The Society of New France
advertisement

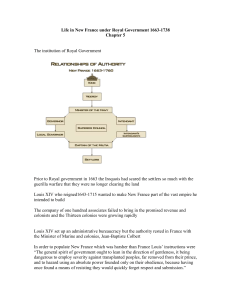
The Society of New France The Royal Government of 1663 Leaving the colony under the control of the chartered companies was not working. In 1663, the name of the king of France put New France directly under his authority. Copy the diagram on p. 83 ***100% for sure going to be on exam!*** Vocabulary Filles du Roi - Young Frenchwomen, either orphans or beggars, who were sent to the colony at the state’s expense in order to marry colonists. Dowry - The goods a woman brought into her marriage. The colony under Louis XIV The naval minister wants to encourage 2 things. He sends the the first intendant, first intendant, to make sure this happens. Soldiers are sent to fight the Aboriginal group. France wants to increase the population to 2 economic reasons Increasing population The State encourages more engagés be brought and offers seigneuries to military rank The problem is there is far more men than women. Jean Talon has young women brought over to marry men. The state provides money to bring into a marriage for each woman. The State gives rewards to type of family Increasing Population Because of these measures, the population grows from # to # in just 10 years Ensuring the colonists’ subsistence Talon wants the colony to no longer depend on country Wants the colony to produce more thing Talon pays more attention to how land is used and threatens person for not developing their land Diversifying Economy Talon wanted to increase the number of types of industries in the colony 4 types of industries Expanding Territory (p.88) In 1665, the territory of New France continued to grow into the Ohio Valley. The Huron, France’s trading partner, were wiped out by the Iroquois. The French now explored further into the continent to get furs on their own. Along the way they claim land before the English and convert Aboriginals. Territory and Voyageurs (p.89) The French also settled Louisiana at the mouth of the Mississippi River which governed over the Illinois Country. Young Frenchmen who hunted and traded furs in the Pays d’en Haut (Great Lakes region) on their own were called voyageurs. So many people started doing this that the State required people to get a license to hunt and trade furs. Franco-Aboriginal alliance (p.90) The Iroquois only traded furs with the English. Iroquois pressure other Aboriginal groups to only trade with them. The French and its Aboriginal allies in the Great Lakes fight the Iroquois. In 1701, the French, Iroquois, and other Aboriginals sign the Great Peace of Montreal which stops the fighting and gives the French control of the Fur Trade. Canadien Society 18th Century (p.91) The economy continues to diversify New France joins the Triangular trade New France exports furs, wood, agricultural products, and fish. Imports sugar, coffee, and manufactured products Example of mercantilism: New France is a market where the mother country can sell its products. Hierarchical Society (p.92) Three classes of Society: Nobility, Clergy (the Church), and the Third Estate (the people) Nobility and Clergy have special privileges and legal status. They rule over society. Third Estate includes seigneurs and bourgeoisie. Aboriginal and African slaves are not considered to be a part of society. The Church in 18th century (p.95) Still extremely important in everyday lives of people. The Church owned many seigneuries and employed a lot of engagés. The Church was also involved in politics. A bishop was on the Sovereign Council, take part in negotiations, act as a spokesperson for the King. French to Canadien (p.96-97) Slowly the people in New France are becoming less like French Europeans in their lifestyle and becoming this new group of Canadiens They had to adapt to the environment and the resources available. Aboriginals influenced how they dressed, moved around, and what they ate. (Ex: fur coats, canoes, corn) Because they had worked so hard to clear the land, the Canadien feel that it belongs to them