New France 1534 - 1763

The French Regime: 1663-
1760
M y M a g i c 1 0 0 i t e m s l i s t
M y N e w s p a p e r
6 k e y p o i n t s o f N e w F r a n c e
The broken promise of the
Company of 100 Associates was the catalyst for great change in
New France.
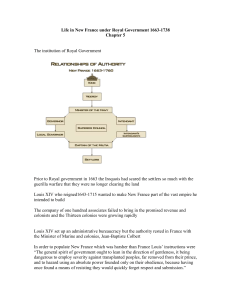
Royal Government: 1663
The King of France was upset that the fur trade companies did not keep their promise about bringing settlers.
Culture
Absolutism
A belief that the ruler King or
Queen was said to receive his or her power directly from
God and was their representative on earth.
Economy
Diversification:
The act of introducing variety.
When the king takes control NF will evolve from 1 pillar (Fur) to 6 pillars….
Jean Talon
Jean Talon was sent by the King of France to find out the problems in New France.
He was the first
Intendant of New
France
Jean Talon
The First Census
In order to find out the problems, Jean Talon completed the first census.
Refer to your copy in our package and answer all the questions.
Jean Talon
He found 3 main problems.
-Not enough women
-No protection for the colony
-Not enough people staying in New France
Jean Talon
His solutions:
A) Bring over specific groups of immigrants:
-les Filles du Roi
Soldiers
Soldiers from the
Carignan Salieres
Regiment.
Engagés
They were hired workers
(on a contract) with little rights.
-Jean Talon and the King hoped they would stay after their contract was up
But only a few did
Incentives for population growth
-Baby Bonuses for couples who had at least
10 children
- Fines on men and women who remained unmarried 14 and 16.
-Men could not get involved in fur trade if they weren’t married
Promoted the Seigneurial
System
To organize the settlement of people in
New France in an organized way by fixing rights and duties of the Seigneur and Censitaire.
Territory continued to expand due to exploration for the fur trade
2. Composition of the Population a) 1663
Total: 3000 people
Mainly male, French origin & native b) 1760
Total: 65,000
Mixed population:
Canadiens & French
Amerindians & Blacks,
Some were slaves.
Main reason for population growth.
a) Lots of babies natural increase..In fact
NF had one of the highest rates in the world.
b) Traditional
Catholic.
Canadien families are
Catholic church promoted large families.
c) It was not uncommon for families to have 10 or more children.
Seigneurial System
A) French method of organizing the territory
B) Long rectangular plots of land along a body of water.
C) Components of each seigneury: Mill, seigneur’s land, church, common land
Triangular Trade
1.
2.
There was ongoing trade between New France,
France and the French West Indies.
How triangular trade works: a) The colonies provide raw materials b) The Mother Country would transform those raw materials into manufactured goods.
c ) C) The Mother Country would then sell the manufactured goods to the colonies (usually for a ridiculous amount of money)
Triangular Trade
RESOURCES:
• Furs
• Fish
MANUFACTURED GOODS: CLOTH, METALS, LIQUOR
RESOURCES:
•
RUM
• Slaves
Diversification
1.
With the help of Jean Talon, and other intendants (Hoquart, etc) the economy of
New France becomes diversified.
Meaning: the economy does not rely solely on the Fur trade
Agriculture:
1. Population growth led to an increased demand for goods. Mainly FOOD!
A) Jean Talon encouraged the creation of more Seigneuries, this created a surplus in goods, which could now be sold for PROFIT!
B) Wheat becomes a staple product.
2. Impact on the Land
A) Further development of the Seigneurial
System
B) Construction of mills
C) More public markets
3. Impact on the People
A) Higher standard of living
B) Economy was no longer based on self-sufficiency
C) Higher demand for specialized workers
d) Increased number of people in the cities.
Shipping and Ironworks
1. Demand
A) France needed ships for its Navy, and to export products to their colonies.
B) Many industries expanded because of this:
Iron, tar, and rope.
2. Impact on the land
A) Mineral exploration for iron ore in Mauricie.
(In the Canadian
Shield)
B) New areas develop
Problems with the economy during the
French Regime.
1. The economy of New France became dependent on manufactured goods from their
Mother Country.
2. The fur trade is still the main attraction.
3. Lack of money being made in New France.
4. Not enough specialized workers.
Culture
a) Catholic religion continues to play a big role.
b) The idea of Absolutism still dominates. (symbols of the King are everywhere: Fleur de Lys)
2. The Independent Spirit of the HABITANTS:
A) Because of the distance & lack of control from the
Mother Country the French Canadian peasants
(habitants) were forced to take care of themselves.
B) They developed an “Independent Spirit” or in other words a Self Reliance.
2. The Independent Spirit of the HABITANTS:
C) Their contact with the Aboriginals helped them to do this.
They blended the 2 cultures to create their own.
D) Examples: use of birch bark canoes, snowshoes, building new types of houses to suit the weather, fur trading without a permit.
Power
1. The Great Peace of Montreal (1701)
A) Amerindian nations are not doing well (diseases and wars)
B) More than 1,300 Amerindians, from forty different nations, gathered near Montreal. They came from the Mississippi Valley, the Great Lakes, and Acadia.
C)Many were lifelong enemies
1. The Great Peace of Montreal (1701)
D) They agreed there would be no more wars between the French and the Amerindians.
E) Thirty-eight nations signed the treaty, including the Iroquois.
F) The Iroquois promised to remain neutral in any future conflict between the French and their former allies, the English colonists of New England.
The State and the administrators of the colony:
A) The Bishops, Intendants and Governors (The
B.I.G. 3 of Royal Government) all demanded things from France.
Examples: More money, more military resources, more land (for themselves).
B) For the most part, they did not get what they wanted.
C) France had little to no interest in their colony in the mid 1700’s.
3. The State and the Habitants:
A) The “regular” people were at the lowest level in
Royal Government.
They had no say in the colony.
3. The State and the Habitants:
B) Means (ways) of control:
To ensure (make sure) that the rules/laws of the colony were followed, the state used three principal means of control:
The Army
Public Punishments
Public Hangings Public Whipping
Public Shows of Power and Wealth
Chateau St-Louis Intendant ’ s Palace