Imperialism Notes Template
advertisement

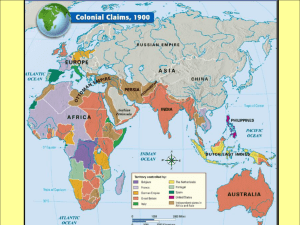
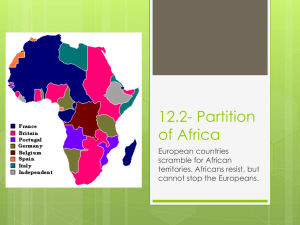
Imperialism Roots of Western Imperialism 1870-1914: Age of Imperialism (one country takes control of another country). Merchants exploring and trading with a new area. Mother country would develop that area for own gain. Europe, US, and Japan were the dominant. Types of Control ____________________-set up by large groups of people from one country living together in a new place ______________________-loyal officials ruled over the indigenous people ______________________________-local ruler kept title but pledged alliance to conquering country. Countries set up __________________________________________-an area of interest for that country. National Rivals Nations believed they would be _________________________________________. Large ________________________ became important. Imperialism would lead to world conflict. Economic Motives Industrialism created the need for ______________________________. Countries did not want to depend on other nations, imperialism became even stronger. Nations would conquer or develop other nations for raw materials. They also sought _______________________________________________ Cultural Motives Industrialized nations had a duty to spread ____________________________________ around the world. The White Man’s Burden A poem by _________________________________ used to sum up western attitude towards nonwesterners. It was their __________________________________ to impose their values and religion on other people. Missionaries Missionaries were sent all over the world to spread ___________________________. They helped build schools, and many had medical training and helped established hospitals. European Claims in North Africa: France 1830-France occupied the _________________________________________________. Algerians resisted French rule for the next 60 years. 1881-France took over Tunis. Became a _____________________________________. Under French control until 1956 England 1854-Egypt allowed French company to build the _____________________________ connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Egypt bought almost half the stock in the company putting Egypt in debt. To avoid bankruptcy, sold stock to England in 1875. England now had a _____________________________________ and controlled this area for decades. Fashoda Crisis The French and the English wanted control over the __________________________ (Egyptian colony) on the Upper Nile River. The English wanted to build dams and control the water flow in the lower Nile. 1881-Revolution broke out in the Sudan. Muslim leader, __________________________________, led a revolt against Egyptian rule. Called himself Al-madhi-“The Expected One.” The British invaded Sudan to put down rebellion. The British won easily. The French also decided to get involved. Marching 3,000 miles from the Congo, France and England met at _____________________________. The French could not defeat the British and gave the Sudan to England. The became known as the ____________________________________________. European Claims in Sub-Saharan Africa Europe had already carved up Africa by 1900 for ___________________________________: each interested European country competing for its own interests. West Africa Major center of the__________________________________________. Abolished in early 1800’s, slave centers turned to others forms of trade-_________________________________________. Europeans began to push inland to gain control of the sources of the products. The French defeated ________________________________ and captured ________________________ British moved from Gold Coast and met resistance from the Ashanti. England eventually controlled all of Ashanti Territory. Competition for Central and East Africa 1869-New York Herald hired Henry Stanley to find ___________________________________missionary disappeared in Central Africa 1871-found him. “____________________________________.” Stanley wrote many newspaper articles about his adventure, gaining interest from _____________________________________________ of Belgium. Leopold colonized area known as the Congo. Sold rights to businesses to take raw materials. Took huge amounts of Congo’s natural rubber. Leopold used slave labor. 1908-Leopold turned colony over to Belgium government. Europe colonized East Africa. Famine made the local tribes too weak to resist colonization. Competition for Southern Africa Colonization began in 1652. Dutch sailors found ___________________________________-supply station to East Indies. Grew into a colony called Cape Colony. Early 1800’sthe British took it from the Dutch The Boers When British took control, people left the colony. A massive migration-_______________________occurred. Descendants of the original Dutch settlers called Boers. Spoke Afrikaan. As Boers migrated came into contact with Zulu Nation. Lead by ___________________________________, the Zulus held off the Boers for many years. The British joined the Boers and defeated the Zulu Nation. Cecil Rhodes _____________________________________ were discovered in Orange Free State and Gold in Transvaal-population rush to Southern Africa. Rhodes arrived in Cape Colony in 1870, Hoped climate would help tuberculosis. He moved to Orange Free State and within 20 years completely controlled South African diamond production. Later organized colony of ________________________________________________________ Boer War 1895-Rhodes sponsored a rebel group to overthrow ___________________________________. It failed 1899-_________________________________ broke out. British vs the Boers. 1902-British won and now mined for gold and diamonds. Boers were allowed to keep using Afrikaan and keep their farms 1910-united all Boer colonies with Cape Colony-Union of South Africa. Beginnings of Apartheid. Effect of Imperialism on Africa Europeans controlled all levels of Government. Europeans believed Africans could not rule themselves. Benefits: New crops, farming methods, medicine, roads and railroads, and communication. Many Africans did not give up their culture and resisted European ways. They did not give in to the greed and selfishness of Europe. Expansion in Asia: British Imperialism in India Mid 1800’s British East India Company controlled much of India. 1857-Indian soldiers _______________________________. England took direct control of Indian policy in over half the country, rest split into states. Indian prince head of each state. Princes who allied with England rewarded. England built an _____________________________ and moved into India. The British built schools and educated people of India India Nationalism Movement for self-rule began in late 1800’s. 2 fronts: Gradual independence and right now Japanese Response to Imperialism At first Japan resisted Western influences. But began to expand and industrialize Meiji Restoration 1868-Sumarais overthrew the Tokugawa Shoguns and returned the emperor to power. The Samurai wanted a government that resembled a more western style. Japanese were allowed to choose their type of work, and everyone required to go to school. 1899-Adopted new Constitution giving limited voting rights and setting up 2 house National Assembly called a diet. Real power lay with a small group of leaders loyal to the emperor.