Human Geography of Europe
advertisement
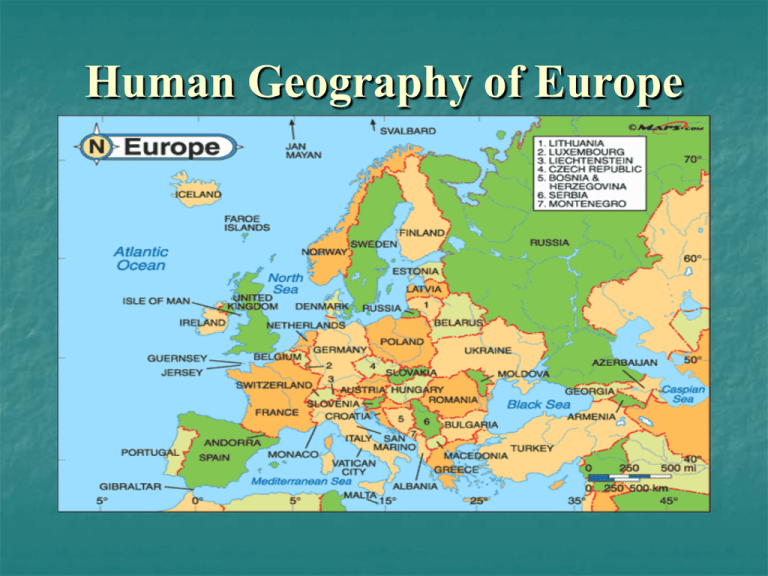
Human Geography of Europe Human Geography 48 countries and micro-states 732 million people One of the most densely populated realms in the world. The core of Western civilization: Greek and Roman Population Dilemma -0.2 natural increase (Stage 5) 9% drop by 2050 Aging or graying population More people over 60 in some countries than under 20 Immigration from North Africa and Middle East is complicated and divisive. Population Density Netherlands over 1000 ppsm United Kingdom 630 ppsm Germany 599 ppsm France 282 ppsm United States 80 ppsm The European Union 27 countries Brought together primarily as an economic and political venture. Capitals – Brussels and Strasbourg Seemingly borderless continent Dropping of tariffs but increasingly legalistic with rules and controls Cultural nation-state issues are still very important. The EURO 22 European countries use the currency 16 EU countries plus several smaller non-EU countries use it. Which major EU countries chose not to use it? UK, Denmark, Sweden Established in1999 Banknotes an coins began in 2002 Paper money looks the same throughout, coins have national symbols on them. The EURO Nation-States Related to the ethnic and cultural aspects that have evolved throughout history. Directly tied to a piece of territory. Conflict and war have been associated with boundary systems of the nationstate. Dates to the Peace of Westphalia in 1648 Multi-Lingual Region Language families: Latin (Romance) Germanic Slavic Celtic Finno-Urgic Baltic Hellenic Thracian-Illyrian Latin – Italian, Spanish, French, Portuguese, Romanian Germanic – German, English, Norwegian, Dutch, Swedish, Danish, Icelandic Slavic – Russian, Polish, Czech, Ukrainian, Slovenian, Serbo-Croatian Celtic – Irish Gaelic, Scots Gaelic, Welsh, Breton Finno-Urgic – Finnish, Estonian, Hungarian Baltic – Lithuanian, Latvian Hellenic – Greek Thraco-Illyrian - Albanian Religion dominated by Christianity Religion’s Geographic Division Division of Europe is essentially a North/South divide. Southern Europe remains largely Catholic as a result of the influence of the Roman Empire and the Vatican City’s primacy. Northern Europe developed into a Protestant realm after the Protestant Reformation beginning with Luther in 1519. The Catholic South Focal point is the Vatican within Rome. Countries that are pre-dominantly Catholic are: Italy, France, Spain, Portugal, Croatia, Ireland, Poland, Slovenia, Czech and Slovak Republics, Austria, Hungary, Lithuania, and Latvia. Also, southern Germany, southeastern Switzerland, southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium, and a sizable minority in England. The Protestant North Pre-dominantly Protestant nations are: United Kingdom, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, and Iceland. Also, northern half of Germany, northern Netherlands, western Belgium, and western Switzerland. Eastern Orthodox Christianity Primarily found in Eastern Europe. Countries such as: Greece, Russia, Serbia, Ukraine, Montenegro, Macedonia, Bulgaria, Belarus, Romania, and Moldova. Islam in Europe Islam is on the rise with over 30 million in Europe today. Primarily coming from North Africa, Middle East, and South Asia. Significant numbers in France, United Kingdom, Belgium, Spain, Italy, Germany, Sweden, Netherlands, Denmark. Pre-dominant Muslim countries include: Albania, Kosovo, Bosnia, and Malta. Clash of Cultures France and the headscarf issue Train bombing in Spain – post 9/11 Subway and bus bombings in the UK Murder of Dutch filmmaker Theo Van Gogh Danish cartoon controversy Minaret ban in Switzerland The Jews of Europe Jews once numbered over 9.5 million. The Holocaust cost 6 million Jews their lives. Only 1.2 million Jews remain in Europe (excluding Russia). Largest concentrations in cities such as London, Paris, Amsterdam, Brussels, and Antwerp. Recent Conflict and Resolution The Cold War and the Fall of the Iron Curtain The Balkanization of Yugoslavia The “Troubles” of Northern Ireland The Iron Curtain and it’s Fall Communist Soviet Union sets up satellite governments in Eastern Europe after WWII The Berlin Wall Erected in 1961 in an attempt by the East German government to prevent people from fleeing to the West. The Fall of the Wall After the failure of communism becomes evident, East German police no longer stop people as they begin to tear down the wall. This began on the night of November 9, 1989 The Chain Effect From 1989 – 1991 a domino effect across Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union led to the dissolution of communist governments. Subsequently, new (old) nations emerged, boundaries changed, and new maps were created. On the Map 15 independent countries came from the 1 former Soviet Union Germany was re-unified as one country Czechoslovakia would become two nations Yugoslavia would violently become 6 independent nations (7 if Kosovo is included) The Balkanization of Yugoslavia 10 years after the death of Yugoslavia’s dictator Marshal Joseph Tito, and as the Iron Curtain fell, Yugoslavia would begin a violent implosion. Several former independent nations starting with Slovenia and Croatia in 1991, begin to declare their independence. Yugoslav President and Serbian nationalist Slobodan Milosevic reacts with military force. The Bosnian War After the central region of BosniaHerzogovina declares its independence, Serb militias, with backing from Milosevic begin an attack on ethnic Bosnian Muslims that becomes a modern day genocide. From 1992-95 over 250,000 people would be killed and the beautiful capital city of Sarajevo would be nearly destroyed. Sarajevo – 1984 Winter Olympics Kosovo (90% ethnic Albanian) Northern Ireland Part of the United Kingdom Northern 6 counties of Ireland Only part of the UK in 1921 1960’s began to see violence in Northern Ireland between Catholic/Irish and Protestant/British. 3,400 people have been killed in fighting over the years. Future? Currently approximately 55% British/Protestant 44% Irish/Catholic Birthrates suggest a more balanced and possible Irish majority in the years to come. Will it lead to Ulster becoming part of the Republic of Ireland?










![South east presentation resources [pdf, 7.8MB]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005225551_1-572ef1fc8a3b867845768d2e9683ea31-300x300.png)
