R7 Imperialism
advertisement

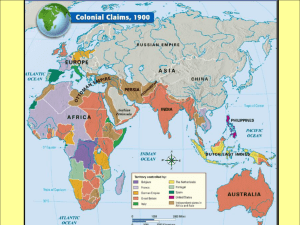
Chapter 25 New Imperialism New Imperialism ► In 1880’s Europe began an unprecedented expansion into Africa and Asia. New Imperialism Built on a foundation of technological advances 1. Fire Arms ► ► Breech loading Rifles rapid fire weapons (Gatling Gun) 2. Transportation ► Steamships, Suez Canal 3. Communication ► Telegraph 4. Medicine ► Quinine, an effective treatment for Malaria New Imperialism Motivating Factors 1. Capitalism ► Markets for industrial goods ► Source of raw materials New Imperialism Motivating Factors 2. Social Imperialist ► Viewed imperialism as a means of solving domestic issues ► Example: Overpopulation New Imperialism Motivating Factors 3. Exploration ► European Scientist (geologist, botanist, cartographers) scrambled all over the word ► Published descriptions and statistics on native peoples, lists of flora and fauna, maps. New Imperialism Motivating Factors 4. Nationalism ► Colonies seen as a way of showing the power and importance of the nation on a global scale New Imperialism Motivating Factors 5. Religion ► Missionaries wanted to convert nonChristians ► Christian missionaries first Europeans to penetrate central Africa New Imperialism Motivating Factors 6. Social Darwinism ► Belief that white races should be sovereign over people of Africa and Asia. ► Goal to improve the moral and material well being of non-whites ► “bind your sons to exile, to serve your captives needs” New Imperialism Motivating Factors 7. Balance of Power ► Nations wanted colonies so that other nations would not get them India ► British dominance of India began after withdrawal of French after Seven Years War (1756-1763) ► During 19th century independent Indian territories fell under British Control ► Sepoy Rebellion 1857 - British East India Company replaced by a centralized colonial structure ► 1877 Queen Victoria declared Empress of India ► India was the “jewel in the crown” of the British Empire China Informal Empire ► Spheres of Influence - European states controlled economy of China ► “treaty ports” European nation gained direct control over a series of ports along coast ► Boxer Rebellion- armed uprising, 200 westerners killed - Europe responded with direct military intervention, received increased concessions, China forced to pay indemnity Imperialism in Asia ► Russians controlled Manchuria ► French controlled Indo -China (Vietnam) ► Dutch controlled Indonesia ► U.S.A. controlled Philippines, Hawaii Africa ► Prior to 1875, Europeans had only limited territorial claims in Africa Egypt ► Suez Canal completed in 1869 (Britain and France) ► 1882 nationalist revolt in Egypt threaten European control of Canal ► Britain responded with show of strength ► Chaos resulted, British restored order ► British occupied Egypt ► Joint British and Egyptian forces occupied Sudan Tunisia ► French heavily invested in Tunisia ► Financial crisis in Tunisia led to French occupation in 1881 Sub-Saharan Africa ► King Leopold II of Belgium establishes: ► International Association for the Exploration and Civilization of Central Africa in 1876 ► Headquarters in Brussels ► Focused not on science or ending slavery, instead on making territorial claims ► In response, European powers began push inwards from Coastal outposts Berlin Conference 1885 ► Europeans feared “mad scramble” for Africa would lead to conflict in Europe. ► Berlin Conference established rules for settlement of Africa ► Coastal Settlement would give nation claim to adjacent inland territory ► Allowed Germany and Italy to occupy unclaimed pieces of Africa Berlin Conference 1885 ► Territorial lines paid no attention to ethnic, tribal and linguistic characteristics of indigenous population. ► No native Africans participated in Berlin Conference Fashoda Crisis (1898) ► As French troops pushed East from West Africa. - Wanted empire stretching west to east across North Africa ► British troops pushed South from Sudan. - Wanted empire from north from Egypt to Cape Town ► Brink of war over obscure outpost ► French chose to give way rather than fight Boer War 1899-1902 ► Conflict between Dutch speaking farmers, the Boers, and British government. ► Britain had acquired Cape Colony during wars of French Revolution ► The Boers resented British rule ► The Great Trek 1835-1837- Boers literally leave Cape Colony and establish two (racists) republics across Orange River Boer War 1899-1902 ► Diamonds were discovered in the Boer Republics in 1870’s-1880’s. ► Prospectors, many British poured in ► Cecil Rhodes gained monopoly on diamond production (founder of De Beers, Rhodes Scholarship) ► Became Prime Minister of Cape Colony ► 1899 Boers declared war on British ► British occupied Boer Republics after 2 years of guerilla resistance Cecil Rhodes ► ► ► "I contend that we are the first race in the world, and that the more of the world we inhabit the better it is for the human race...If there be a God, I think that what he would like me to do is paint as much of the map of Africa British Red as possible...“ “Remember that you are an Englishman, and have consequently won first prize in the lottery of life.“ "In order to save the forty million inhabitants of the United Kingdom from a bloody civil war, our colonial statesmen must acquire new lands for settling the surplus population of this country, to provide new markets... The Empire, as I have always said, is a bread and butter question" British Rule in Africa Scramble for Africa ► Almost all of Africa divided among Europeans ► Exceptions: Ethiopia and Liberia Africa 1914