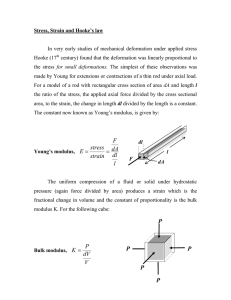
Elasticity Elasticity is a measure of the deformation of an object when a force is applied. Referred Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GhUGNBuBfFA or https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XRKkjm4cuFE Stress: Stress is force over area. 𝜎= 𝐹 𝐴 Where For Area of Wire A = Area in 𝑚2 r= Radius in m D=Diameter in m For Force 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 𝐷 𝑟= 2 𝐹 = 𝑊 = 𝑚𝑔 Where 𝑔 = 9.8 𝑚⁄𝑠 Types of Stress Tensile Stress If the deforming force or applied force results in the increase in the object’s length then the resulting stress is termed as tensile stress. For example: When a rod or wire is stretched by pulling it with equal and opposite forces (outwards) at both ends. Volumetric Stress When the deforming force or applied force acts from all dimensions resulting in the change of volume of the object then such stress in called volumetric stress or Bulk stress. In short, when the volume of body changes due to the deforming force it is termed as Volume stress. Shear Stress When the direction of the deforming force or external force is parallel to the crosssectional area, the stress experienced by the object is called shearing stress or tangential stress. This results in the change in the shape of the body Strain: Strain is change in length over original length. 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 = Tensile Strain X=l 𝛥𝑥 𝑥 Volumetric Strain X=V Shear Strain Modulus of Elasticity: it is a measure of how easily any material can be bent or stretched. λ= Elastic Modulus Young's modulus (Y) Bulk modulus (B) Shear modulus or Rigidity modulus (S) 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 Definition Tensile strain Bulk strain Shear strain Nature of strain Change of shape and size Change of size but not shape Change of shape but not size Hooke’s Law Hooke's law states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material. Stress-Strain Curve: Referred Link, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OdU4t6JD6aE Material Property: The term "property" is a qualitative or quantitative measure of response of materials to externally imposed conditions like forces and temperature. Following are the properties w.r.t Stress and Strain (Elaborate both Topics) Referred Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9qcqfp5d6aA Term ELASTICITY Definition The ability of a material to return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed Example: Steel, Spring۔ PLASTICITY The ability of a material to permanently change its shape without breaking when a force is applied. Ex: Rubber band. Strength The ability of a material to withstand external forces without breaking or deforming. STIFFNESS The resistance of a material to bending or deformation when subjected to a force. E.g. Steel beam is more stiffer or more rigid than aluminum beam. DUCTILITY The ability of a material to be stretched into a wire or thread without breaking. Ex: Platinum, Iron, Copper, Aluminum and Zinc. Malleability The ability of a material to be shaped or formed into various shapes without breaking. E.g Lead can be readily rolled and hammered into thin sheets but can be drawn into wire. RESILIENCE The ability of a material to absorb energy when subjected to stress and then release it when the force is removed, without permanent deformation. Hardness Ability of the material to withstand plastic deformation or indentations ( )کھوکھیلproduced in the material. BRITTLENESS The tendency of a material to break or fracture under stress, without significant deformation. Ex: glass Creep The slow and gradual deformation of a material over time when subjected to a constant load or stress. Fatigue The weakening or failure of a material over time due to repeated or cyclic loading. Slogan Gain Orignal Shape Permanently change Hard to broken Hard to deformed To make wire To make sheets To absorb energy Resist plastic deformation Tendency to Break Deformation over time Weakening over time