Ottoman Empire
advertisement
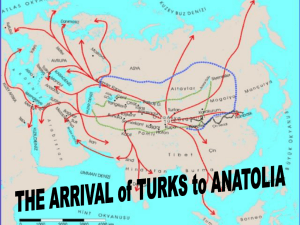
OTTOMAN EMPIRE By: Alyssa Ayala, Cassidy Cain, & Jen Fahr THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE Establishment The Creation Location Period of Time it Existed Religion Impact on Europe Foreign Relations The Rising of the Ottoman Empire The Golden Age (1481-1566) The Downfall of the Ottoman Empire Significance of the Ottoman Empire ESTABLISHMENT Othman (Osman) founded the Ottoman Empire around 1307 Turkish tribal chief Founded the dynasty called Osmanli (Sons of Osman) Seljuks- strongest tribe of the Turks who established themselves in Asia minor The Mongols defeated the Seljuks in 1283 and Othman emerged as the leader of the Turks in the fight against the Byzantine Empire THE CREATION This empire was created by Turkish tribes in Anatolia It emerged in Asia Minor after the breakdown of the empire of the Seljuk Turks Ottoman Turks began to take over the other states and ending all other Turkish dynasties The Ottomans achieved many victories and were able to place large parts of the Balkan Peninsula under their rule Ottoman’s now have a stable empire LOCATION Ruled parts of southeastern Europe, the Middle East, and East Africa for more than 600 years Includes Anatolia, the Balkans, Crimea, Hungary, parts of Syria, Arabia, and North Africa LOCATION PERIOD OF TIME IT EXISTED Existed form 1301-1922 One of the largest and longest lasting Empires in the world Stayed a strong empire because it was ruled by a single family for 7 centuries Reached it’s height from 1520-1566 Began to decline in 1571 1922 the sultan was overthrown ending the empire RELIGION Main religion was Islam Islamic ideals and laws form the basis of their society, government, and law The Suleiman was regarded as the religious leader of Islam and Muslims Other religions were ensured protection in the empire IMPACT ON EUROPE Many European countries ignored the expansion of the Ottoman Empire They viewed the Turks as a threat to Christian civilization People, such as Luther and Desiderius Erasmus, saw the Turks as a sign of God’s anger toward Europe They urged for repentance and reform The Ottoman Turks became less of a concern to Europe as the Renaissance continued FOREIGN RELATIONS Military alliance with France, England, and the Netherlands Wars against Habsburg Spain, Italy, and Habsburg Austria THE RISE OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE 1 . Gained landed in the northwest corner of the Anatolian Peninsula by the Seljuk Turks due to their assistance in fighting the Mongols 2. Expanded westward to control Bosporus and the Dardanelles, which were two straits that connected the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea. (Byzantine Empire previously controlled this land) 3. They expanded into the Balkans Ottoman rulers claimed the name of sultan and built a strong military by developing an elite guard called janissaries 4. New Technology Janissaries used firearms to spread the Ottoman Empire 1400- defeated the Serbs and annexed Bulgaria THE GOLDEN AGE (1481-1566) Three sultans ruled the Ottoman Empire at its height: Beyazid (1481-1512)- extended empire into Europe, added outposts to the Black Sea, put down revolts in Asia Minor, and turned the Ottoman Fleet into a major Mediterranean naval power Selim (1512-1520)- eliminated all competition for his position, established control over the army, and moved south and eastward into Syria, Mesopotamia, Arabia, and Egypt Suleyman I the Magnificient (1530-1566)- captured Belgrade in 1521, captured Rhodes in 1522, broke military power of Hungary, and waged three campaigns against Persia THE DOWNFALL OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE The Battle of Lepanto (1571) Beginning of the downfall Conflict between the Ottoman and Habsburg empires extended to Mediterranean Sea Turkish navy fought against Spain and Venice Destruction of the Turkish fleet Government Became weaker and parts of the empire began to act independently Murad III (Ruled 1574-95) the Caucasus were conquered and Azerbaijan seized Ottomans were driven out of the Caucasus and Azerbaijan in 1603 and out of Iraq in 1604 THE DOWNFALL OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE Ottomans were at war with European enemies for 41 years Lost Blakan territory and all possessions on shores of the Black Sea Selim II (ruled 1789-1807) attempted to reform empire and navy but he failed and was overthrown Mahmud II (ruled 1808-39) empire was in desperate straits “Sick Man of Europe” (1850 -1922) Ottomans forced to sign the Treaty of San Stefano which would end their rule in Europe except for Congress of Berlin Abdulhamid II (ruled 1876-1909) developed strong ties with Germany and fought on their side in World War I Mohammed VI fled in 1922 after the sultanate was abolished SIGNIFICANCE OF THE OTTOMAN EMPIRE Universalized the civilizations of East and West Influenced Islamic religions in the Middle East and Persia Provided a strong and organized military Had a centralized political structure One of the largest, longest lasting and most successful empires BIBLIOGRAPHY " O t t o ma n E mp i r e . " G a l e E n c y c l o p e d i a o f W o r l d H i s t o r y : G o v er n m e n t s . Vo l . 1 . D e t r o i t : G a l e , 2 0 0 8 . G a l e Vi r t u a l R e f e r e n c e L i b r a r y . W e b . 7 M a r. 2 0 1 4 . " O t t o ma n E mp i r e . " Re n a i s s a nc e : A n E n c y c l o p e d i a f o r S t u d e n t s . E d . P a u l F. G r e n d l e r. Vo l . 3 . Ne w Yo r k : C h a r l e s S c r i b n e r 's S o n s , 2 0 04 . 1 3 2 - 1 3 4 . G a l e Vi r t u a l R e f e r e n c e L i b r a r y . W e b . 7 M a r. 2 0 1 4 . " O t t o ma n s a n d O t t o m a n E mp i r e . " Th e Mi d d l e A g e s : A n E n c y c l o p e d i a f o r S t u d e n t s . E d . W i l l i a m Ch e s t e r J o r d a n . Vo l . 3 . Ne w Yo r k : Ch a r l e s S c r i b n e r 's S o n s , 1 9 9 6 . 1 8 6 - 1 8 9 . G a l e Vi r t u a l Re f e r e n c e L i b r a r y . We b . 7 M a r. 2 0 1 4 . " I n t r o d u c t i o n t o t h e R i s e a nd Fa l l o f t h e O t t o ma n E mp i r e ( Fo u r t e e n t h t o S e ve n t e e n t h Ce n t u r i e s ) . " G a l e E n c y c l o p e d i a o f W o r l d Hi s t o r y : Wa r . Vo l . 1 . De t r o i t : G a l e , 2 0 0 8 . G a l e Vi r t u a l Re f e r e n c e L i b r a r y . Web . 7 Ma r. 2014. h t t p : // e n . wi k i p e d i a . o r g / wi k i / Te r r i t o r i a l _ e vo l u t i o n _ o f _ th e _ O t to m a n _ E mp i r e h t t p : // www. m i d e a s t we b . o r g / Mi d d l e - E a s t - E n cyc l o p e d i a /o t t o m a n .h t m h t t p : // www. u m i c h . e d u / ~ t u r k i s h / l i n k s / o t te m p _ b r h i s t . h t ml h t t p : // www. b b c . c o . u k /r e l i g i o n / r e l i g i o n s / i s l a m/ h i s t o r y/ o t t o ma n e m p i r e _ 1 .s h t ml h t t p : // l o s ti s l a m i c h i s to r y. c o m / i s l a m - a n d - t h e - o t t o ma n - e mp i r e /