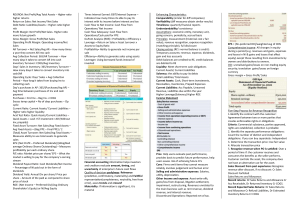
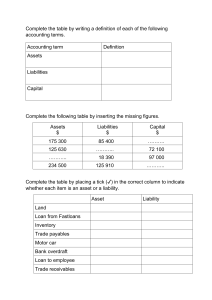
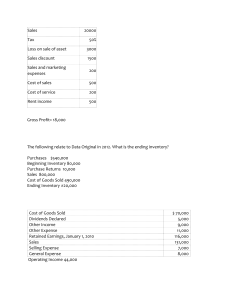
ROI/ROA: Net Profit/Avg Total Assets – Higher ratio higher returns Return on Sales: Net Income/ Net Sales Debt Ratio: Liabilities/Assets – Higher ratio higher risk Profit Margin: Net Profit/Net Sales- Higher ratio more future growth Gross Margin: Gross Profit/Net Sales Operating Profit Margin: Operating income/Net Sales AR Turnover = Net Sales/Avg AR – How many times a year they convert AR into cash Avg Collection Period: 365/AR Turnover – How many days it takes to convert AR into cash Inventory Turnover: COGS/Avg Inventory Days’ Sales in Inventory: 365/Inventory Turnover – How many days it takes to convert inventory into cash/AR Operating Cycle: Days’ Sales + Avg Collection Period – How long it takes from buying Inv to collecting cash Day’s purchases in AP: 365/(Purchases/Avg AP) – Avg time between purchases of Inv and cash payment Purchases = End Inv – Beg Inv + COGS Excess temp capital = No of days purchases – Op cycle Current Ratio: Current Assets/ Current Liabilities – Higher ratio higher liquidity Acid Test Ratio: Quick Assets/Current Liabilities – Quick Assets = cash +ST investment +AR (Without Inv, prepaids) Fixed Asset Turnover: Net Sales/Avg Fixed Assets – Avg Fixed Assets = (Beg PPE – Final PPE) / 2 (Total) Asset Turnover: Net Sales/Avg Total Assets – Measures ability to use total assets to generate sales EPS: (Net Profit – Preferred Dividends)/(Weighted average Ordinary Shares Outstanding) – Measures profitability per each ordinary share P/E ratio: Market price per share/ EPS – What the market is willing to pay for the company’s earning stream Dividend Payout Ratio: Cash Dividends/Net Income – Percentage of NI paid out in the form of dividends Dividend Yield: Annual Div per share/ Price per share – Amount of Div paid as compared to share price of stock ROE: (Net Income – Preferred Div)/Avg Ordinary Shareholder’s Equity) or NI/Avg Equity Times Interest Earned: EBIT/Interest Expense – Indicates how many times its able to pay its interest with its income before interest and tax Cash Flow to Net Income: Cash Flow from Operations/ Net Income Cash Flow Adequacy: Cash Flow from Operations/Cash paid for PPE DuPont Analysis (ROE)= Profitability x Efficiency x Leverage = Return on Sales x Asset turnover x Assets to Equity Ratio Profitability= Ability to generate net income per sale Efficiency= Ability to generate sales using assets Leverage= Using borrowed funds instead of invested Financial accounting information helps investors and creditors evaluate amount, timing, and uncertainty of enterprise’s future cash flows Quality of decision usefulness: Relevance (predictive, confirmatory, materiality) and Faithful representation(completeness, neutrality, free from error), asses trends and crossref Materiality: If information is significant, it is material Enhancing Characteristics: Comparability (similar for diff companies) Verifiability (diff measures obtain similar results) Timeliness: quarterly financial reports Understandability/ consistency Assumptions: economic entity, monetary unit, going concern, periodicity, accrual basis Principles: measurement (historical cost v fair value), revenue recognition, expense recognition (matching principle), full disclosure Closing entries (RE’s normal balance is credit): Temporary accounts: revenue, expense, dividends, gain and loss accounts Debit balances are credited to RE, credit balances are debited to RE Liquidity: Meet short-term cash obligations Current Assets/ Current Liabilities Solvency: the ability to pay its debts Total Liabilities/ Total Assets Current Assets: Cash, Short-term investments, Receivables, Inventories, Prepaid Expenses Current Liabilities: Acc Payable, Unearned Revenue, Liabilities due within the year Higher Leverage(Solvency) Higher ROE Income Statement Pros: Help users evaluate past performance, provides basis to predict future performance, help users assess risk of achieving future CFs Cons: Firms omit items they cannot measure reliably, involves judgement and human error Selling and administrative expenses: Salaries, utility, depreciation. Other Income and expense: Asset write-offs, gains/loss from disposal, litigation settlement, impairment, restructuring, Revenues unrelated to the main business such as rent revenue, dividend revenue, and interest revenue. Discontinued Operations: Reported net of tax. EPS = (NI–preferred DD)/weighted avg of OOS Comprehensive Income: All changes in equity during a period (e.g. revenues and gains, expenses and losses in NI & gains and losses that affect equity) except those resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. OCI: unrealised gains/losses on non-trading equity security; translation gains/losses on foreign currency Gross margin = Gross Profit/ Sales Five-Step Process for Revenue Recognition 1.Identify the contract with the customer: Agreement between two or more parties that creates enforceable rights or obligations Criteria: Commercial substance, parties approved, rights are established, collection is probable 2. Identify the separate performance obligations: Count the number of distinct and independent obligations. If you can buy separately: Independent 3. Determine the transaction price: Use fair value 4. Allocate transaction price 5. Recognize revenue when PO is satisfied: Over a period of time if: the customer receives and consumes the benefits as the seller performs, Customer controls the asset, the company does not have an alternative use for the asset. Sales Discount from past experience: Recognize revenue after discount, if no discount: Cr Sales Discount Forfeited Sales Returns and Allowance: Record returns: Dr Sales Returns and Allowance Cr Acc Receivable, Dr Returned Inventory Cr COGS. Record Expected Sales Returns: Dr Sales Returns and Allowance Cr Refund Liabilities, Dr Estimated Inventory Returns Cr COGS Long Term Contracts: Usually a single PO Spanning several reporting periods, Seller bill purchaser at interval Revenue Estimation Methods: Percentage of Completion: +amortisation of intangibles + Increase in liabilities - decrease in accrued expense Contract asset: when seller provides G&S on account, has the right to consideration from customer Contract liability: seller’s obligation to transfer G&S since consideration already received from customers (i.e. unearned revenue) CIP: an inventory account used to accumulate costs as incurred in project (i.e., material, labor, and overhead), plus any recognized gross profit; contract asset Billings on Construction: A contra-asset account to accumulate billings sent to clients for periodic “progress payment” contract liability Journal Entries 1. Construction in Progress: Dr CIP Cr Cash, Material, Labour 2. Billings: Dr Acc Rec Cr Billings on Construction 3. Revenue Recognition: Dr CIP(Gross Profit) Dr Cost of Construction Cr Revenue from LT contract Cost Recovery Method: When reasonable estimate revenue: Cost = Revenue, current period profit = 0, recognize revenue at completion Journal Entry: Dr Cost of Construction, Cr Revenue from LT C Statement of Cash Flows To provide information about cash receipts and cash disbursements during a period -To complement the Income Statement and Balance Sheet -Information about cash flows from operating activities, when combined with information about cash flows from other activities, can provide information helpful in assessing future profitability, liquidity, and long-term solvency Free Cash Flow = +CF from Operating Activities + Interest Expense - CAPAX(Capital expenditure) - Dividends paid Net cash flow from operating activities is determined by eliminating noncash expenses and noncash revenues from net income. Financing: - Dividends paid + increase in bond/note payable Balance Sheet Income Statement Historical Cost Change in accounting methods Use estimates Management discretion: fraud Values omitted Values Omitted Expenses: Decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of - outflows or depletions of assets or - incurrence of liabilities Common Reasons for Discontinued Operations: - Closure of Redundant Division Post-Merger - Cutting Off Unprofitable Division - Discontinuation of Product/Service with Limited Market Demand - Fire Sale for Liquidity (i.e. Urgent Need for Cash) - Mismatch of Business Division with Core Operations Change in contract terms while it is ongoing: -Companies determine whether a new contract (and performance obligations) results or whether it is a modification of the existing contract. -Account for as a new contract if: Promised goods or services are distinct, and The company has the right to receive an amount of consideration that reflects the standalone selling price of the promised goods or services. Companies provide a range of disclosures: -Disaggregation of revenue. -Reconciliation of contract balances. -Remaining performance obligations. -Cost to obtain or fulfil contracts. Other qualitative disclosures: Significant judgments and changes in them. Minimum revenue not subject to variable consideration constraint. ASSURANCE WARRANTY: Straight away revenue When incur cost for assurance warranty, debit to expense Payables causes an increase in liabilities and a decrease in expense thus it decreases income statement but there is no cash outflow yet so we have to increase CFO Only affects Operating Cash Flows, so only Operating Cash Flows section looks different, but that too will result in same number in cash flow from operations Indirect method provides more direct links to I/S