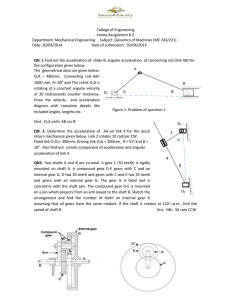
Technology Notes term 1-3 Question 1: Design Skills "The design process is a step-by-step method that helps you solve problems by coming up with creative ideas Design Process Skills ● Investigate/Research: ○ Understanding the problem or opportunity through research, user feedback, and analysis. ● Design/Ideate ○ Generating creative ideas and potential solutions to address the identified problem. ● Prototype ○ Creating tangible representations (prototypes) of design concepts to visualise and test. ● Evaluate/Testing ○ Gathering feedback through testing and evaluation of prototypes, often involving real users. ● Refine ○ Making improvements to the design based on feedback and testing results. Question 2: perspective drawings and gears ● Orthographic Projection- A Drawing of an object which include the 3 sides ● First Angle Orthographic- Front view in top left, side in top right & top in bottom left. This has 3x 2d drawings Front Side TOP ● ● ● ● Gears Wheels w evenly spaced teeth on their outer rim. They are attached to an axle and can be turned by a power source that can be human, mechanical or electrical Used to change speeds in complex machines by changing the size or direction of a turning force. They transfer movement, heat & speed Each gear has a different effect according to ○ Teeth Arrangement ○ Angle at which the meshing occurs ○ Direction of the axles Gears do the following ○ Increase/decrease speed ○ Change the direction of motion ○ Multiply or increase turning force Spur Gear- A wheel with teeth around it’s edge ● Inline system- When gears act in the same plane and direction ● Counter rotation in series gear train but idler gears are added to make the same rotation ● When 2 gears are the same size, they turn @ the same rpm How to calculate velocity ratio of 2 different sizes of spur wheels - Velocity ratio= Teeth on driven / Teeth of Driver - 12/24 - 1:2 Bevel Gear System ● Cone shaped with 45° cut teeth used to turn rotation 90° ● Smaller one turns faster than bigger ● Crown & Pinion- Type of bevel gear ○ Crown gear can mesh with bevel or spur e,g hand beaters Rack & Pinion ● Change rotational movement into linear movement ● Pinion is the gear while the rack is the metal strip with corresponding teeth Worm Gear Systems Speed ↓Force↑ ● A gear that produces 90° change in rotation movement and slows down the speed of movement Question 3 Pascal's Principle Pressure exerted on one part of a hydraulic system will be equally transformed. Without any loss, in all directions to other parts of the system Pneumatics ● Controls mechanisms through compressed air e.g air, nitrogen ● Gas has air between it which can be compressed ( potential energy )& when it expands again, it releases energy ● Advantage- Cheaper than hydraulic ● Disadvantages- Air is compressed easily so it’s not good for precise work ○ Air is dangerous coz it’s unpredictable and kickback can occur Hydraulics ● Controls mechanisms using oil/ liquids & since oil is a lubricant, it reduces friction and does not freeze like water ● Powerful, no air gaps, used in several industries ● Electrical pumps drive the oil into cylinders ● Advantage- Effective bcz pressure is consistent. The force is transferred directly & immediately ● Disadvantage- Leaks are messy & expensive ● Learn Hydraulic Jack Diagram ● Smaller area= larger pressure ● MA transferred thru liquid- Smaller piston pushing a bigger one - MA> 1 & vice versa Ohm's Law V- Voltage I- Current R- Resistance Question 4 Question 5 I don’t have any notes so here's questions 1. - Describe the steps involved in the design process for a mine. Include at least three key stages and explain why each stage is important in ensuring the safety and efficiency of mining operations 2. - Explain how environmental considerations are incorporated into the design process of a mine. Provide two examples of design features or practices that mines can implement to minimise their environmental impact. Discuss why these considerations are crucial for sustainable mining practices. Question 6 ● Structural Member- Support that is an important part of a building ● Dynamic Force- Moving Static- Not moving ● Unbalanced force- F1>F2 Balanced Force- F1=F2 Loads ● Load- Force acting on a structure that is supporting a weight ● Even Loads- When loads are balanced/positioned in a way that no movement occurs ● Uneven Loads- Vice Versa There's an elevator with cables that go up & down. This is a structure.This structure works with forces. When the elevator is pulled upwards, it’s dynamic forces. It has a 80kg limit, if exceeded pls lose weight bcz ur causing an uneven load making the cables snap and hit the ground. This is contact forces. If there's an earthquake and the wall with the cables breaks, it’s non contact forces Structures ● Materials must resist tension, compression & shear force ● Forces Acting on Materials- Tension-Pulling object from both ends potentially making it longer ● Compression- Pushing ● Torsion- Twisting of an object. Cross bracing prevents torsion ● Shear Force- A force that tries to break materials apart -Construction Materials ● Metals ● Non Metals ● Synthetic material ● Natural Materials -Properties ● Mass & Density ● Hardness ● Stiffness ● Flexibility ● Resistance to corrosion ● Prevention of corrosion Question Something Ratchet & Pawl- Gear Mechanism that can lock to prevent a load from rolling backwards Purpose- to allow movement in one direction while preventing it in another ● The ratchet is a gear specially slanted teeth, curved on 1 side & straight on the other ● Pawl is a spring loaded lever that hooks onto the gears teeth openings ➡️➡️➡️➡️➡️ ➔ When the ratchet is rotated, the pawl climbs the curved edge of the teeth ➔ As the pawl passes over the flat edges of the teeth, it falls into a dip & the spring locks ➔ Now it can only move in one direction Diagram is on Pg 74