Powerpoint - Woodland R
advertisement

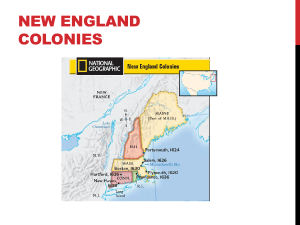
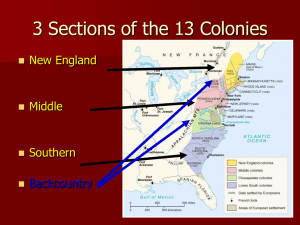
War in Europe England and Spain were rival powers in Europe in the 1500s Spain had the most wealth and greatest navy because of exploration After the British defeated the Spanish Armada it opened exploration of the Americas to other Europeans Early Settlements 1583 – Sir Humphrey Gilbert claimed Newfoundland for England 1585 – Sir Walter Raleigh settled Roanoke Island off North Carolina - they returned after a difficult winter 1587 – John White brought new settlers to the island and returned to England for supplies By the time he returned the settlers had disappeared Left a gatepost carving “Croatoan” Jamestown (1607) Established by the Virginia Company (joint-stock company) Faced many hardships in the early years 1608 – Capt. John Smith was sent to govern the colonies along with others Didn’t find the gold they were searching for Winter of 1609-1610 known as “The Starving Time” Tobacco became the cash crop for the colony Trouble with Native Americans Improved some after Pocahontas married John Rolfe Governing the colony House of Burgesses 2 representatives from each of the 10 towns made local laws King James eventually cancels the charter and VA becomes a royal colony Plymouth (1620) Two factions formed in the Anglican church Puritans – wanted to reform the church Separatists – wanted to form a new church -Became known as the Pilgrims -Fled from England to Netherlands because of harsh treatments Asked the VA Co. for safe passage to settle in VA The Mayflower landed farther north–Cape Cod, MA Pilgrims made a contract to establish law & order Mayflower Compact – beginning of rep. government Native Americans teach them to survive in America Types of Colonies Charter Colony – CT, RI -Est. by groups of settlers receiving a charter from the king -Elected governors and representatives for both houses of the legislature -Britain approved the Governors who couldn’t veto acts of legislation Proprietary Colony – DE, MD, PA -Land given to proprietors by the King -Proprietor ran government; appointed Gov. and Upper house of legislature -Colonists elected lower house representatives Royal Colony – GA, MA, NH, NJ, NC, SC, VA -Ruled by King; appointed Gov. and council -Colonists elected assembly who usually did what king asked New England Colonies Began in 1629 as a royal charter to the Massachusetts Bay Co. John Winthrop was Gov. – main city was Boston The key to success in the colonies was settlement Between 1607 and 1775 almost 1 million settlers moved to the Americas from Britain 1630’s Great Migration 15,000 Puritans leave Europe to escape religious intolerance and economic hardship Improvements in living conditions helped boost pop. Larger families, healthier children, longer life spans Life in New England Soil was difficult to farm – mostly subsistence farming Shipbuilding, fishing industries became the main economic sources Small businesses, craftspeople, etc. flourished in this environment Most people settled in towns Greens or common areas for livestock and military training Meetinghouses for town meetings and church services Colonial Government Mass. Bay Colony created a colonial legislature (General Court) Adult male church members who owned property voted for representatives to the Court Problems within the Mass. Bay Colony While many settlers to the area came looking for religious freedom they were intolerant of others religious beliefs New Colonies form Connecticut – 1636 – Thomas Hooker Settlers moved to the fertile Conn. River Adopted 1st written constitution in America Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Rhode Island – Roger Williams Allowed religious tolerance of all faiths New Hampshire – 1638 – John Wheelwright Didn’t gain independence from MA until 1679 New England becomes a center for Trade Manufactured goods were sent to New England in exchange for fish, furs, fruit, etc. from American colonies Triangular Trade forms 1. Sugar, molasses from the West Indies was shipped to New England 2. Molasses was made into rum and sent to England 3. Rum and manufactured goods from England and the colonies were shipped to West Africa 4. Goods were traded for enslaved Africans who were taken to the W. Indies to work on the sugar plantations The most inhumane part of the journey was the Middle Passage when slaves were brought to the America Middle Colonies 1621 – Dutch West India Co. settles along the Hudson River Colony is called New Netherlands Main settlement is New Amsterdam (Manhattan Island, NY) Because of excellent harbors it becomes the trade center Colonies land was controlled by patroons Ruled like kings with their own courts/laws Populated by colonists from Netherlands, Germany, Sweden & Finland They paid the patroons in labor & crops 1642 – The Glorious Revolution Puritan Parliament led by Oliver Cromwell overthrew King Puritans return to England and those loyal to the king left for America 1658 – The Restoration Cromwell dies and Parliament returns the throne to Charles II in 1660 1664 – English sent a fleet to attack New Amsterdam because they wanted the port city Peter Stuyvesant was Gov. of the colony He had strict laws & high taxes-disliked by colonists Was forced to surrender because he was unprepared King Charles II gives colony to his brother the Duke of York Proprietary colony – renames it New York Owned all the land and controlled the government Most settlers lived along the Hudson River (8,000) various nationalities (Dutch, Swedish, German, Native Am., Puritans, African slaves) The Duke promised they could keep their religions 1683 – Population of New York grew to over 12,000 The Duke appointed a Gov. and Council but the colonists wanted representation 1691 - Received the right to elected a legislature New Jersey Separates The southern part of New York b/w the Hudson and Delaware R. was given away Lord John Berkley and George Carteret became the proprietors - Named the new colony New Jersey after the Isle of Jersey - Offered large tracts of land, freedom of religion, trial by jury, and representative government to attract settlers Because of its lack of harbors it didn’t make the profits Carteret and Berkley had both sold out & by 1702 it was a royal colony Pennsylvania 1680-The King owed William Penn a large sum of money for a loan Penn asked if he could have land in America as payment The Quakers (Society of Friends) Penn was part of this religious group Believed all people had an inner light guiding them to salvations Allowed everyone to experience God in their own way Quakers were tolerant of others beliefs Many feared this because they didn’t use traditional church ceremonies Wouldn’t bow to lords because they believed all were equal Pacifists who refused to fight for political reasons Were often persecuted for their beliefs Pennsylvania was a “holy experiment”–put ideas into practice 1682-Began building Philadelphia-called the “City of Brotherly Love” Penn was the first town planner – designing the city himself Wrote the first Constitution for the colony Negotiated the first treaties w/ Native Americans for selling land Advertised for settlers in pamphlets all over Europe 1683 – 3,000 English, Welsh, Irish, Dutch, Germans arrived 1701-Charter of Liberties gave colonists the right to elect representatives to the legislature 1704-Charter of Privileges allowed the lower 3 counties to form own government became the colony of Delaware (Swedes, Dutch & English) Southern Colonies A labor intensive land The Southern land required a lot of work to maintain the profits of cash crops By 1660 tobacco prices were falling so plantation owners needed more land and labor to continue to make the profits They Used: 1. Scotch/English criminals and prisoners of war from Ireland came to earn release after 7 yrs 2. Indentured servants worked for a certain time to pay for passage to America 3. African slaves were also used on plantations Maryland (1632) King gave to Sir George Calvert (Lord Baltimore) – proprietary colony 1634-Two sons went to America to run the colony-had 200 settlers The land was fertile – didn’t plant just tobacco Diversified with corn, wheat, fruit, vegetables & livestock 1729-Baltimore was the largest settlement in the colony Lord Baltimore gave large tracts of land to relatives, English aristocrats and promised 100 acres to each settler, 100 to their wife, 100 for each servant, & 50 for children Aristocrats owned huge plantations that had to be farmed Introduced indentured servants and slave labor 1760s – hire astronomers Charles Mason & Jeremiah Dixon to map it lay out the entire boundary using stones with both families crests Religious Freedom Meant as a safe place for Catholics – Calvert’s sons had also allowed Protestants and they soon outnumbered the Catholics 1649 – Act of Toleration – gave both religions the right to worship 1692 – Protestants controlled assembly and made Anglican Church the official church for the colony Virginia Virginia continued to grow from 1607 (Jamestown) Plantations took all the tidewater land-new settlers moved west Native Americans were unhappy with being forced off land 1640’s–Gov. William Berkeley–keeps settlers from moving west Western settlers like Nathaniel Bacon were unhappy felt they weren’t represented in the colonial gov’t. settled west of the territory anyway Native Americans attacked & government refused aid 1678-Bacon’s Rebellion Led western settlers to attack Native Americans Governor condemned these actions Bacon marched on Jamestown – set fire to it Berkeley fled into exile but Bacon suddenly dies and English send troops to restore order Results of rebellion Showed England colonies wouldn’t be confined Colonial government created a militia to fight Indians Opened up more land for settlement The Carolinas Charles II found the colony and gave land to large proprietors Constitution written by John Locke Northern part was settled by small farmers, they did not have any port cities of their own Southern part had fertile farmland and the harbor city of Charleston Cash crops – rice and indigo (blue gold) Many settlers came from Barbados (English Colony in Bahamas) Brought their slaves with them Rice was also a labor intensive crop and slavery began to grow Northern settlers were angry because they weren’t allowed a part in the government Seized control from the proprietors and divided the colony in 1729 into North & South Carolina Georgia (1733) – James Oglethorpe 1. It was a colony for debtors to make a fresh start 2. A military barrier between the English and the Spanish 3. Religious refugees also came there Savannah was the main city Oglethorpe’s laws Ban slavery, Catholics, and Rum in the colony Also limited the size of land grants Settlers complained and Oglethorpe lifted all bans except slavery Colonial Culture Religion – Great Awakening Strong religious values were established in the colonies from 1720-1740 Family Men were head of the household Voting rights only applied to white men who owned property Women participated in the decision making within the house In cities and towns they worked outside the home some Education Valued in society – Literacy rates were 85% men, 50% women Many schools were run by women from their homes Quakers ran schools in the middle colonies Craftspeople opened trade schools for apprentices Harvard (1636) was the first college – Puritans The Enlightenment Said that knowledge, science and reason could improve society Spread ideas through newspaper, lectures, and organizations Held the idea of freedom of speech as a basic right New France Founded Quebec in 1608 Interested in fishing & fur trader Built forts and trading posts to protect their interests 1663 – New France becomes a Royal colony Jean Talon – royal governor – supported further exploration Down the Mississippi River 1670s began to explore the Mississippi River Marquette & Joliet Searched for gold and a water route to the Pacific Found the place the Arkansas R. joined the Mississippi & flowed to the Gulf of Mexico Robert LaSalle Followed the Mississippi to the Gulf - Claimed the region for France 1718 – New Orleans is founded for France Later explorers went west to the Rockies & Rio Grande Growth of New France Seigneuries (estates) – much like patroons Tenant farmers paid an annual rent & worked for the lord a certain number of days Relationships with Native Americans Better than any other European group Trappers & missionaries learned the language & respected their ways French colonies grew more slowly and didn’t push them off their land New Spain Spanish had control of Mexico, Caribbean, Central & South America, western & southern N. America (Southwest & Pacific coast) 1610 - Sent soldiers missionaries & settlers to found Santa Fe to protect borders from other Europeans Spread into Arizona and later Texas after France claimed New Orleans Missions in California Religious establishments along the Pacific coast Used as Spanish claims and to convert Native Americans Often forced Native Americans to labor at the missions also European conflicts in North America 1. Early 1700s many battles broke out between the English & Spain 2. Georgia & Spanish Florida were often fighting 3. France and Great Britain eventually become the greatest rivals