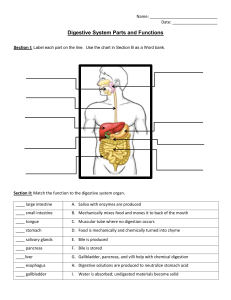
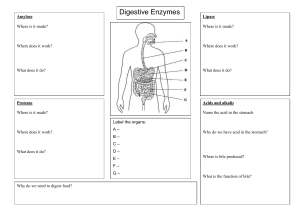
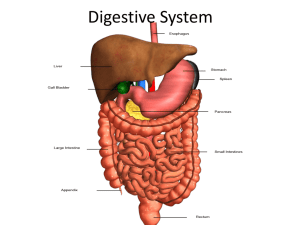
The Digestive System Notes Packet Essential Questions: 1. How do animals (and humans) obtain nutrients? What happens when animals don’t get proper nutrients? 2. How is waste eliminated from the body? 3. What disorders can affect the working of the digestive system? A fistulated cow is a cow with a passageway (cannula) connecting the cow’s rumen (stomach) to the outside. Researchers study how a cow’s stomach works, the microflora in the cow’s stomach, and how fast certain foods are digested. What is scurvy? A condition caused by a lack of vitamin C. A lack of vitamin C means that collagen, a protein found in body tissue such as skin and blood vessels, cannot be replaced, leading to tissue breakdown Adult patients may suffer from bleeding gums, swelling, slowhealing wounds, bruising. Scurvy is a disease of malnutrition, often associated with sailors who were at sea for long periods and had no access to fresh fruits or vegetables. Bleeding gums and tooth loss were some of the first symptoms. What is the function of the digestive system? - mechanical and chemical breakdown of food and the absorption of nutrients -Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal 1. Mucosa - protects tissues and carries absorption 2. Sub-mucosa - glands, blood vessels, nerves 3. Muscular Layer - smooth muscle, pushes food 4. Serosa - lubricates surfaces Draw this! In the small intestine... Villi increase surface area for absorption of nutrients. Celiac disease damages the villi, leaving your body unable to absorb nutrients necessary for health and growth. Gluten in diet triggers immune cells to attack the villi of the small intestine. Mixing Movements mix food with digestive juices Peristalsis - pushes food down the tube Anatomy of the Mouth - the first place of digestion Mouth - begins digestion by chewing and mixing with saliva Tongue - moves food, connects to floor of mouth via FRENULUM Palate - forms roof of oral cavity (hard and soft); Uvula - back of the mouth Palatine Tonsils - part of the immune system Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever. In chronic cases tonsillectomy may be indicated. Teeth INCISORS Canines Premolars Molars Salivary Glands AMYLASE - enzyme breaks down starch into sugars Mucus cells also produce mucus for lubrication during swallowing 1.Parotid Gland 2. Submandibular Gland 3. Sublingual Gland Pharynx nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx STOMACH MUSCLES: Longitudinal, Circular, Oblique Cardiac sphincter ESOPHAGUS FUNDUS CARDIAC REGION Longitudinal muscles LESSER CURVATURE PYLORIC SPHINCTER Circular muscles DUODENUM Oblique muscles BODY RUGAE of stomach Stomach Lining Mucus prevents stomach from digesting itself Rugae - wrinkles within the lining Pepsin - digestive enzyme for breaking down food Chyme - paste released then into the duodenum Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid splashes back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation (Heartburn.) PANCREAS - secretes insulin which breaks down sugars Pancreatic Juice also breaks down fat Both empty into the DUODENUM Liver - functions to create BILE Liver Functions 1. Production of bile 2. Production of proteins 3. Storage of glycogen 4. Storage of vitamins 5. Blood clotting 6. Clears bilirubin 7. Detoxification Bile – yellowish-green liquid aids in digestion, breakdown of fat The liver is an organ that regenerate (regrow) Bilirubin - produced when blood cells break down. Jaundice occurs when liver fails to clear the bilirubin. Causes yellowing of the skin and eyes. Treated with bili-lights. Bili Lights Using bili lights is a therapeutic procedure performed on newborn or premature infants to reduce elevated levels of bilirubin. If blood levels of bilirubin become too high, the bilirubin begins to dissolve in the body tissues, producing the characteristic yellow eyes and skin of jaundice. The Gallbladder liver - stores bile - bile duct connects to duodenum - bile can form gallstones gallbladder 5 Day Old Pasta by ChubbyEmu https://www.youtube.com /watch?v=5ujTYLV2Qo4 pancreas duodenum Gallbladder is removed if gallstones block ducts. Small Intestine Main function: absorption of nutrients 1. Duodenum 2. Jejunum 3. Ileum MESENTERY - supports coils of small intestine and contains blood vessels Greater Omentum (peritoneum) membrane that covers the intestines, stores fat Large Intestine 1. Cecum = start of large intestine, has an attached appendix - Ileocecal valve (between sm. Intestine and cecum) 2. Colon = 4 sections, ascending / transverse / descending / sigmoid 3. Rectum – stores waste before it is expelled from the body 4. Anus -muscular sphincter which controls the exit of waste Ileocecal valve Stomach Transverse Colon Ascending Colon Jejunum Cecum Appendix Rectum Descending Colon Ileum Sigmoid Colon The Appendix Recent news on the function of the appendix. The appendix acts as a storehouse for good bacteria, “rebooting” the digestive system after diarrheal illnesses. ScienceDaily Article Appendicitis occurs when the structure becomes infected or inflamed. Function of Large Intestine Secretes mucus, reabsorbs water, contains bacteria to aid in digestion (intestinal flora) Mass Movements (defecation) - removes undigested food The main job is WATER REABSORPTION.. The Bristol Stool chart analyzes the consistency of FECES. *Feces is a fancy name for poop. Disorders of the Digestive System A Gastroenterologist is a physician with dedicated training and unique experience in the management of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Colonoscopy Test is used to detect cancer in the colon. Dysentery or Diarrhea Failure to reabsorb water in the large intestine, which leads to watery stool. Dehydration can lead to death. Causes Include: Parasitic Infection (Ameba, Cryptosporidium) Bacterial Infection (Cholera, E. coli, Salmonella) Viruses (Norovirus and other stomach bugs) Food allergy or intolerance Gastroenteritis is a generic name used to describe vomiting and diarrhea Cholera Cholera bacteria causes diarrhea, leading to massive loss of water that can be fatal. Bacteria is transmitted through unclean water sources and contaminated food. The MICROBIOME The average human digestive tract is home to as many as 1,000 species of microorganisms When something upsets the balance of these organisms in your gut, otherwise harmless bacteria can grow out of control and make you sick. One of the worst offenders is a bacterium called Clostridium difficile(or C. diff). Become a Stool Donor at OPENBIOME.org HEPATITIS A, B, C Hepatitis A -caused by eating food or water infected with the virus Hepatitis B & C - transmitted through body fluid (STI) Hepatitis B & C can lead to long term (chronic) disease and even liver failure. Crampy abdominal pain Loss of appetite Bloody stool Watery diarrhea Weight loss Constipation IBS = Irritable bowel syndrome STOMACH ULCERS Burning upper abdominal pain, particularly between meals, early in the morning, or after drinking orange juice, coffee, or alcohol, Treated with antibiotics to kill H. pylori bacteria. Constipation difficulty in emptying the bowels, usually associated with hardened feces. symptoms of chronic constipation include: ● Passing fewer than three stools a week ● Having lumpy or hard stools ● Straining to have bowel movements ● Feeling as though you can't completely empty the stool from your rectum Hemorrhoids swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum may result from straining during bowel movements or from the increased pressure on these veins during pregnancy Can cause pain, itching, and minor bleeding during bowel movements Lactose Intolerance Inability to digest milk, can cause stomach upset Hernia intestines poke through abdominal muscles Malnutrition lack of proper nutrition, caused by not having enough to eat, not eating enough of the right things, or being unable to use the food that one does eat - Scurvy (lack of vitamin C) - Rickets (lack of vitamin D) An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal body functioning that can not be synthesized by the body. Most animals can synthesize their own vitamin C, so they don’t need it in their diet. Exceptions: primates, guinea pigs, fruit bats *What do these animals have in common? (2A)Assignment: Read “Broken Genes” by Nathan Lents, Excerpt from Human Errors Patient presents with bleeding gums and corkscrew shaped hairs on legs. What is the diagnosis? LABEL THIS! esophagus liver gallbladder stomach pancreas duodenum transverse colon ascending colon descending colon jejunum ileum cecum appendix anus rectum LABEL THIS! Liver Right Hepatic duct Common Hepatic duct Cystic duct Common Bile duct Gallbladder Pancreatic duct Pancreas Duodenum