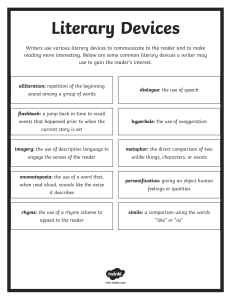
Different Literary Elements Literary elements are information that you have been encountering since your elementary days. These are elements that help the author to express their thoughts, ideas, feelings and emotions in the most aesthetic ways and sometimes also used to conceal and to lighten up the choice of words. Here are the main reasons to use literary devices in your writing: 1. Include special effects in writing 2.Establish connection with your audience. 3.Interests hooks the reader. 4.Use abstract information. 5.Establish clear and vivid pictures with your words. Some common reasons why authors use literary devices are to: 1. Illustrate the storyline; 2. Clarify certain points or concepts; 3. Convey abstract information; 4. Draw attention to important pieces of the story or topic; 5. Engage and captivate readers; 6. Encourage readers to interact with the story a little deeper; and 7. Enhance the reader’s experience. Reasons to Use Literary Elements in Writing The number one rule to writing is to “show, don’t tell”. You have to illustrate the story to your readers. Using literary elements will clearly help the readers to establish the scenarios of the stories. Utilizing these elements will help you to have vivid illustrations. Readers do not want a story to be told but rather to see the storyline by showing it to them. Allusion A literary device that refers to external people, events, or things. These are people who are not part of the story itself. “Don't act like a Romeo in front of her.” – “Romeo” is a reference to Shakespeare's Romeo, a passionate lover of Juliet, in “Romeo and Juliet”. Alliteration Alliteration is a device where an initial consonant sounds is being repeated in the words of a phrase or a sentence. I saw thousands of bats, screeching and screaming which seemed like they saw hunters and tried to fly in different directions. Anaphora Anaphora is a repetition of the same word or phrase at the beginning of successive sentences. It was the best of times, it was the worst of times during the times of challenges like this pandemic time. Diction The specific choice of words used helps determine the style in which the person is speaking or writing. It can be a formal, informal, colloquial, slang or poetic. Anes ganap? It’s the bonggacious fiesta ditetshiwa in the Philippines. Filipino People are united and the whole nation is into it. There are so many anechanech like the colorful decorations and there are variety of foods. Anes pa? Let’s find more-more ganap. Euphemism a mild or indirect word or expression substituted for one considered to be too harsh or blunt when referring to something unpleasant or embarrassing. No one wants to be with him because his attitude is unattractive and substandard to women’s choice. Epistrophe The repetition of a word or phrase at the end of a sentence. I want the best, and we need the best, and we deserve the best. Flashbacks It is an interjected scene that takes the narrative back in time from the current point in the story. In a story about a girl who is afraid of heights, there is a flashback to a time when she fell off of the top of a playground as a young child. Foreshadowing A clue at what will happen next, or at some point, in the story. It was a cold stormy night that would introduce her to eternal darkness, forever changing the course of her life. Hyperbole Extreme exaggeration of a real event or situation. I’m so hungry, I can eat a whole cow. Imagery A literary device that appeals to the reader’s physical senses. As I unveiled the beige curtain of my cottage’s window, I witnessed a picturesque view of Caramoan. It was intensively heaven. Juxtaposition When a writer places two contrasting concepts, people, or events directly side by-side in a sentence or paragraph. In the classic movie The Godfather, when baptism scenes were juxtaposed with murder scenes. Motif when a recurrent element (such as an image, sound, or concept) is found throughout a story, to help develop the theme, or central message. The presence of older female villains in Disney adaptations. Metaphor An implicit comparison between two or more things. Your brother is an angel for me. Simile An explicit comparison between two or more things using the words "like" or "as." My love for you is like this river flow. It won’t stop. Personification When a writer gives inanimate objects or inhuman beings (like animals) human characteristics or attributes. Leaves dance with the wind. Onomatopoeia A word or phrase that conveys the sound of something. Kring… Kring…Kring… The telephone rings. Oxymoron A combination of contrasting, or opposite, words. The experiences that we had were really bitter sweet memories to us. Paradox A sentence or a phrase that appears contradictory, but implies some kind truth. Keep your friends close, and your enemies closer. Assonance Repetition of vowel sounds in every word in a line or a sentence. When we had our vacation, the teachers reached the beach concert of The Meech Band. Consonance Repetition of consonant sounds within the words in a line or a sentence. The female, more than my thumb, are shimmering in their maroon dresses. Question 2 Alliteration is a type of figurative language that involves the repetition of vowel sounds in a series of words. True False Answer Alliteration is a type of figurative language that involves the repetition of vowel sounds in a series of words. True False Multiple Choice Choose the letter that corresponds to the best answer for each question. Answer Which of the following is NOT a type of rhyme in poetry? A. End rhyme B. Slant rhyme C. Internal rhyme D. Parallel rhyme Question 4 What do you call a group of lines in a poem that forms a distinct unit, similar to a paragraph in prose? A. Rhyme scheme B. Stanza C. Meter D. Simile Answer What do you call a group of lines in a poem that forms a distinct unit, similar to a paragraph in prose? A. Rhyme scheme B. Stanza C. Meter D. Simile Fill in the Blank Answer each question by writing the appropriate word. Question 5 What is the term for the underlying message or main idea that a poem conveys to the reader? Answer What is the term for the underlying message or main idea that a poem conveys to the reader? Theme Question 6 What is the term for a comparison between two unlike things, often using "like" or "as"? Answer What is the term for a comparison between two unlike things, often using "like" or "as"? Simile Well Done! Thank you for participating.