Chapter 32 Section 1
advertisement

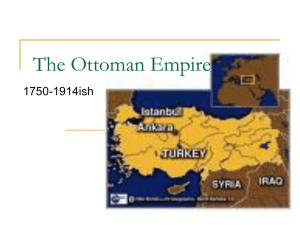
The Ottoman Empire in Decline REVIEW CHAPTER 32 SECTION 1 Prepare for Notetaking Copy the chart for the Ottoman Empire and take notes based on this presentation This will go fast since it is review Notes on major Long term consequences developments in the period Political Economic Social Military Review Questions What factors led to the territorial decline of the Ottoman Empire over the course of the nineteenth century? What territories were lost? 2. Compare the reforms of the Tanzimat era with the program of the Young Turks. 1. Are They Still Calling It an Empire? Decline began in 16th century Continually fought Russians for control of Balkans, Black Sea, and surrounding areas Russia won most conflicts (but not Crimean War) By 19th Century, Ottoman Empire is smaller, less powerful and in danger of collapse Greece, Egypt, and Arabia launch successful independence movements Britain and France try to keep Ottoman Empire up (and gain influence in the region) Military Decline Since 17th Century Lagged behind European armies in strategy, tactics, weaponry, training Janissary corps politically corrupt, undisciplined Provincial governors gained power, private armies Territorial Losses in 19th Century Caucasus and central Asia to Russia Western frontiers to Austria Balkan provinces to Greece and Serbia Egypt gained autonomy after Napoleon's failed campaign in 1798 Egyptian general Muhammad Ali built a powerful, modern army Ali's army threatened Ottomans, made Egypt an autonomous province Economic Decline Less trade as Europeans shifted to the Atlantic Exported raw materials Imported European manufactured goods Heavily depended on foreign loans Foreigners began to administer the debts of the Ottoman state by 1882 Capitulations Extraterritoriality: Europeans exempt from Ottoman law Operated tax-free, levy their own duties in Ottoman ports Deprived empire of desperately needed income Reform Attempt to reform military led to violent Janissary revolt Mahmud II When Janissaries resisted, Mahmud had them killed Cleared the way for reforms Built an European-style army, academies, schools, roads, and telegraph Tanzimat Era (1839-1836) Ruling class sought sweeping restructuring to strengthen state Broad legal reforms Modeled after Napoleon's civic code State reform of education (1846) Free and compulsory primary education (1869) Undermined authority of the ulama, enhanced the state authority Resistance to Reforms Religious conservatives Legal equality for minorities resented by some Young Ottomans wanted freedom, autonomy, decentralization High-level bureaucrats wanted more power, checks on the sultan's power Cycles of Reform and Repression 1876, coup staged by bureaucrats who demanded a constitutional government New sultan Abd al-Hamid II (1876-1909) - autocrat suspended constitution, dissolved parliament, and punished liberals Reformed army and administration: became source of the new opposition The Young Turks Called for universal suffrage, equality, freedom, secularization, women's rights Forced Abd al-Hamid to restore constitution Dethroned him (1909) Nationalistic: favored Turkish dominance within empire, led to Arab resistance Review Questions What factors led to the territorial decline of the Ottoman Empire over the course of the nineteenth century? What territories were lost? 2. Compare the reforms of the Tanzimat era with the program of the Young Turks. 1. Next Up….. Read Section 2 on Russia and complete a chart like the one below for Russia. Put notes in your own words so you can make sure you understood it. Notes on major Long term consequences developments in the period Political Economic Social Military