American Imperialism
advertisement

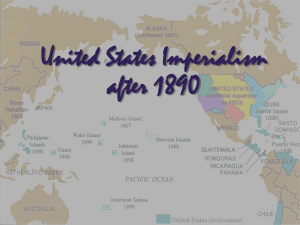
American Imperialism What is Imperialism? • Imperialism is an extension of national territory and economy. • This can be done to open new markets for the economy. • It can be done to gain access to new natural resources for industry to use. • It can be done to gain greater security for a country. • Imperialism can also boost national pride. • Finally, Imperialism can be seen as a mission for different groups. It can be social (think Social Darwinism) and religious. How the Media Played a Role • Different newspapers of the day promoted US Expansion. • The way they achieved this was to promote US Nationalism. • Jingoism is the extreme form of this. • Famous names tied to this movement were W.R. Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer. • Their papers (In NYC and other cities) advocated US involvement in foreign affairs as well as territorial expansion. Examples of US Imperialism Pt.1 • The Spanish American War • In the 1890s, Cuba was still a Spanish colony. • The Cubans tried to revolt several times and the Spanish fought back with great brutality. • The US Media (newspapers of Hearst and Pulitzer) sensationalized the events in what would be known as “Yellow Journalism” • President McKinley resisted the call to help the Cubans until……. Examples of US Imperialism Pt. 1 • February 15, 1898 • The US Battleship Maine explodes and sinks in Havana, Cuba. • 260 American sailors die in the attack. • The Yellow Journalists jump on the story, accusing the Spanish of attack. • In April of 1898 Congress authorizes the US to take action to liberate Cuba. • Congress also passed the Teller Amendment, stating we would not colonize Cuba, allowing selfdetermination. Examples of US Imperialism Pt. 1 • The first move occurred in the Spanish colony of the Philippines. • The US quickly took control of the Philippines with the help of Filipino rebels. • The US then annexed the Philippines, making it a new US territory. • The US also annexed Guam, which is still a US territory today. • During this time, the US was fighting in Cuba and decisively beat the Spanish in Santiago Bay and San Juan Hill. • By 1909 Cuba was out of US control, but Puerto Rico was annexed. Puerto Rico is still a US territory today. • Out of the Cuban conflict emerged a national hero—Teddy Roosevelt and his “Rough Riders” Discussion Question • In the space below, write the question and your answer: • Why might the US want to annex the Philippines? Why Puerto Rico? Examples of US Imperialism Pt. 2 • The Annexation of Hawaii • Hawaii offered many strategic advantages for the US. • Midway between N. America and Asia, it was an excellent place for a Navy base (Pearl Harbor was began in 1887). • It had a strong agricultural base (plantations for sugar cane, tropical fruit. • One of the biggest producers in Hawaii (at the time an independent nation) was Sanford Dole. Examples of US Imperialism Pt. 2 • Due to lobbying of Congress from US sugar producers, Hawaiian Sugar producers now had to pay tariffs on imported sugar. • A way to avoid this and become profitable again was to have Hawaii become part of the US. • Sugar producers, helped by members of the US military, overthrew Hawaii’s Queen and formed a new government with Dole as its leader. • The US then annexed Hawaii as a territory in 1897. • Hawaii became as state in 1959. Other Imperialistic Moves • The US sought to offset European power in Asia. • The US worked with European countries that had “Spheres of Influence” in China to create an “Open Door Policy”. • This policy would allow the US to trade with China. • This policy was not very successful. • When the US took part in putting down the nationalistic Boxer Rebellion in China (1900), the treaty allowed for the US to gain trade privileges with China. “Big Stick” Diplomacy • On the assassination of President McKinley, Theodore Roosevelt became President. • Roosevelt believed in the US being involved in foreign affairs to protect its “sphere of influence”. • The “Stick” is US military power. But wait, there’s more! (Imperialism) • To use “the big stick” of military power, the US had to be able to move it quickly. • The US sought a quick way to move the navy and troops from the Atlantic to the Pacific. • The best way would be through a canal in Panama. • But there were problems.. • Panama was controlled by Columbia and they did not want the US to build the canal. • The US backed the Panamanian nationalist rebels and removed the Columbians from Panama. • In exchange, Panama allowed the US to govern and control the canal zone. • Construction began in 1904 and ended in 1914. • The canal is still in use today, but now Panama has full control of it. A New Manifest Destiny • Manifest Destiny is an American policy dating to the early 19th century. • It stated that had the right to expand across the North American continent. • Teddy Roosevelt changed this a little and said that the US has the right to intervene in the Western Hemisphere to protect its interests. It gave the US “International Police Power”. • This policy still is a major practice in US foreign policy today. Discussion Question • In the space below, write the question and your answer: • Should the US have been/still be an International Police Force? Why or Why not?