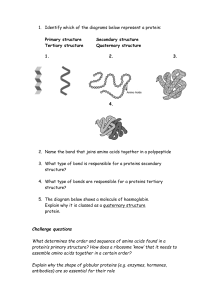
QUARTER 4-MODULE 4 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE PROTEINS LESSON 5 Biomolecules 2 Proteins 4 COMPONENTS OF PROTEIN Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Consists of amino acids – 20 standard amino acids THE DISCOVERY OF PROTEINS Proteins were first described by the Dutch chemist Gerardus Johannes Mulder and named by the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1838.Mulder carried out elemental analysis of common proteins and found that nearly all proteins had the same empirical formula, C400H620N100O120P1S. THE DISCOVERY OF PROTEINS The term "protein" to describe these molecules was proposed by Mulder's associate Berzelius; protein is derived from the Greek word πρώτειος (proteios), meaning "primary", "in the lead", "standing in front", Mulder went on to identify the products of protein degradation such as the amino acid leucine. Prior to "protein", other names were used, like "albumins" or "albuminous materials" (Eiweisskörper, in German). Monomers Amino group Carboxylic acid group Amino acids are the monomers of proteins. WHAT IS AN AMINO ACIDS referred to as the BUILDING COMPONENTS of proteins. These biomolecules are involved in several biological and chemical functions in a human body and are the necessary ingredients for the growth and development of human ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS VS. NON -ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Different Structures of Proteins Video Different Structures of Proteins The Uses & Functions of Proteins in our Bodies ENZYMES - Special proteins that speed up chemical reactions - Biological catalysts FIBROUS PROTEIN VS. GLOBULAR PROTEIN •Structural or Fibrous protein – which means these proteins helps to maintain cell shape by providing a scaffolding. •Ex. Bones, Cartilage, Blood vessel •Functional/Globular – this means globular proteins carry out a specific biological function in the body. FIBROUS PROTEIN VS. GLOBULAR PROTEIN SOURCES OF PROTEIN IN OUR DIET IMPORTANCE OF PROTEINS LESSON 6 NUCLEIC ACIDS - Discovered by Friedrich Miescher in 1869. He collected used bandages, to wash out the white blood cells contained in the pus. - Miescher noticed a precipitate of an unknown substance. Its properties during the isolation procedure and its resistance to protease digestion indicated that the novel substance was not a protein or lipid because it contained large Johannes Friedrich Miescher amount of phosphorous. (1844-1895) was a Swiss - He isolated the substance from the nucleus of leukocytes of wash out bandages containing pus. physician and biologist. He was the first scientist to isolate nucleic acid. NUCLEIC ACIDS • Miescher named the substance “nucleic” (pronunciation: nu-cle-ic) – after the Latin word for core, nucleus. • The substance contained: • Carbon • Hydrogen • Oxygen • Nitrogen • Phosphorous SUB-UNITS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS a. Pentose Sugar (Ribose and Deoxyribose) b. Phosphoric Group – derived from phosphoric acids c. Nitrogen Base TYPES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acids • Store and transfer generic information • Found in the nucleus only • Encodes information used to assemble proteins. RNA – Ribonucleic Acids • Found in the nucleus and cytoplasm • Reads DNA-encoded information to direct protein synthesis. DNA NUCLEOTIDES Biological molecules 25 COMPARISON OF DNA AND RNA STRUCTURES STRUCTURE Sugar DNA Deoxyribose RNA Ribose Nitrogenous Bases A, G, C, T A,G, C, U Double stranded Single stranded Yes No Strands Helix BIOMOLECULE MEMES ? HOW WELL YOU LEARNED? 1. JAY LEARNED THAT WHENEVER HE EATS PROTEINS FOODS, HE IS SUPPLIED WITH AMINO ACIDS. WHICH STATEMENT BELOW IS TRUE ABOUT AMINO ACID? • a. Amino acid is the building block of proteins for the rebuilding of the body system. • b. Amino acid is the building block of protein for providing instant energy for cells. • c. Amino acid is the building block of nucleic acid for energy production for human consumption. • d. Amino acid is the building blocks of nucleic acid found in hormones and cell membrane components. 2. THE RNA IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE TEMPLATE IN THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS. WHICH IS NOT THE COMPONENT OF RNA? •a. thymine •b. adenine •c. guanine •d. cytosine 3. THE SUGAR IN RNA IS ___________, THE SUGAR IN DNA IS _____________. Write your answer __________________________________ 4. A TYPE OF BIOMOLECULE THAT PROVIDES FUNCTIONAL AND STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONS TO CELLS Write your answer ______________________ 5. KIKO WONDERS WHY SIBLINGS RESEMBLE EACH OTHER, OR HOW A MOTHER AND HER DAUGHTERS LOOK ALIKE. WHICH BIOMOLECULES ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS RESEMBLANCE? Write your answer ______________________ LET’S FIND OUT IF YOU GOT IT RIGHT! 1. JAY LEARNED THAT WHENEVER HE EATS PROTEINS FOODS, HE IS SUPPLIED WITH AMINO ACIDS. WHICH STATEMENT BELOW IS TRUE ABOUT AMINO ACID? • a. Amino acid is the building block of proteins for the rebuilding of the body system. • b. Amino acid is the building block of protein for providing instant energy for cells. • c. Amino acid is the building block of nucleic acid for energy production for human consumption. • d. Amino acid is the building blocks of nucleic acid found in hormones and cell membrane components. 2. THE RNA IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE TEMPLATE IN THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS. WHICH IS NOT THE COMPONENT OF RNA? •a. thymine •b. adenine •c. guanine •d. cytosine 3. THE SUGAR IN RNA IS ___________, THE SUGAR IN DNA IS _____________. Write your answer Ribose, Deoxyribose 4. A TYPE OF BIOMOLECULE THAT PROVIDES FUNCTIONAL AND STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONS TO CELLS •Proteins 5. KIKO WONDERS WHY SIBLINGS RESEMBLE EACH OTHER, OR HOW A MOTHER AND HER DAUGHTERS LOOK ALIKE. WHICH BIOMOLECULES ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS RESEMBLANCE? •Nucleic Acids END OF DISCUSSION