PPT on Appeasement
advertisement

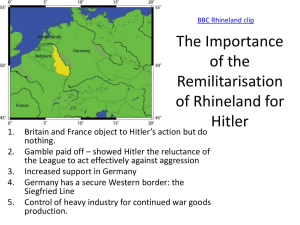
Aim: Was the policy of appeasement cowardly or logical? Do Now: What is the message of this cartoon? Hitler’s Foreign Policy was built on three aims • To abolish the Treaty of Versailles • To create a “Greater Germany” by uniting all German speaking people • The creation of Lebensraum - living space for the German people The Treaty Of Versailles • The German Army was limited to 100,000 men • Germany had to pay reparations to the allies • Germany had to accept the War Guilt Clause (231) • Germany lost 13% of its territories and all her colonies • Created Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia which were ethnically heterogeneous, and had substantial German pop. LEBENSRAUM • Hitler’s Greater Germany would have a population of over 85 million people • Germany’s land would be insufficient to feed this many people • Hitler intended to expand eastward towards Poland and Russia as many Germans lived in northern, eastern, and southern Europe (as a result of WWI displacement). • Russians and Poles were Slavs-Hitler believed them to be an inferior race of and so Germany was entitled to take their land. The Remilitarization of the Rhineland, March 1936 • “I have little doubt that if we had then told Hitler bluntly to go back, his power for future and larger mischief would have been broken. But, leaving entirely aside the French, there was no section of British public opinion that would not have been directly opposed to such an action in 1936” – Winston Churchill Historiography of Nazi Foreign Policy – Do you think Hitler had a grand plan for Europe? • Historians debate the relation between Hitler's decision to remilitarize the Rhineland in 1936 and his broad long-term goals. • Those historians who favor an "intentionist" interpretation of German foreign policy such as see the Rhineland remilitarization as only one "stage" of Hitler's stufenplan (stage by stage plan) for world conquest. • Those historians who take a "functionist" interpretation see the Rhineland remilitarization more as ad hoc improvised response on the part of Hitler to the economic crisis of 1936 as a cheap and easy way of restoring the regime's popularity. • It seems that though Hitler did have a "program" for world domination, that the way in which Hitler attempted to execute his "program" was highly improvised and much subject to structural factors both on the international stage and domestically that were often not under Hitler's control. Creation of a Greater Germany • Hitler wanted a single homeland for all German speaking people • After Versailles millions of Germans were living in Foreign countries • The Treaty of Versailles had forbidden the union of Germany and Austria- The Anschluss APPEASEMENT • A policy aimed to prevent aggressors from starting wars by finding out what they want and agreeing to demands that seem reasonable • Neville Chamberlain was the British Prime Minister that negotiated with Hitler in 1938 at Munich Conference Chamberlain on Munich Agreement – “Peace in our Time” What do you notice about the speech, and how he was received? Munich Agreement – Sept. 1938 Nazi Occupation of Czechoslovakia, 1938-1945 A woman in the Sudetenland greets incoming German troops Czechs expelled from the border with tears and a Nazi salute. looking for new home, October 1938 LANDMARKS OF APPEASEMENT • 1933 - Germany leave the L of N - start to rearm in secret • 1935 -Anglo-German Naval Agreement, Abyssinian Crisis, German announces conscription. • 1936 - Remilitarization of the Rhineland • 1938 - (March) Anschluss • 1938 - (Sept) Sudetenland crisis and the Munich agreement • 1939 - Germany take over the rest of Czechoslovakia (March) • 1939 - Britain and France abandon appeasement and guarantee to defend Poland • 1939 – Germany invades Poland (Sept. 1) – Two days later France and Britain declare war on Germany marking beginning of WWII BRITAIN AND APPEASEMENT British Conservative MP and future PM Winston Churchill • Most politicians wanted to avoid war • The people of Britain wanted to avoid war • Britain had only a small army and air force • Many people thought of the Sudetenland in the same way they had about Austria – Germany had a legitimate claim to these lands • Winston Churchill was a severe critic of appeasements but he was in a minority. "We have suffered a total and unmitigated defeat... you will find that in a period of time which may be measured by years, but may be measured by months, Czechoslovakia will be engulfed in the Nazi régime...And do not suppose that this is the end. This is only the beginning of the reckoning. This is only the first sip, the first foretaste of a bitter cup which will be proffered to us year by year unless by a supreme recovery of moral health and martial vigour, we arise again and take our stand for freedom as in the olden time.“ – Winston Churchill on the Munich Pact The results of Appeasement • Europe saved from earlier war? Possibly though some historians argue that if the Czechs, French, British and Russians had stood up to Hitler he would have been defeated, and would have faced war on two fronts • Czechoslovakia was abandoned, and weakened by the loss of important military defences and resources • Germany gained the Sudetenland- another step towards the Greater Germany – stronger strategic positioning. • Britain and France gained time to build up their armed forces, but so did Germany • Hitler decided Britain and France were unlikely ever to oppose him by force • Stalin was offended at being excluded from the talks and decided he could not rely on Britain to help the USSR stand up against Germany – partially led to Nazi-Soviet (Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact) Pact 8/1939