Engineering Materials Properties: Lecture Notes
advertisement

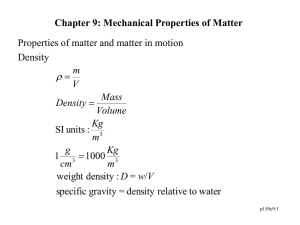
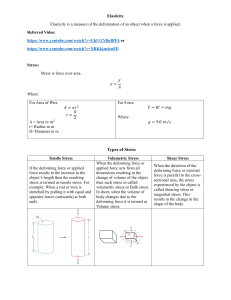
PROPERTIES OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS EM NOTES # 2 PROPERTIES OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS • Chemical Properties – concerned with the chemical properties of materials particularly in connection with corrosion, alloying, compound formation and so forth • Physical Properties – a description of physical behavior of a material includes characteristics such as specific heat, thermal conductivity, coefficient of expansion, color , refractive index, density and electrical resistivity. • Mechanical Properties- Characteristics such as strength, hardness, machinability, ductility, elasticity and plasticity are great interest to the engineers in selecting materials for machines, structures and determine sizes of various members to support loads adequately. • Strain – is a deformation caused by the application of an external force, When the materials is under strain the material has undergone some deformation as the result of the application of an external force • Stress-When internally distributed forces which tend to resist deformation may be defined qualitatively as stress. Three types of stress: tension, compression, shear. all three kind of stress will be found in a material subjected to a load , Like for example in bending a combination of tension and compression and some shear. • Elasticity – the property of regaining the original shape upon the removal of the external load . All materials are elastic although the range of elasticity varies greatly in different material. For stone elasticity is small whereas rubber deformation Is big. The elasticity in engineering does not refer to the amount of elastic deformation but to the completeness of recovery after the removal of the load. • Hooke’s Law- states that within the elastic range of materials stress is proportional to strain. • Bulk Modulus of Elasticity sometimes called the volume modulus. This condition indicates equals stresses I all directions • Modulus of Rupture – of a material is a computed strength which does not bear a specific relationship to the maximum stress the material will sustain before fracture. • Plasticity- if a force is applied to a material the relative position of the atoms is changed and if when the force is removed the atoms return to their original positions. The material is said to have been in a state of elastic strain. • Resilience- The capacity of materials to absorb energy within the elastic range • Ductility- is that quality of a material by virtue of which it may be plastically elongated. • Toughness- The area under the the stress strain diagram up to the breaking point is related to the amount of energy necessary to cause failure per unit. Toughness means difficult to break . • Malleability- If a material can be severely deformed plastically in compression without fracture • Hardness- for engineering materials means many things , hardness sometimes means resistance to scratching, resistance to wear, resistance to penetration , resistance to cutting.