CH16
advertisement

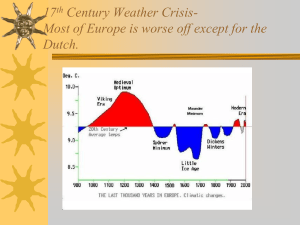
World History: The Earth and its Peoples Chapter 16 The Transformation of Europe, 1500-1750 Objectives • Be able to show how the religious reformation and dynastic rivalries further divided the people of Europe at a time when greater unity seems desirable. • Be able to describe how royal centralization increased the unity and power of Spain, France, and England. • Understand how states policies with regard to economic growth and military reorganization, warfare, and diplomacy enable northern European countries to move ahead of Spain. • Be able to analyze the relationships between climate change, human-induced environmental change, and social change in Europe. • Understand the ways in which witch-hunts, the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment reflected different European views of the natural world and of human society. Religious and Political Innovations New Modern Era 1) Reformation 2) Christian Europe unity – competition Religious Reform – economic prosperity • Renaissance • St. Peter’s Basilica – corruption • Pope Leo X (Medici) (1513-21) • indulgences – Martin Luther (1483-1546) • challenge to Pope Leo • faith over works Lutheranism Religious and Political Innovations Protestant Reformation – rejection of Pope’s authority • word of God & Bible – Lutheranism • salvation through Jesus Christ • German-speaker appeal – printing press John Calvin (1509-1564) – Protestant – Institutes of the Christian Religion • Salvation is predestined • simplification of church rituals – rejection of celibacy; pro-marriage Catholic Reformation – Society of Jesus (1534) – Ignatius of Loyola Failure of Empire, 1519-1556 Holy Roman Empire – federation of Germanic states • Ottomans (Vienna) – Charles V - 1519 • • • • Habsburg Austria and Spain Holy Roman Emperor Goal: unite Europe Opponents – King Francis I – Luther’s Reformation • • German Wars of Religion (1546) Peace of Augsburg (1555) – Breakup of empire – Catholicism or Lutheranism Royal Centralization, 1550-1750 Key Ingredients 1) Talented rulers (advisors) – Jean Colbert (France) – Robert Walpole (Great Britain) 2) Long tenure – Spain 6 (1556-1759) – France 5 (1574-1774) Increased Power • limit of church power – Roman Catholic – King Philip (Spain) • Inquisition – King Henry of Navarre (France) • Catholic Conversion • Edict of Nantes Royal Centralization, 1550-1750 Increased Power – King Louis XIV (France) • Revocation of Edict of Nantes – King Henry VIII (England) • • • • Katharine of Aragon Archbishop of Canterbury 1533 head of Church of England monasteries and convents • limit of noble power – uniformity in law - 1750 • intendants • army – vernacular • nationalism over Latin Absolutism & Constitutionalism Absolutism – no check on power – France • Estates-General – not called to session • efficiency in tax collection • selling high office – Palace of Versailles Constitutionalism – written constitution checks power – Great Britain • coerced loans • Scottish rebellion 1642 – King Charles I Absolutism & Constitutionalism English Civil War – House of Commons 1642 • Two sides – Lords • bishops and nobles – Commoners • Puritans • “Rump” parliament – Charles I executed (1649) – Oliver Cromwell (1649-1660) • Glorious Revolution (1688) – William of Orange – Mary Stuart • Refusals to call parliament Building State Power Powerful Military – firearms – large standing armies • drilling techniques • France – naval superiority • ramming to maneuverability • cannon technology • England – 1588 - end of Spain’s dominance • Balance of power – War of Spanish Succession • 1701-1721 • Austria/ Prussia/ England Building State Power Economy – commercial elite alliances – trade and taxes ratio • Spain – Protestants, Dutch, Muslim, Jew – religious uniformity • Dutch – 1560s and 1570s revolts – sales tax and Catholicism – greatest trading nation by 1600s • commercial shipping • England – financial revolution • France – aristocracy wins out Dutch Revolts The Dutch Dutch Trade Routes Urban Society Growth of Urban Areas – wealthy merchants • bourgeoisie – town dwellers • capital reinvestment – monarchial alliances • state revenues – family / ethnic networks • poor – “deserving” and “unworthy” • marriage – partner choice – later / smaller families Urban Society Business Practices – family funded • banks – big business / government – security • joint-stock companies – limit of risk and reward – monopolized overseas trade • stock exchanges • insurance companies Technology – refinement of existing – spread of printed material Rural Society Average Person in 1500-1750 – decline in serfdom – conditions worsen – war and drought • Little Ice Age (1590-1700) – few degree drop – potatoes and maize • deforestation – iron industry – effect on rural poor • gentry – bourgeoisie estates • rebellions – tax increases; food shortages Realm of Ideas European Thinking – folklore & Christian teaching • natural / supernatural • witchcraft – social tensions & poverty – Scientific Revolution • natural causes • Nicholas Copernicus – heliocentric • Galileo Galilei – The Starry Messenger • Isaac Newton – forces of gravity – Enlightenment • power of reason • John Locke (1690) – Second Treatise of Civil Government