Mental Health, Relationships, and Social Influences Overview
advertisement

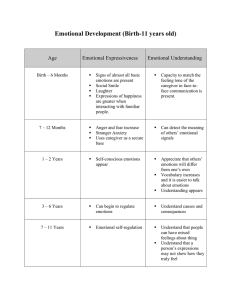
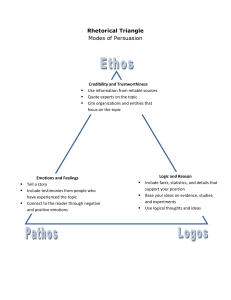
d. Depression - refers to the lack of will to live, feel and do anything. e. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder the aftermath of a traumatic event–that affects the mental health of an individual. f. Autism Spectrum Disorder - a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the mental growth of a person. g. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - the inability of an individual to focus themselves on something without getting distracted. MENTAL HEALTH - It refers to the emotional, social and psychological well being of a person and ability to cope up with stress. COMPONENTS OF MENTAL HEALTH 1. Perceived Self-efficiency - the self-esteem of an individual. 2. Subjective well-being - the way an individual sees themselves. 3. Autonomy - an individual recognizes their own identity, alone. 4. Competence - the capability and ability to recognize and perform one’s own skills. 5. Intergenerational Independence the capability of an individual to live separately from their family. 6. Self-Actualization - an individual attained all the goals they longed for—emotional, mentally, socially and spiritually. MENTAL PROBLEM - The temporary change in one’s psychological state that can affect their lifestyle. MENTAL ILLNESSES/DISORDER - Diagnosed mental problem that greatly affects one’s capability to live and function on their own. a. Schizophrenia - extreme level of hallucinations happens in a person. b. Bipolar Disorder - extreme mood swings. c. Anxiety - also called as panic disoder that affects one’s mind and ability to breathe. GOOD SELF CONCEPT + HEALTHY BODY = GOOD MENTAL HEALTH Physical Health also affects mental health as the energy influences the hormones. Resilience is also needed in mental health as this refers to the ability of a person to withstand stress and maintain a healthy mental state. Adaptability refers to the ability of a person to adjust to changes. EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE - It refers to the ability to understand, recognize and manage emotions. EMOTIONS - It refers to the reactions an individual has after a specific event. a. Primary Emotions - simple and initial b. Secondary Emotions - complex DOMAINS OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE 1. Self Awareness - refers to the ability to recognize your emotions. 2. Self Regulation - refers to the ability to control your emotions. 3. Social Skills - refers to the ability to socialize with others. 4. Motivation - refers to the ability to maintain a positive attitude. 5. Empathy - refers to the ability to empathize and validate others. LOVE - Strong affection COMMITMENT - The act of binding yourself FISHER’S THREE STAGES OF FALLING IN LOVE 1. Lust - driven by the sex hormones. 2. Attraction - driven by the neurotransmitters; dopamine serotonin and norepinephrine. 3. Attachment - involves commitment STEPS IN MANAGING EMOTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Recognize your emotions Own your emotions Discernment Take Action EMOTIONAL RESPONSES - The emotional reactions an individual has after a certain event. TYPES OF EMOTIONAL RESPONSES 1. Passive Response - weak responses wherein you don’t control your emotions–but others. 2. Aggressive Response - a response with a negative attitude as perceived to be rude. 3. Assertive Response - a positive type of response in a respectful way. PERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS RELATIONSHIP - connection between two or more people–involves understanding. ELEMENTS OF PERSONAL RELATIONSHIP I. Attachment - the bond a person has with their mother. This affects the attachment they'll create in the future. Ainsworth. a. Secure attachment - the child has a stable relationship with the primary caregiver. b. Avoidant attachment - the child has an unresponsive relationship with the primary caregiver. c. Anxious-ambivalent attachment the child has an unstable relationship with the primary caregiver. II. Attraction - the act of likeness usually associated with the physical appearance. a. Transference Effect - first impression; like or dislike. b. Propinquity Effect - the sense of familiarity leads to attraction. c. Similarity Effect - attracted because of similarities. d. Reciprocity Effect - attracted to people who like us back. e. Physical Attractiveness - the attraction due to physical appearance. f. Personality Characteristics and Traits - attracted to either emphatic persons or socially competent persons. 3. Kindness 4. Actions matches words 5. Vocal with feelings and thoughts. SOCIAL RELATIONSHIPS - LOVE AND INTIMACY - strong feeling of affection and attraction towards the other person. STENBERG’S TRIANGULAR THEORY OF LOVE Interaction between two or more people. . SOCIAL INFLUENCE - Things, beliefs, attitudes, actions that one individual can adapt from another. VARIETIES OF SOCIAL INFLUENCE 1. Intimacy - deepened level of understanding and communication. 2. Commitment - the act of consistency 3. Passion - the intense state; sexual attraction. EIGHT KINDS OF LOVE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. III. Non-Love Liking Romantic Love Infatuation Fatuous Love - fantasy love Empty Love Companionate Love Consummate Love - ideal love Commitment - the act of consistency; both words and action. It is defined as binding yourself into an action. KEEPING HEALTHY RELATIONSHIPS 1. Honesty 2. Respect 1. Compliance - agree to follow something without really agreeing with the thought itself. 2. Conformity - a change of behavior as a manifestation of another person. 3. Conversion - a wholehearted change of actions. 4. Obedience - doing something due to the influence of authority. 5. Persuasion - due to the influence of appealing to reason or emotion. FILIPINO VALUES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Friendship Pakikisama Pakikiramdam Bayanihan Utang na Loob Tampo LEADERSHIP THEORIES - A leader is the head of the group that can influence the group itself by their actions and words. 1. Trait Theory - personality of a leader 2. Behavioral Theory - leadership is a learned behavior 3. Charismatic Leadership Theory commands by charisma 4. Situational Theory - no specific style of eldership. 5. Transactional Theory – negotiations 6. Transformational Theory engages with followers 10. Foster family: 11. Gay or Lesbian family: 12. Immigrant family: 13. Migrant family: FAMILY HEREDITY - There is a 40% to 50% chance of personality traits being passed on through heredity. - This refers to the acquired traits of an offspring from their parents GENOGRAM - Graphical representation of the family history. . FOLLOWERSHIP THEORIES 1. A make-it happen attitude 2. Willingness to collaborate 3. The passion of growth FAMILY STRUCTURES AND LEGACIES FAMILY - Two or more persons living together that share resources, beliefs and influences one another. DIFFERENT FAMILY STRUCTURES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Nuclear family Extended family Step families: Single parent family: Adoptive family: Bi-racial or multi-racial family: Trans-racial adoptive family: Blended family: Conditionally separated families: PERSONS AND CAREERS CAREER - A profession that can match one's capability and skills. CATEGORIES OF CAREER DEVELOPMENT THEORIES 1. Trait Factor - skills are assessed. 2. Psychological - dominant personality is assessed. 3. Decision - mind over passion thing 4. Life-Space Theory - the continuous learning process for humans. POSITIVE IMPACTS ON SOCIETY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Self-concept or self-identity Personal Preferences Motivation Self-confidence Personal skills 6. 7. 8. 9. Personality Characteristics Personal Health Emotional Consideration Self-sabotaging thoughts