The Great War: The World in Upheaval
advertisement

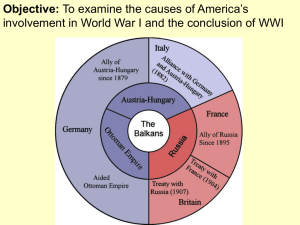
The Drift Toward War Long Term Causes Nationalism Imperialism Militarism Alliances Triple Alliance – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire Triple Entente – France, Russia, Britain Short Term Causes Assassination of the Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria by Serbian nationalists triggers war between alliance systems. The Drift Toward War The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s plan to defeat France swiftly while the Russian army was mobilizing. Moving the massive Germany army took time and the Schlieffen Plan failed at the Battle of the Marne. Set the course for a long and deadly conflict. Global War After the domino effect of the alliance systems pulled most European countries into the war, a total war with devastating impact ensued. Mutual Butchery Stalemate Trench Warfare New Technology: Machine Guns, Poison Gas, Tanks, Planes, Submarines, Long Artillery Had devastating affects Battle of Verdun – 315,000 French deaths, 280,000 German deaths. Only 160,000 identifiable bodies as the were so badly mutilated that they were unrecognizable. Global War Total War: The Home Front As war took men away from jobs, unemployment disappeared and women were required to fill the gaps. After the war, many women did not retain their jobs when the men came back Rationing Limited the amount of goods / resources people on the home front could use in an attempt to preserve resources for the war Propaganda Biased communication meant to sway public opinion and maintain support for the war Censorship Governments censored news and arrested dissidents and pacifists. Global War Conflict in East Asia and The Pacific The European war took on global consequences as colonies became embroiled in it, and third parties like Japan, the Ottoman Empire, and U.S. got involved. Japan took advantage of Germany’s focus on Europe to confiscate German positions in Asia and the Pacific. Allied themselves with the Allied Powers (Britain, France, U.S.) Issued the secret 21 Demands to the Chinese government during this time as well in their attempt to establish complete control of China Became apparent Japan intended to dominate all of Asia. Global War Battles in Africa and Southwest Asia The Allies in Africa had a more difficult time conquering German possessions there. British, French, and Belgian forces fought along with African, Arab, and Indian forces in fierce battles with German Troops and colonials. Disease in the jungles killed many groups Ottoman Empire at war Joined the Central Powers and fought the Russians and British for control of the Dardanelles. Had initial success against the British, but in the end were unsuccessful. Ottoman Empire became Turkey after WWI. The End of the War The Russian Revolution 1917 – Internal protest and military struggle led to Tsar Nicholas II abdicating the throne, ending 300 years of Romanov rule Provisional government took over and continued to wage war In the midst of this unrest, Vladimir Lenin led to the Bolsheviks to prominence eventually gained control of Russia, ending their participation in the war and focusing on moving Russia forward. Focused on “Peace, Land, and Bread” The End of war U.S. Intervention and the Collapse of the Central Powers President Woodrow Wilson initially promised neutrality Reason for Intervention in April 1917 German unrestricted submarine warfare Lusitania sunk in 1915 killing 123 Americans Zimmerman Note Economics Central Powers Collapse U.S. intervention ended the stalemate German people and soldiers began to revolt, causing internal problems. War ended with an Armistice on November 11, 1918. The End of War The Paris Peace Conference War was devastating – 15 million dead and additional millions dying in the difficult years following the war. Treaty of Versailles at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919 ended the war, but laid the foundation for continuing problems Woodrow Wilson (U.S.), Georges Clemenceau (France), Lloyd George (Britain) dominated the conference Soviet Union and Central Powers not invited Fourteen Points League of Nations Reparations – Germany blamed and had to pay! Boundaries redrawn throughout Europe.