countries has experienced one or more terrorist attacks in the past ten years?
1. Sri Lanka
2. United Kingdom
3. Russia
4. Indonesia
5. all of the above
Explanation: Terrorism takes many forms and is motivated by many factors. Each of these countries has experienced a recent terrorist attack from groups based either inside or outside the country.
09.12 Which of these countries is not currently a member of the European Union (EU)?
1. France
2. Greece
3. Norway
4. Finland
5. Poland
09.12 Which of these countries is not currently a member of the European Union (EU)?
1. France
2. Greece
3. Norway
4. Finland
5. Poland
09.13 Redrawing legislative district boundaries for partisan purposes, to give an advantage to a particular political party or candidate, is known as:
1. sectionalism
2. reapportionment
3. redistricting
4. gerrymandering
5. self-determination
09.13 Redrawing legislative district boundaries for partisan purposes, to give an advantage to a particular political party or candidate, is known as:
1. sectionalism
2. reapportionment
3. redistricting
4. gerrymandering
5. self-determination