Nation Building in the political world
advertisement

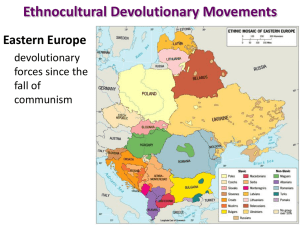
Political Geography is the study of the political organization of the world. “We prefer self government with danger to servitude with tranquility.” Kwame Nkrumah, first president of Ghana, 1960 To understand political geography we must revisit economic systems. Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory has three basic components. Core Semi-periphery Periphery CORE-PERIPHERY MODEL Wallerstein’s theory stated that the world moved toward capitalism around 1450 and encompassed the globe by 1900. This means that world economies produced goods for the world market in order to make a profit. In order to make a profit, countries (economies) sought out the cheapest labor, raw materials, and markets. Everything today operates in a “world economy” and has since 1900. This is a result of colonialism – setting up an interdependent global economy. WHAT DO YOU KNOW ABOUT? wwwwhw Canada Iraq Belgium Sudan Dem Rep Congo India/Pakistan Czechoslovakia Koreas Tibet Area of the world with the most conflict in the past 25 years. Sierra Leone Angola Liberia Zimbabwe Rwanda Somalia Mozambique Uganda World Systems and Political Power Are economic and political power the same? Name two countries today that are economically powerful, yet wield little political power? In today’s world, how many countries have the power to bring the world economy to a standstill? Is this political or economic power? In a political system, “states” promote unification by choosing government structure that promotes “nation building” and quells division within. Common structure of government include “federal” and “unitary.” Until 1945, most European countries were unitary. The power was based in the capital. The culture of the capital was defined as the nations capital. The administrative framework of a unitary government is to ensure that the government controls all aspects of the state. Until 1945, most European countries were unitary. The power was based in the capital. The culture of the capital was defined as the nations capital The administrative framework of a unitary government is to ensure that the government controls all aspects of the state. Representatives come to the capital to receive directions on how to implement the government decisions back home. In a Federal System, the “state’s” territory is organized into regions, substates, provinces, etc… In a de-centralized federal system regions have a great deal of control over policies and funds. Would you consider the USA today a weak or strong federal system? Does a federal system insure success? Successful examples: Unsuccessful examples: The most important international experiment in federalism is being attempted in: Kurds Sunnis Shiites Nation Building in the political world. The term initially referred to the new African countries who gained their independence from European colonialism in the 1960’s. The intent was to help create viable countries, often with many different ethnicities, into a “state” that was more important than the individual group. Examples Bosnia Iraq There have been many nations that have become strong, viable countries since independence. Can you identify these? Not to scale Devolution: The movement of power from a central government to regional governments (or the complete breakup of a country). The government of Spain recognizes the supremacy of regional governments. Genius question. What type of government does Spain have? Ethno-cultural devolution movements. The biggest and best example of devolution in the past century would be: The breakup of the Soviet Union is a perfect example of devolution. The USSR broke into 15 countries, in most cases based on ethnicity. Other examples of modern devolution. When the UK joined the European Union in 1973, Scottish leaders felt they would be playing a diminished role in the UK. A referendum was held to determine if Scotland would remain a part of the UK. Scottish leaders banked on the fact that the North Sea oil revenue would go to Scotland, not the UK. The referendum was soundly defeated throughout the UK, even in Scotland. Who does this sound similar to today? In 1997 another vote “devolved” the UK and gave more power to the regional parliaments in Scotland and Wales. Devolution is driven by economics and ethnicity. There is always an undercurrent in Catalonia and the Basque region to leave Spain. The Basques don’t share a cultural connection with most of the Spanish state. Separatists have gone through periods of terrorism in Spain in order to force a separation. Catalonians feel they carry too much of the economic load in Spain. They have 6% of the territory, 17% of the population, but produce 40% of all industrial exports in the country. Italy also suffers from the pressure of devolution. There is a large and growing divide between the industrial north and the agrarian south. Name a country we studied earlier with two distinct groups in the country? Hints: 1. the north (Flanders) speaks Flemish, the south (Wallonia) speaks French 2. The north is far economically advanced compared to the south 3. As of today, the federal government is barely functioning – and the country is doing fine. What devolution in the USA? No, not that one! The other one. GEOPOLITICS The relationship between geography, power, politics, and internal relations. The German School of Geopolitics: Based on the writings of Fredrich Ratzel who declared that states were “organic.” The life of a state resembles a living organism. It extends from birth, maturity, decline, and death. In order for a state to prolong its existence it requires “nourishment”, or, territory. If the state is confined, it will atrophy. (economics?) Ratzel’s students used this theory to justify German expansionist policies in the 1930’s. Alfred Mahan developed his theory of sea power based on the success of the British Empire controlling the world’s seas for hundreds of year. If a country controls access to the sea lanes, in peace or war, they dictate the ebb and flow of traffic. The British colonies and its navy had a symbiotic relationship. The colonies provided the British Navy with ports to refit and restock while they also provided the military might to maintain the colonies. Mahan felt the USA could not become a major player in the commerce or military institutions around the world due to a lack of ports around the world for bases. Geopolitical theory is also based on the “British and American” school. After Raztel’s publication, Sir Halfrod Mackinder published his theory in the Royal Geographical Society’s journal. Mackinder was concerned with “power” relationships. He wrote at a time when “the Sun Never Set on the British Empire.” His contention was that power was wielded on land, not on the sea. He who rules Eastern Europe commands the heartland. He who rules the heartland commands the world island. He who rules the world island commands the world. Mackinder's Heartland theory states that “he who controls the Heartland controls the world.” Spykman developed the Rimland Theory. The focus of the Rimland is to contain the Heartland. Nicholas Spykman theorized that the “heartland” was surrounded by the Rimland and the Rimland must contain the heartland in order not to upset the balance of power in the world. When this was written in the 1930’s, Japan was conquering much of East Asia and Germany was threatening to upset the balance of power the British had maintained. It was in the interest of this “containment” idea that the American government (who had their own sphere of influence that could be affected) must work to contain the disruptive forces. This “containment” policy was later transferred to relate to the Soviet Union during the Cold War. This containment policy still has its lingering effects. Many former Soviet “satellite” states in Eastern Europe have been invited to join NATO and/or the European Union. Russia has not been invited. Geroid O’tauthail studied American political reasoning and concluded that Americans see the world in an “Us vs Them” context. American cultural logic: “Us” is pro-democracy, independent, self reliant, self sufficient, and free. “Them” encompasses those who are against those things. “In regards to the terrorists, “you are either with us or against us.” Devolution and the Cold War. In the 1980’s Reagan pursued winning the Cold War by escalating military spending. In a famous speech he called the Soviet Union “the evil empire” and refused to negotiate on Soviet terms. The US military buildup was the final straw that brought down a tottering Soviet Union. The Cold War was over. Europe’s 9/11 was November 9, 1989, the fall of the Berlin Wall. The communist governments of Eastern Europe fell like dominoes, concluding with the fall of the Soviet Union. With the fall of the Soviet Union, the world became bipolar. The balance of power had shifted to only one political superpower. A “New World Order” was spoken of where national interests continue to merge. Much of the ill will of the world towards the USA is the use of “hard power” and unilateral decisions. There are no real answers to the power question in the world, only a matter of perspective. There is growing consensus that new “power groups” will emerge to fill the void left by the Soviet Union. One potential adversary is China. What should keep the USA and China from being embroiled in military conflict? There could also be a number of regional states that band together to form strong alliances. Today, there is a new “them” for many Americans. They don’t control borders or have an army or economy. They are radical Muslims and they hate America and what it represents. Historically, the world is a more dangerous place when there isn’t a “balance” of power. American hegemony is not viewed in a positive sense in today’s political world. But, when there is conflict in the world, what number is called? 1-800-USA








![Model_and_Theory_Chart[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008565077_1-f7a3d3b1b3bb86c6e31ff39e95c26da5-300x300.png)