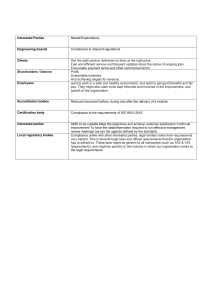
GENERIC MANUAL ON ISO 9001:2015-ALIGNED QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR GOVERNMENT HOSPITALS AND MEDICAL CENTERS Generic Manual on ISO 9001:2015-Aligned Quality Management System for Government Hospitals and Medical Centers Copyright @ 2020 by Development Academy of the Philippines All rights reserved Cover and Manual Design: Mariel R. Mañibo The information provided in this document are from the writers. It does not necessarily state or reflect the views of the Academy and its collaborators. This publication, once printed, is considered uncontrolled and may be used only for reference. Latest version of this document is available online. No part of this publication may be reproduced, sold, stored, or transmitted in any form. Published by Development Academy of the Philippines through the Productivity and Development Center Government Quality Management Program Development Academy of the Philippines DAP Building, San Miguel Avenue, Ortigas Center, Pasig City Tel. (02) 8631 09 21 | (02) 8631 21 37 Website: www.dap.edu.ph E-mail: gqmpo@dap.edu.ph PRODUCTIVITY AND DEVELOPMENT CENTER Cotabato Regional and Medical Center | Amang Rodriguez Memorial Medical Center | Mindanao Central Sanitarium | Eastern Visayas Regional Medical Center | Margosatubig Regional Hospital | Dr. Jose Rizal Memorial Hospital | Ilocos Training and Regional Medical Center | Cagayan Valley Medical Center Technical Writers Racquel M. Barbecho Ephraema S. Gutierrez Consultants Ronald Armin F. Ocampo Arnel C. Nuñez Aileen A. Ricohermoso Angela C. Vargas Project Team Evangeline M. Macariola Leanne Kym Jane J. Lozañes Arianne P. Flores Adrian A. Ramirez Ritchell T. Furigay-Cunanan Philip Jourdan E. Olimpiada Mariel R. Mañibo Copyeditor Joanne Liezl Q. Nuque PREFACE Why install QMS in Government Hospitals? Health care service providers are expected to provide the highest quality health care to all its stakeholders. Quality health care corresponds to patient-focused care, which means: giving top priority to patient safety while addressing vulnerability; providing compassionate patient care; providing timely and effective treatment; complying with applicable treatment protocols; ensuring effective, efficient and secured patient and hospital/medical center records management; providing effective and readily accessible communication channels; and, ensuring reliable hospital/medical center support services. With these in mind, hospital/medical centers need an extremely low tolerance for poor quality services primarily because human lives are at stake. In the Philippines, health care is a top priority of the government in terms of funding support for hospital facilities and equipment, subsidized health care services, and other health care programs to ensure equitability and accessibility of the public, especially the underprivileged Filipinos, to needed health care services. With the adoption of the Universal Health Care Act, hospital/medical centers in the Philippines are mandated to provide integrated and comprehensive health care to all Filipinos by ensuring equitable access to quality and affordable health care goods and services as well as protection against financial risks. Government hospitals/medical centers, which include retained hospitals/medical centers of the Department of Health (DOH) and operated hospital/medical centers of local government units, e.g., district and city hospitals/medical centers, play major roles in the successful implementation of Universal Health Care in the country. The DOH-retained hospitals/medical centers deliver tertiary, rehabilitative, and specialized health care services while the LGU-operated hospitals/medical centers deliver primary, secondary, and long-term care. There are about 721 public hospitals/medical centers in the country, 70 of which are DOH-retained. As early as 2010, the DOH has mandated all its retained hospitals/medical centers to establish a quality management system (QMS) and obtain an ISO 9001 certification. These hospitals have proven that establishing ISO 9001 Quality Management System greatly benefited them in terms of: • • • • • • • increased compliance with local and international care standards, policies, and regulations; reduced medical procedure errors; clearly defined administrative procedures; improved attitude of medical personnel toward patients and their relatives; improved hospital/medical center facilities and environment; better and more secured records management; and, increased satisfaction of patients and their relatives. Purpose of this QMS Manual This QMS Manual is designed and developed for the purpose of interpreting the ISO 9001:2015 Standards in the context of government hospitals/medical centers (GHMC), which refers to all public hospitals/medical centers in the Philippines, i.e., DOH-retained, specialty hospitals/medical centers, and LGU-operated hospitals/medical centers. This shall serve as a reference document in establishing, documenting, implementing, and sustaining an ISO 9001:2015 QMS. How to use this QMS Manual This QMS manual is designed to provide generic and customizable content for easy and prompt adoption by GHMCs at all levels and sizes. Below are reminders and instructions in using this manual: A. The layout of the manual can easily be adopted by simply replicating the file. B. In customizing the header: GHMC Logo Name of GHMC Revision No. 0 Quality Management System Manual Effective Date DD/MM/YY Section 1. Introduction • • • • • Page No. 1 of 2 Place the approved logo of the GHMC in the “GHMC Logo” part and ensure consistency of the logo used in all sections of the QMS manual. Change “Name of GHMC” to the actual name of the hospital/medical center. The “Revision No.” refers to the number of times that the document is updated. “Effective Date” refers to the reckoning date of QMS implementation. The Manual is divided into several sections to make revisions easier. By doing so, revisions can be done in specific section/s only without revising the entire manual. This also means that each section starts with page 1 C. At the bottom part of the last page of each section, indicate the signatories. At a minimum, there should be “prepared by” and “approved by” signatories. (align second and succeeding lines with the first letter of the first line) Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC Usually, the QMS Leader prepares the QMS Manual. The QMS Leader is the designated member of management who oversees the establishment, implementation, and evaluation of QMS within the GHMC. The approving authority is the Chief of the GHMC. D. The contents of each section can be copied, taking note of the following customizations: • • • • • Change “Government Hospital/Medical Center” and “GHMC” into the name of the hospital/medical center or its acronym; Change Section 2 Hospital/Medical Center Profile; Change or remove practices, documents, records, controls and other content/s that are not applicable to the hospital/medical center; Change the names of offices, departments or units in blue italics font; and/or Remove other section/s or content/s that are not applicable to the hospital/medical center. E. Sample forms and templates as well as sample contents of documented information are provided in the body of each section or in annexes to aid in the preparation of the required documented information of the hospital/medical center. F. NOTES” contained in boxes may be found in the succeeding sections, which provide guidance or special instructions that may be considered in customizing this QMS Manual. Remember to delete or exclude these notes when copying the contents. A. Scope of the GHMC’s QMS The GHMC’s QMS covers the Provision of Patient Care Services. The scope covers the management, operations, and support processes of the GHMC as indicated in the Process Map. There is no ISO 9001:2015 requirement that is not applicable in the GHMC’s QMS. NOTE 3.1 GHMC may exclude ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.3 Design and Development with the justification that patient care services are based on local and international standards, thus there is no actual design and development activities in the course of the delivery of patient care services. However, some GHMC consider the development of clinical pathways, which are required by Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC) among government hospitals, as design and development activity, thus no exclusion. G. As the QMS Manual for the GHMC is being developed and customized, it would help the writers if a copy of the ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 9001:2015 Standards, including relevant reference documents, e.g., issuances from oversight agencies, internal policies/guidelines, standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, among others, are readily available as references. H. Upon the completion of the final draft of this QMS Manual, present and discuss the contents with the key officers and staff to gather additional inputs and suggestions, if any. Incorporate revisions, finalize, and seek approval of the relevant authorities within the GHMC. Overview of the Manual Selections Each section of the QMS Manual has its specific purpose. The Manual intends to ensure that the GHMC’s QMS is completely described for its intended users, which include the management and employees, the external auditors, and other relevant interested parties. Section 1.0 Introduction - This section provides the purpose and applicability of the QMS Manual. This also defines the controls needed to ensure appropriate identification and traceability of document; formatting and media; and, review and approval for suitability and adequacy. Section 2.0 GHMC Profile – This section is an overview of the GHMC to provide the users with the right perspective of its mandate, overarching goals and policies, and the organizational structure it operates on. It may also refer to the organizational context of the GHMC. However, if the GHMC already has an established and updated Operations Manual or other documents with similar purpose and contents, the GHMC may opt to delete this section and instead provide cross-reference/s when describing or presenting the profile of the GHMC. Section 3.0 Definition of Terms – This section defines the different terminologies, technical or common, that are used in the entire QMS Manual. This provides an assurance that terms are appropriately used and interpreted in the context of the GHMC. The definition of terms indicated in this section may be customized depending on how the GHMC defines them. Section 4.0 GHMC and Its Context – This section refers to the specific translation of the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 4.0 into the context of the GHMC. It intends to clearly describe how the GHMC identifies its internal and external issues as well as the needs and expectations of its relevant interested parties. It also includes the description of the scope of the GHMC’s QMS and presents the high-level process map that provides an illustration of the QMS processes and their interface to deliver expected outputs and desired outcomes of the GHMC. Non-applicable ISO 9001:2015 requirement/s and justification for its non-applicability is also defined in this section. Section 5.0 Leadership and Governance – This section translates the ISO 9001:2015 Clause 5 into the context of the GHMC. It describes how the GHMC Management demonstrates its commitment to the establishment, implementation, and sustainability of the QMS as well as the GHMC Quality Policy. Section 6.0 Management and System Planning – This section describes how the GHMC performs its planning based on the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 6.0. The planning activity includes: (a) identifying risks and opportunities from the identified internal, external, and customer-related issues; (b) planning to address the identified risks and opportunities; (c) implementing and evaluating the effectiveness of actions taken; (d) setting quality objectives and planning to achieve desired outputs and results, ad (e) planning of changes that could affect the QMS. Section 7.0 Management System Support - This section describes all the processes that provide support services for the provision of patient care services. Practices on how support services are provided effectively and efficiently to all individuals/units/offices of the GHMC are generally identified and described in this section. Section 8.0 Provision of Patient Care Services – This section gives an overview of the processes performed by the GHMC in the provision of patient care services. It is designed to include how the GHMC addresses the specific requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8. All the controls needed to effectively and efficiently perform the patient care processes are described in this section to serve as a guide to the users. Section 9.0 QMS Performance Evaluation – This section discusses the different evaluation mechanisms of the GHMC to ensure that process performance is properly checked and assessed at appropriate stages. It has considered the specific requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 9 to ensure that the required monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of processes are adopted and implemented by the GHMC. Section 10.0 Continual Improvement – This section describes the specific requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 10.0, which highlights the importance of continually improving and sustaining the QMS. This also defines the need to ensure that nonconformities are identified and corrective actions are taken to eliminate the causes of nonconformity and prevent its occurrence or recurrence within the GHMC. Section 1.0 - Introduction 01 Section 2.0 - GHMC Profile 02 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 - GHMC History Mandate Vision, Mission, and Core Values Organizational Structure Functional Description Section 3.0 - Terms and Definitions 08 Section 4.0 - GHMC and its Context 13 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 - Understanding the GHMC and its Context Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Relevant Interested Parties Scope of the GHMC’s QMS GHMC’s QMS and its Processes 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 - 17 Demonstration of Leadership and Governance Focus on Patients and Relevant Interested Parties Quality Policy Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities Section 6.0 - Management System Planning 20 6.1 - Addressing Risks and Opportunities 6.2 - Management System Objectives 6.3 - Planning of Changes Section 7.0 - Management System Support 26 7.1 - Management System Resources 7.2 - Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources 7.3 - Management of Organizational Knowledge Section 8.0 - Provision of Patient Care Services 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 - Operational Planning and Control Requirements for Products and Services Design and Development of Clinical Pathways Control of External Processes, Products, and Services Patient Care Services and Treatments 35 TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 5.0 - Leadership and Governance Section 9.0 - QMS Performance Evaluation 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 - 46 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation Stakeholders’ Feedback Management Internal Quality Audit Management Review Section 10.0 - Continual Improvement 51 10.1 - Improvement of the GHMC 10.2 - Corrective Action Annexes 53 A. List of Needs and Expectations of Relevant Interested Parties B. Risk and Opportunity Register C. Corrective Action Request Form TABLE OF CONTENTS Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 1. Introduction Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 1 The Quality Management System (QMS) Manual of the Government Hospital/Medical Center (GHMC) documents the structure and design of the GHMC’s QMS, the interconnectedness of the processes that constitute the QMS, and the operational arrangements, which support the quality assurance activities and hospital/medical center standards. Thus, it defines the critical elements of the key processes of the GHMC’s QMS with reference to relevant policy issuances and provides a holistic and integrative view of the GHMC’s QMS. This QMS Manual, which also articulates the GHMC’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement, is intended to be used by all the offices, departments, or units of the GHMC. It defines and clarifies policies, systems, and procedures adopted to implement and continually improve the GHMC’s QMS. Likewise, it serves as a reference and a guide for GHMC personnel in decisions and actions related to: (a) the performance of their day-to-day tasks; (b) ensure awareness and consistency in the implementation of processes as well as conformance to planned arrangements; (c) compliance with legal requirements; and (d) providing relevant stakeholder requirements. This QMS Manual is a controlled documented information. Thus, its review, revision, and re-issuance are subject to existing policies and procedures. Revision and re-issuance are reflected when there are changes in the QMS such as change in management and/or organizational structure, operational process/es improvements, shifts in strategic direction, among others. Controlled copies of this QMS Manual are issued to authorized copyholders identified by the Records Office/Unit for safekeeping and prompt updating of necessary revisions. NOTE 1.1 The GHMC may indicate the sites or offices covered by its QMS to define the scope and applicability of the policies and guidelines set forth. Additional information such as the management’s reason for establishing the QMS and the expected outcomes of the established QMS may also be added here. NOTE 1.2 The GHMC may refer to any document (e.g., policy issuance, memorandum, procedure, etc.) that defines the specific controls for this Manual to ensure proper identification, traceability, relevance, suitability, and adequacy. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 1 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 6 2.1 GHMC HISTORY NOTE 2.1 A brief background or history of the GHMC may be included in the QMS Manual to establish the context of the GHMC. It will help the users learn more about the historical milestones and how the GHMC came to be, where, and what it is now. 2.2 MANDATE NOTE 2.2 The GHMC’s mandate will help set the tone of its QMS. It will ensure that the scope of the QMS is within the mandate of the GHMC. Moreover, the main reason for the GHMC’s existence, i.e., providing quality health care to all should be emphasized in the QMS scope statement. 2.3 VISION, MISSION AND CORE VALUES NOTE 2.3 The statements of the GHMC’s vision and mission may also be part of the QMS Manual to ensure the users’ awareness of the long term goals of the organization. This is also indicated as part of the QMS Manual to ensure the alignment of the QMS policies and objectives to these long term goals. The core values, on the other hand, enables the users to better imbibe the values upheld by the organization in their day-to-day tasks. 2.4 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE NOTE 2.4 The organizational structure of the GHMC shows how roles, responsibilities, and authorities in the GHMC are defined, as part of the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 Clause 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities. Moreover, the documented information on organizational structure serves as a supporting document to define the scope of the QMS because it shows the different offices/ units that are covered in the GHMC’s QMS. The organizational structure should show the offices, departments, or units of the GHMC, and NOT the names and pictures of the offices and staff. This will avoid unnecessary revisions when there are changes in the assignments of personnel. Moreover, office/department/unit functions remain the same even after the changes in personnel assignments are implemented. 2 Emergency Roomand Non-Surgical • Emergecny Service Complex • Internal Medicine • Neurology • Payward • Pediatrics Surgical: • Anesthesia • Obstetrics-Gynecology • Ophthalmology • Operating Room Complex • Orthopedics • Surgery • Urology Health Programs: • TB Dots • Smoking Cessation • Non-Communicable Disease • Immunication Program • Pre-Natal and Family Planning • Violence and Injury Prevention Clinical Areas: • Emergency Room • Out-Patient Department • Operating Room • Delivery Room • Ward • Intensive Care Unit • Central Supply Room Nursing Division Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Patient Support Services • Admitting and Information Unit • Medical Records • Nutrition and Dietetics • Pharmacy • Medical Social Service Unit • Patient Assistance and Complaints Desk (PACD) Financial Management: • Accounting Unit • Budget Unnit • Billing and Claims Unit • Cash Management Unit General Services • Engineering Unit • Linen and Laundry Unit • Housekeeping Unit • Security Unit Internal Administrative Management: • Human Resource Management Unit • Procurement Unit • Property and Supply Management • Central Information Management Unit Hospital Operations & Patient Support GHMC Logo Out-Patient and Ancillary: • Pathology and Laboratories • Radiology • Radiotheraphy • Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Medical Division Office of the GHMC Chief Name of GHMC Revision No. Page No. 0 Effective Date 2 of 6 Sample Organizational Structure 3 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 6 2.5 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION NOTE 2.5 A complete list of the functional description of the offices, departments, and units listed in the organizational structure should be enumerated in this QMS Manual. It will be a good reference for the users to know the responsibilities of offices, departments, or units with respect to the processes covered by the QMS. Should the GHMC have no clear description of duties and responsibilities, this will be a good opportunity to discuss and clarify the roles of each office, department, or unit. Sample of Functional Description of a GHMC CHIEF OF GHMC The chief of hospital/medical center assumes the overall management and administration of the hospital/medical center, including the formulation of policies, programs, strategies, and plans to achieve the desired results of the Quality Management System. The chief shall oversee the day-today activities of the hospital/medical center. MEDICAL SERVICE DIVISION It is the responsibility of the Medical Service Division to: deliver quality out-patient and in-patient care; ensure the continuing medical education and training for the medical and paramedical personnel; and, assist the Chief of Hospital/medical center in the formulation and implementation of policies and programs. Departments under Medical Division include Internal Medicine, Pediatrics, OB-Gyne, Surgery, Orthopedics, Anesthesia, Ancillary, among others. NURSING SERVICE DIVISION The Nursing Service Division provides full support in the provision of patient care services. Responsibilities include: recording of medical history and symptoms; collaboration with medical team to plan for patient care; advocacy for health and well-being of the patient; monitoring of patient health and recording signs; administration of medications and treatments; handling and operation of medical equipment; monitoring of implementation of diagnostic tests; and, educating patients about management of illnesses. 4 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 6 Units under Nursing Service Division include Emergency Room, Out-Patient Department, Operating Room, Delivery Room, Ward (Service) and Central Supply Room. The major health programs of the Nursing Service include the: Tuberculosis Directly Observed Treatment (TBDOTS); Smoking Cessation Program; program for non-communicable diseases, which include advocacies on healthy lifestyle, immunization program, pre-natal and family planning programs, and, violence and injury prevention program. HOSPITAL OPER ATIONS AND PATIENT SUPPORT SERVICES (HOPSS) DIVISION The HOPSS Division directs and manages the activities and functions of units under its supervision and implements policies and guidelines for the delivery of effective and efficient support services. Units under the HOPPS are Internal Administrative Management, Financial Management, General Services and Patient Support Services. Human Resource Management Unit – This unit develops and administers comprehensive the Human Resource Management Plan, which includes recruitment, selection, promotion, separation, welfare and benefits, training, and other personnel actions and transactions. Procurement Unit - This unit develops and administers a comprehensive plan of systematic management of procurement and acquisition of supplies and materials, health care equipment, vehicles, services, infrastructures, work and other required logistics for the effective and efficient delivery of quality service. Property and Supply Management Unit – This unit receives, stores, issues, and conducts an inventory of supplies, materials and equipment, and disposes of unserviceable/condemned hospital/medical center properties. Central Information Management Unit – This unit develops and administers a comprehensive plan of systematic management of data and research for the improvement of acquisition, utilization of finances, assets, and development of human resources, operating systems and procedures. Accounting Unit - This unit directs and coordinates the systematic recording of all financial transactions, preparation of financial statements and relevant reports, and maintenance and safekeeping of books of accounts. Budget Unit – This unit directs and coordinates with the persons concerned in the consolidation and preparation of the budget proposal, work and financial/operational plans, including its implementation and monitoring. 5 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 6 Billing and Claims Unit - This unit implements proper charging system, by recording all hospital/ medical center procedures, services, medical supplies, drugs and medicines incurred by patients regardless of patients’ classification, including claims, fees and use of facilities and other nonpatient services. Cash Management Unit - This unit directs, controls, and ensures the proper disbursement and collection transactions of the hospital/medical center. Engineering Unit – This unit prepares and implements comprehensive preventive/corrective/ rehabilitative maintenance program of biomedical, electronic and communication equipment, electrical, mechanical, structural, civil works, physical plant, motor vehicles, and other health care equipment/devices. Linen and Laundry Unit – This unit provides laundry services, and ensures an adequate supply of clean linens for patients and other hospital/medical center units. Housekeeping Unit – This unit provides and maintains clean, safe, and sanitary facilities and environment for hospital/medical center personnel, patients, and clients. Admitting and Information Unit – This unit directs and controls the centralized registration and documentation of admission and discharge of patients, including providing information. Medical Records Unit – This unit directs and ensures an organized system of processing, analyzing, maintaining and safekeeping of all patients’ records, measuring the quality of patient care through the written data in the sequence of events covering the diagnosis, treatment, and discharge of patients. Nutrition and Dietetics – This unit directs, maintains, and ensures the provision of safe, high quality, and nutritious food to patients and personnel. Pharmacy – This unit directs and implements programs, projects, and activities for the provision of safe, affordable, and efficacious drugs and medicines consistent with the Generics Act of 1988, Philippine National Drug Formulary, and DOH policies, rules and regulations. Medical Social Service Unit – This unit directs and implements the programs, projects, and activities on social services which include social casework, multi-sectoral networking and linkages in understanding the socio-behavioral and economic plight of patients and their families for the holistic approach in their management and treatment. 6 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 2. GHMC Profile Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 6 of 6 Patient Assistance and Complaint Desk (PACD) –This unit assists patients with their complaints, evaluates their concerns, and facilitates immediate action for their needs. A PACD Officer on duty helps clients when filling-out a complaint form and forwards it to the department and/or unit concerned. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 7 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 3. Definition of Terms Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 5 The GHMC adopts the following terms and definitions within its QMS Manual. Where no definition is provided, the GHMC adopts the definitions provided in ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management SystemFundamentals and Vocabulary. Annual Procurement Plan (APP)– a requisite document that the hospital must prepare to reflect the necessary information on the procurement of goods, services, and infrastructure within the calendar year. Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) – designated organic office within the hospital/medical center to monitor procurement activities and discharge functions mandated through the Republic Act No. 9184. Calibration – an activity conducted to verify or control quality through comparison of measurement values delivered by a device/equipment/tool/test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy measuring equipment or in the case of other resources/tool, applicable standards or acceptable methodology. Civil Service Commission (CSC) – an oversight agency that administers and enforces rules and regulations for the hiring, promotion, and other related matters relating to government employees. Clinical Pathways – standardized, evidence-based, multidisciplinary management plans, that identify appropriate sequence of clinical interventions, timeframes, milestones, and expected outcomes for a homogenous patient group. Commission on Audit (COA) – an oversight agency that has the power, authority, and duty to examine, audit, and settle all accounts pertaining to the revenue and receipts of expenditures or uses of funds and properties of government offices. Consequence (as risk and opportunity criterion) – degree of impact of the risk or opportunity identified to the attainment of the hospital’s objectives and enhancement of patient satisfaction, if not treated Continual Improvement – a recurring activity or effort to improve products, services, and processes to help increase the organization’s ability to fulfill requirements and enhance the satisfaction of relevant interested parties. Control – any measure or action that directs or influences the process toward effectiveness and efficiency; includes any policy, procedure, practice, process, technology, device or method that modifies or manages processes. Controlled documents – documents that are official and updated, the distribution and maintenance of such are managed by the responsible unit for safekeeping and promptly updating necessary revisions. Corrective Action – an action taken to a nonconformity detected to address the system failures and prevent its recurrence; usually recorded in a Request for Action form. 8 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 3. Definition of Terms Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 5 Data Privacy Act or DPA/Republic Act No. 10173 – an act protecting individual personal information in ICT (information and communication technology) systems in the government and the private sector. Department of Budget and Management (DBM) – the oversight agency that monitors the sound, efficient, and effective management and utilization of government resources. Department of Health (DOH) – the principal health agency that holds the overall technical authority on health as it is both a national health policy-maker and regulatory institution. Document – documented information maintained by the hospital; contains policies, procedures, instructions, and reference information. Document Custodian – designated personnel or unit of the hospital tasked to manage the generated documents and records. Documented information – information required to be controlled and maintained or retained by the hospital and the medium on which it is contained, e.g., manuals, procedures, hospital policies. Executive Order No. 02 s.2016 Freedom of Information Bill – requires all executive departments, agencies, bureaus, and offices to disclose public records, contracts, transactions, and any information requested by a member of the public, except for matters affecting national security and other information that falls under the inventory of exceptions. External documents – issuances, specifications, requirements and other documented information from other government agencies, suppliers and system standards; documented information that are NOT created within the hospital. Hospital – a place devoted to the timely maintenance and operation of facilities for the diagnosis, treatment, and care of individuals suffering from illness or deformity or in need of other medical or nursing care (Republic Act No. 4226). Infection control - discipline concerned with preventing nosocomial or hospital care-associated infection; a practical (rather than academic) sub-discipline of epidemiology. Internal documents – policies, guidelines, memo, and other documented information internally generated/originated within the hospital. Internal Quality Audit (IQA) – systematic, independent, and documented process for obtaining audit evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled. IQA Team – a mobilized team within the hospital responsible for conducting the audit or performing the audit program. 9 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 3. Definition of Terms Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 5 Likelihood (as risk and opportunity criterion) – the probability of occurrence of the risk or opportunity, when not addressed. Management Review – An evaluation of QMS performance by the GHMC’s Chief/Head and its Management that includes formal meeting/s, review, and status reporting of required agenda for the purpose of gathering information as inputs to decision-making toward continual improvement. Masterlist of Documents – register of internal and external documents maintained by the Document Custodian; contains information like title, document code, effective date, and the like. Monitoring and measuring resources – devices/equipment/tools/tests needed by the hospital to provide evidence of conformity of product or services to determined requirements, e.g., cardiac monitor, blood pressure apparatus, psychiatric tests, among others. National Archives of the Philippines (NAP) – a government agency that guarantees the preservation and accessibility of public documents and records through its formulation and implementation of a records management and archival administration program for the efficient creation, utilization, maintenance, retention, preservation, conservation, and disposal of public records including the adoption of security measures and vital records protection program for the government. Needs and expectations – feelings, needs, and ideas that patients and other relevant interested parties, either explicitly or implicitly stated, have toward certain products or services provided by the hospital. Nonconformity (NC) – non-fulfillment of a requirement, i.e., hospital policy, documented procedure, statutory and regulatory requirements as well as client requirements. Obsolete copy –outdated documented information for archiving. Office Performance Commitment Review (OPCR) – a performance evaluation tool that all heads of offices accomplish; must officially identify and declare the targets for the rating period and be in accordance with the overall strategy map and commitments of the GHMC. Opportunities – set of circumstances that can lead to the adoption of new practices, launching of new products and services, addressing new clients and other desirable and viable possibilities to address the GHMC’s needs. Organizational knowledge – specific knowledge to the organization, generally gained by experience, which is used and shared to achieve the objectives of the hospital; can come internally, such as intellectual property, lessons learned from failure and successes, or the results of improvements; or it can come externally from conferences, customer knowledge, or supplier knowledge. Patient – the main client of the hospital who receives medical care and attention. 10 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 3. Definition of Terms Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 5 Stakeholders’ satisfaction survey – a methodology to measure how patients and their significant others feel about the hospital or their experience with the hospital. Performance targets – the desired level of performance as measured by indicators that represent success at achieving hospital outcomes. Personal protective equipment (PPE) – garments worn to minimize exposure to hazards that cause serious workplace injuries and infection, which may include safety glasses, shoes, masks, respirators, coveralls, vests, and full body suits . Philippine National Drug Formulary – an integral component of the Philippine Medicines Policy, which contains essential medicines list and ensures rational prescribing, dispensing, and administration of medicines. Process – set of interrelated or interacting activities that use inputs to deliver an intended result, e.g., provision of patient care services is a process with a set of interacting activities performed by authorized offices, departments or units, and personnel to ensure patient safety and treatment. Process Map – planning and management tool that visually describes the interaction of interdependent processes. Quality Management System (QMS) – management system to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. Quality Objectives – result to be achieved by the hospital; can be strategic, tactical or operational. Quality Policy – intentions and direction of the hospital as regard to the quality of its management system. Records – documented information retained by the hospital; provides evidence of implementation of the QMS. Records Disposition Schedule (RDS) - documents the major records (including electronic records) related to the activities of each office; identifies temporary and permanent records; provides mandatory instructions for the retention and disposition (retirement or destruction) of each record based on their temporary or permanent status. Relevant Interested Parties – persons or organizations that can affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by the hospital decision or activity; also refer to stakeholders in this Manual. Republic Act No. 9184 Government Procurement Reform Act – prescribes the necessary rules and regulations for the modernization, standardization, and regulation of the procurement activities of government offices. 11 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 3. Definition of Terms Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 5 Request for Action (RFA) form – the tool used to document the nonconformities, including those from audit findings, and the corresponding root causes, corrective action plans and results of the implementation of the corrective action plan. Risk – effect of uncertainty on objectives; often described by an event, a change in circumstance or a consequence; characterized and measured in terms of its consequence and likelihood. Risk analysis - a process that is used to understand the nature, sources, and causes of the risks identified, to estimate the level of risk; used to study consequences and likelihood, and to examine the controls that currently exist. Risk and opportunity register – the documented information used to review and monitor the context of the hospital and its corresponding risks, opportunities and treatment or action plan. Significant others – the family, companion or guardian of the patient during the time of care and treatment by the hospital. SWOT analysis - (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis) a framework for identifying and analyzing the internal and external factors that can have an impact on the viability of a hospital’s performance and stakeholders’ satisfaction. Statutory and regulatory requirements – obligatory requirements specified by the country’s authorities and mandated by legislative bodies. Top management – person or group of people who direct and control the hospital; usually refers to the Executive Committee or Management Committee. Treatment plan – the plan of action to mitigate risks and take advantage of opportunities. Validation of processes – collection and evaluation of data prior to delivery of products and services to establish evidence that the process as well as the product or service is capable of delivering its intended results. World Health Organization (WHO) – a specialized agency of the United Nations that is concerned with international public health; with a function of proposing conventions, agreements and regulations, and making recommendations with respect to international health matters. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 12 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 4. GHMC and its Context Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 4 4.1 UNDERSTANDING THE GHMC AND ITS CONTEXT During the strategic planning and target setting of the GHMC, the management identifies internal and external issues through SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis. The GHMC determines internal issues (i.e., values, culture, and knowledge) and external issues (i.e., legal, market, cultural, technological, social, economic, international, national, regional and local) that are relevant to its purpose and strategic direction; and, that can affect its ability to achieve holistic, safe, responsive, complete, and compassionate patient care services. 4.2 UNDERSTANDING THE NEEDS AND EXPECTATIONS OF RELEVANT INTERESTED PARTIES The GHMC clearly understands its relevant interested parties, which include patients, patients’ significant others, hospital management and staff, suppliers, and other key external stakeholders. Through analysis, the needs and expectations of these relevant interested parties, which are listed in Annex A, are identified and considered during plannig activities. 4.3 SCOPE OF THE GHMC’S QMS The GHMC’s QMS covers the Provision of Patient Care Services. The scope covers the management, operations, and support processes of the GHMC, as indicated in the process map below. NOTE 4.1 GHMC may exclude ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.3 Design and Development with the justification that patient care services are based on local and international standards. Thus, there is no actual design and development activitites in the course of the delivery of patient care services. However, some GHMC consider the development of clinical pathways, which are required by the Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (Philhealth) among government hospitals, as design and development activity; thus, Clause 8.3 is not an exclusion. NOTE 4.2 Medical Centers have Research and Training as one of its core functions, other than the provision of patient care services. This Manual does not cover this function. However, should the GHMC decide to include Research and Training in the QMS Scope, it has to be integrated into the process map with specific details added as a separate section after Section 8.0. 13 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 4. GHMC and its Context Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 4 4.4 GHMC’S QMS AND ITS PROCESSES The GHMC’s high-level process map, Figure 1, illustrates that processes of the GHMC’s QMS and their interaction in providing patient care services. The process map is divided into three groups of processes, namely: • • • Management Processes - processes needed for oversight and governance of GHMC’s quality management system; Opetations Processes - processes needed to realize the planned activities in performing processes and allow GHMC to deliver the intent of the output of the operations, i.e., provision of patient care management services, that define the core of GHMC’s service; and, Support Processes - processes needed to manage the resources necessary to ensure the satisfactory performance of the provision of patient care management services. These three groups of processes (with appropriate controls over the external providers of products, services, and processes) are working together to provide an integrated and comprehensive health care as the end goal of the GHMC’s QMS. A. Management Process The GHMC, through its planning activities, sets directions, policies, and work and financial plans for the operations to perfrom and deliver the desired outputs and organizational outcomes. it also implements regular monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of the GHMC’s QMS through accomplishment reporting, exercutive committee meetings, management reviews, internal audit, and analysis of stakeholders’ feedback, among others. B. Operational Processes The GHMC’s operational processes refer to the provision of patient care services that include, but not limited to, the following: (a) receiving and registration of patients; (b) initial assessment and treatment in the out-patient department and emergency room; (c) laboratory diagnostics; (d) inpatient care and treatment; (e) disposition and discharge of patients; and, (f) care for discharged patients. Controls for the patient and relevant interested parties’ requirements and operational inputs, GHMC processes, and patient care services and products are applied by the concerned units or departments to ensure an integrated and comprehensive health care. C. Hospital/Medical Center Support Processes The hospital/medical center’s support processes provide the necessary administrative and logical support to the operations for the effective delivery of patient care services. Support processes include the administrative services, ancillary services, financial management, and hospital/medical center information management. 14 Patient & Relevant Interested Parties Performance Evaluation Diagnostics • Laboratory Exams • Diagnostic Imaging • Other Diagnostic Services In-Patient Care & Treatment • Admission • Medical Treatment • Nursing Care • Dietary Services • Pharmacy • Medical Social Service Financial Management Procurement of Goods and Services Ancillary Services Revision No. Quality Management System Manual Section 4. GHMC and its Context Page No. Patient & Relevant Interested Parties’ Satisfaction Performance Targets Externally-Provided Products, Services, and Processes Management of Hospital/ Medical Center Information Hospital/ Medical Center Infrastructure Disposition & Discharge of Patients • Discharged • Referral • Expired Continual Improvement Hospital/Medical Center Operations and Patient Initial Assessment & Treatment • Consultation • Out-Patient • Care and Treatment Core Processes Provision of Patient Care Services Management System Planning Human Recource Management Receiving & Registration of Patients: • Issuance/ Retrieval of Patient Record • Triaging Leadership & Governance Management Processes GHMC Logo Needs and Expectations Internal and External Issues Name of GHMC 0 Effective Date 3 of 4 Figure 1. Sample GHMC Process Map Patient Care Services 15 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 4. GHMC and its Context Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 4 NOTE 4.3 The process map may be changed based on how the GHMC prefers to illustrate the interaction of processes covered in the QMS. Use the terms more commonly and appropriately used in the GHMC. Ensure that all key processes performed by all offices, departments, and units are included in the process map. Key processes refer to the major processes. There is no need to include sub-processes. Instead, sub-processes may be defined in the respective sections of this QMS Manual and/ or in the Procedures Manuals and other documented procedures. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 16 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 5. Leadership and Governance Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 3 5.1 DEMONSTR ATION OF LEADERSHIP AND GOVERNANCE The GHMC Executive Committee (ExeCom) includes the chief of hopsital/medical center, the departments/ section Heads, and the service/division Heads. The management views its QMS as a strategic asset that will help in achieveing their organizational goals and in the continual improvement of GHMC as an organization. It provides evidence of leadership and commitment through the following: • • • • • • • Active involvement in the establishment, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of the QMS; Establishment of the quality policy and quality objectives, i.e., Office Performance Commitment Review (OPCR), Division Performance Commitment Review (DPCR), and Balanced Scorecard; Integration of the GHMC’s QMS with its operations, promotion of the process approach and risk-based thinking; Provision of appropriate and adequare resources, dissemination of the importance of conformance to requirements; Ensuring achievement of the intended results of its QMS; Creating a work environment that encourages the GHMC’s management and staff to contribute to the effectiveness of QMS; and Encouraging continual improvement and providing support to all the management and staff of the GHMC. NOTE 5.1 The top management may be referred as Execom or Mancom. This may be customized based on the applicable terminology. NOTE 5.2 The quality objectives of the hospital/medical center may also refer to a balanced scorecard, or other planning, documents specifying the performance targets for a year. 5.2 FOCUS ON PATIENTS AND RELEVANT INTERESTED PARTIES The GHMC management ensures that the needs and expectations of the patients and other relevant interested parties as well as the statutory, regulatory, and other relevant requirements are determined to ensure the delivery of integrated and comprehensive health care services towards stakeholders’ satisfaction. This is accomplished through the conduct of regular and effective communication with the patients and other relevnt interested parties through various feedback management mechanisms, such as the conduct of Stakeholders’ Satisfaction Survey to gather relevant feedback on the delivery of the GHMC’s services, and the presence of a Patient Assistance and Complaint Desk (PACD) to ensure that complaints and issues of relevant interested parties are addressed in a timely manner. 17 Revision No. Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 5. Leadership and Governance 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 3 5.3 QUALITY POLICY The GHMC maintains its Quality Policy, which is documented in Figure 2 of this QMS Manual. The Quality Policy specifies the GHMC’s commitment to deliver the highest standard of quality health care services that is compliant with statutory, regulatory, and other relevant requirements to ensure an integrated and comprehensive health care and attain stakeholders’ satisfaction. This policy is communicated to ensure that it is understood at all levels of the hospital/medical center. Employees’ comprehension and understanding of the quality policy may be verified through, but not limited to, QMS audits, management reviews, and staff meetings. The GHMC management is responsible for ensuring that the quality policy is appropriate to the hospital/ medical center’s mandata and provides a framework for establishing and reviewing quality objectives and goals. This is reviewed at least once a year to ensure continuing improvement and suitability to the GHMC’s mandate and thrusts, including the relevant stakeholders’ requirements. Figure 2. Sample Quality Policy The GHMC Quality Policy We, the GHMC management and employees, are dedicated to fulfilling the highest quality patient care services to delivery an integrated and comprehensive health care to the Filipinos. We shall provide quality, compassionate, effective, efficient, equitable, and holistic health care services; comply with all pertinent laws, locl, and international health care standards; and continually enhance our skills, upgrade hospital/medical center facilities and equipment, sustain the availability of safe and quality medical supplies. NAME Hospital/Medical Center Chief NOTE 5.3 The Quality Policy in this QMS Manual may be signed by the hospital/medical center chief. It should be issued as an approved documented information using the GHMC’s existing system for internal issuances, e.g., memo. It may be approved and issued earlier than the approcal and issuance of this QMS Manual, for early dissemination and implementation. Some best practices to ensure awareness of employees of the Quality Policy include recitation during flag ceremonies and posting of Quality Policy on strategic places (e.g., desktop/laptop wallpapers, hallways, among others). 18 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 5. Leadership and Governance Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 3 5.4 ORGANIZATIONAL ROLES, RESPONSIBILITIES, AND AUTHORITIES The responsibilities and authorities of all personnel and functions within the GHMC are defined in the approved organizational structure, issued special orders/personnel orders, functional/organizational charts, job/position descriptions, and manuals or work procedures. Although some authority may be delegated, the overall responsibility and accountability of the GHMC’s QMS, including the management of changes, as may be needed, remains with the GHMC’s top management. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 19 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 6. Management Systems Planning Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 6 6.1 ADDRESSING RISKS AND OPPORTUNITIES During the strategic planning of the GHMC, an analysis of the needs and expectations of the relevant interested parties and the internal and external issues is done. Through this, the GHMC identifies risks that it needs to address to prevent negative effects on its performance as well as the opportuniteis that it wants to pursue to improve its performance. The organizational level issues are identified through the SWOT analysis, where strategies are determined and planned to ensure that the internal strengths are utilized to address weaknesses, minimize threats, and take advantage of opportunities. These are usually documented in the GHMC Strategic Plan. Each office, department or unit also identifies process-related risks and opportunities with corresponding treatment/action plans. These risks and opportunities are registered in Annex B, where risk and opportunity level is analyzed through the impact of consequence and the likelihood to happen, and treatment plans are identified, implemented, monitored, and evaluated regularly. The results of the evaluation of the effectiveness of the actions taken to address risks and opportunities are discussed during management review. Below are the instructions in filling out the Risk and Opportunity Registers: • • • • • • • • Risk/Opportunity Description - Define risk/opportunity area, short description of risk/ opportunity event, and its consequences. What can go wrong (risk) or what can happen (opportunity)? What are the impacts/consequences if it foes go wrong (risk) or it actually happens (opportunity)? Risk/Opportunity Causes - Describe the risk/opportunity event cause/s. What would cause it to go wrong? Or for it to happen? Current Controls/Situation - Describe any existing policy, procedure, practice or mechanism that acts to minimize the risk or maximize the oppotunity. What is in place now that reduces the likelihood of this risk occuring or its impact if it does occur? What is being done to maximize the benefits of the opportunity if it does occur? Likelihood - Rate the level of the likelihood of occurence of the current risk/opportunity from 1 to 5 based on the appropriate criteria below. How likely is this risk/opportunity to occur? Severity - Rate the level of impact from 1 to 5 based on the appropriate cirteria below. To what extent would the impact/consequence of this risk/opportunity be if it occurs? Risk/Opportunity Magnitude - Multiply the rating for Likelihood and Consequence. The product, based on the criteria below, is used to determine whether the risk or opportunity level is high, medium or low, and the corresponding level of action that needs to be taken. Treatment Plan - Describe the actions to be undertaken for the risks/opportunities requiring further treatment, as indicated in the criteria set forth. Responsible - Identify the office, department, or unit responsible ot implement the treatment plan. 20 Name of GHMC Quality Management System Manual GHMC Logo Section 6. Management Systems Planning • • Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 6 Target Date - Define the target date of implementation of the treatment plan. Risk/Opportunity Rating After Treatment - Evaluate the risk/opportunity after completion of the treatment plan by reassessing using the criteria for likelihood of occurrence and consequence. The GHMC uses the following criteria as reference in analyzing the likelihood of risks and opportunities: Rate Risk/Opportunity Likelihood Rare 1 Not known to happen Low 2 Low occurrence of one (1) in a year Medium 3 Known to happen, occurrence of one (1) in a quarter High 4 Very likely to happen, occurrence of more than one (1) in a quarter Very High 5 Highly likely to happen, occurrence of one (1) in a month In analyzing the severity of risks, the following rating scale is used: Rate Risk Severity Insignificant 1 Not known to happen Minor 2 Low occurrence of one (1) in a year Significant 3 Known to happen, occurrence of one (1) in a quarter Major 4 Very likely to happen, occurrence of more than one (1) in a quarter Catastrophic 5 Highly likely to happen, occurrence of one (1) in a month 21 Revision No. Name of GHMC Quality Management System Manual GHMC Logo 0 Effective Date Section 6. Management Systems Planning Page No. 3 of 6 LIKELIHOOD The following table shows the risk ratings where the likelihood and severity criteria are mapped out. The higher the number means the higher the prioritization/degree of treatment plan to be done in order to minimize the negative consequences of risks: Rare 1 2 3 4 5 Low 2 4 6 8 10 Medium 3 6 9 12 15 High 4 8 12 16 20 Very High 5 10 15 20 25 Insignificant Minor Significant Major Catastrophic SEVERITY In analyzing the benefits of opportunities: Rate Opportunity Consequence Not Very Beneficial 1 No perceived calue for improvement and sustainability Not Beneficial 2 Pursuing the opportunity will slightly improve QMS and its sustanability Moderately Beneficial 3 Pursuing the opportunity will considerately improve QMS and its sustainability Beneficial 4 Pursuing the opportunity will highly improve QMS and its sustainability Very Beneficial 5 Pursuing the opportunity will greatly improve QMS and its sustainability 22 Revision No. Name of GHMC Quality Management System Manual GHMC Logo Section 6. Management Systems Planning 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 6 LIKELIHOOD Meanwhile, the following table is used for the identification of the opportunity ratings, in which the higher the value, the better is the effect to the QMS: Rare 1 2 3 4 5 Low 2 4 6 8 10 Medium 3 6 9 12 15 High 4 8 12 16 20 Very High 5 10 15 20 25 Not Very Beneficial Not Beneficial Moderately Beneficial Beneficial Very Beneficial SEVERITY The following table shows the criteria in addressing risks and opportunities ratings, individually. It has three (3) levels of priority, which serves as a guide for management’s treatment plan on risks and opportunities: Risk/ Opportunity Rating Opportunity 10 - 25 Treatment Plan Risk Opportunity High Take immediate appropriate action to eliminate the risk Pursue the opportunity 5-9 Medium More frequent monitoring of performance/complaints May consider pursuing the opportunity 1-4 Low No action required No action required Moreover, the following table shows a matrix used as basis whenever specific programs, activities, and projects are proposed toward the improvement of the QMS such as the proposal of new policies, procedures, reorganization, opening of new programs etc. Risk High HR/HO HR/MO HR-LO Medium MR/HO MR/MO MR-LO Low LR/HO LR/MO LR-LO High Medium Low Opportunity 23 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 6. Management Systems Planning Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 6 The GHMC updates the Risk and Opportunity Register where the last column indicates the reassessment of the risk and opportunity after completing the implementation of the treatment plan. If the risk rating lowers and the opportunity rating remains high or even gets higher, it means that the treatment plan is effective, otherwise, the GHMC Chief reviews the Registers to evaluate the effectiveness of actions taken, and take subsequent action thereafter. NOTE 6.1 The GHMC may have other risk assessment guidelines being used. This is also acceptable and may be used provided that the minimum requirements of the ISO 9001:2015 standard Clause 6.1, Actions to Address Risks and Opportunities, are fully met. NOTE 6.2 For further reference on the Risk Management System, please refer to ISO 31000:2018 Risk Management Guidelines. 6.2 MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES The GHMC management ensures that quality objectives, including those needed to meet the requirements for the delivery of patient care services, are established at relevant functions and levels within the organization through the Office Performance Commitment Review (OPCR) documents. Each office, department, or unit also prepares operational plans, work and financial plans, annual procurement plans, documented procedures, among others, to define clearly the activities to be performed, responsibilities of offices and individuals, and the resources needed generally to attain the set quality objectives. The GHMC management ensures that the planning for the QMS is carried out in order to meet the general requirements of QMS as well as the GHMC’s quality objectives by preparing and continually reviewing and measuring patient care processes and services, organizational structures and operations plans, and documenting management and work processes. These processes of monitoring, documenting, reviewing, and measuring ensure that the integrity of the QMS is maintained when changes to the QMS are planned and implemented. 24 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 6. Management Systems Planning NOTE 6.3 Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 6 of 6 The GHMC may also use any other form of document, e.g., balanced scorecard, to document the quality objectives. The quality objectives should be: • specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound; • established at all levels, functions, and processes within the GHMC, which means that all offices/units and processes have quality objectives and these are aligned with the overall objectives of the GHMC; • consistent with the overall direction and commitments of the GHMC established in the Quality Policy; • supported by the necessary resource in order to achieve them; • monitored, reviewed, and evaluated regularly; and, • communicated and cascaded to all employees. 6.3 PLANNING OF CHANGES The GHMC prepares transition plans, project work plans, and other similar documented information whenever needed to ensure that operations of the hospital/medical center are not affected in times of management and operational changes. NOTE 6.4 If the GHMC has existing guidelines on managing changes in the organization, e.g., Change Management Plan or Change Management Procedure, this should be mentioned in this section. Ensure that existing practices to manage organizational changes are also mentioned here. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 25 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 9 7.1 MANAGEMENT SYSTEM RESOURCES The GHMC determines and provides the necessary resources to ensure that the QMS is maintained, sustained, and continually improved. These resources include human resource, infrastructure and work environment, budget and finance, procured goods and outsourced services, and documented information. NOTE 7.1 Note that additional support services may be provided, as appropriate to the GHMC. The titles of each sub-section should reflect the actual name of the process/es used by the GHMC NOTE 7.2 In some GHMC, the unit in-charge of support processes may not be responsible for the GHMC infrastructure management and financial management. The GHMC may revise and customize this section as applicable. A. Human Resource Management GHMC believes that human resource is its greatest asset. Thus, it ensures to provide: an effective recruitment, selection, and placement; relevant learning and development interventions; effective performance management; and, employee welfare and development in accordance with the CSC’s PRIME HRM. NOTE 7.3 The GHMC may also cite the Philhealth’s Benchbook in maintaining the requirements for accreditation, particularly on GHMC personnel, if PRIME HRM is not yet implemented. 1. Recruitment, selection, and placement The recruitment, selection and placement of personnel are based on the existing CSC rules and regulations. While the CSC Qualification Standards set the minimum qualification for hiring, the GHMC may set its specific standards both for medical and non-medical personnel as basis for hiring to ensure that they could perform their functions competently and at par with applicable local and international standards. The GHMC and Credentials Committee ensures that the recruitment, selection, and placement procedures are implemented in accordance with the minimum standards of the CSC and the DOH, i.e., equal opportunity policy. All appointments are made based on merit to attract sufficient applications from potential candidates for appointment with the skills, qualities, abilities, experience, and competencies deemed as necesssary to the job. The Human Resource Management Unit (HRMU) observes the regulatory requirements that apply to the recruitment 26 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 9 To ensure effective delivery of patient care services, the GHMC augments its manpower requirement through the employment of personnel under Job Order or Contractual status. 2. Learning and development The GHMC is committed to continually and strategically address the competency needs of its employees and ensure continual improvement to adapt to the ever-changing health environment and keep abreast of technological and technical advancements in their respective medical fields. The HRMU assesses the competencies of all the GHMC employees periodically through the Competency-Based Training Needs Analysis where employees’ current levels of competency, behavior, skill or knowledge, in one or more areas, are identified and compared with the required competency standards established for their positions or other positions within the GHMC. Another form of competency assessment is through the performance evaluation of the employees, i.e., Individual Performance Commitment Review (IPCR), where the immediate supervisor assesses the competency gaps of an employee based on his/her performance and recommends appropriate action plans to address those gaps. The results of assessments are used in the preparation of the office, department or unit annual learning and development (L&D) plan which contains the human resource development interventions such as in-house and externally provided technical and behavioral training courses, education program, coaching and mentoring, on-the-job training, and other formal and informal interventions, for each employee. These are consolidated and reviewed by the HRMU, together with the Professional Education, Training, and Research Office (PETRO), ensures the proper consolidation and coordination of all personnel professional education, training, and research activities and develops the GHMC L&D Plan for the year. The plan also includes the conduct of the regular programs initiated by the HRMU such as orientation for new employees, values orientation, stress and time management courses, and team building workshops. The effective implementation of the L&D Plan is supervised and monitored by the HRMU through facilitation, documentation, and evaluation of the in-house training and other internally initiated L&D interventions, for traceability and continual improvement of the L&D activities. The evaluation of the effectiveness of the L&D interventions is done through the Course Evaluation Form that is being accomplished by the employees. The Course Evaluation measures the attainment of the course objectives, appropriateness and relevance of the course to the job of the participants, effectiveness of the methodology and resource persons, and the appropriateness of the training venue and other training logistics. Also, after three to six months of attending the course, the immediate supervisor is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the course in improving employee performance in relation to the course attended. The results of these evaluation mechanisms are used continually improve the type of L&D intervention. 27 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 9 3. Performance management The GHMC believes that career advancement is one of the most important elements for employee satisfaction and retention in the GHMC. Thus, through the semestral rating of the IPCRs of the employees, the immediate supervisor provides clear career paths to motivate them and make them more focused at work. Employees are provided with opportunities to expand their skill sets, handle additional responsibilities that can lead to promotion, acknowledge accomplishments, and offer a tailored career advancement plan that aligns with their personal and professional goals. The promotion of employees are done through recommendations that are being reviewed by the Personnel Selection and Recruitment Board (PSRB) and the Medical Credential Committee in accordance with the CSC rules and regulations. 4. Employee welfare and benefit Other than the statutory benefits for the employees, the GHMC provides welfare and benefits as well as rewards and recognition schemes to keep the employee motivation high, improve camaraderie, ensure their health and safety, and promote employee satisfaction. These include mandatory government benefits and other approved benefits issued by the GHMC, regular teambuilding activities, birthday celebrations, etc. B. GHMC Infrastructure Management The GHMC ensures the provision of adequate, conducive, safe, and sanitary infrastructure to efficiently deliver the needed health care services. Among the infrastructure provided and maintained are GHMC building, facilities, utilities, and equipment which include, but not limited to, electrical power distribution, elevators, PWD access, air-conditioning units, water supply and drainage system, emergency power generator, ICT equipment, and biomedical equipment. A standard procedure is maintained by the GHMC for the identification of needs and requirements for new, and/or modification or repair of its existing infrastructure and facilities 1. Facilities and equipment Health Engineering and Maintenance Unit (HEMU) ensures that infrastructure, equipment, and facilities such as building, workspaces, and associated utilities are appropriate and are properly maintained to achieve conformity and provide a safe environment in compliance with local, national and/or international codes, standards, and regulations on the construction and operation of the GHMC facilities and utilities. 28 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 9 HEMU also implements the preventive maintenance of all infrastructure, facilities, and equipment of the GHMC and responds to repair requests to ensure its availability and serviceability at all times in support of GHMC operations. 2. GHMC vehicles HEMU is also responsible for ensuring the adequacy, availability, and serviceability of the service vehicles and ambulance through the conduct of daily monitoring of fuel, oil, gauges, and other accessories and regular preventive maintenance such as the change oil, parts inspection, etc. It is also responsible for ensuring that ambulance drivers are licensed and trained in accordance with the ambulance services guidelines. 3. Housekeeping The primary function of the Housekeeping Section (HS) of the GHMC is the maintenance of a clean, sanitary, and safe environment for patients and GHMC employees. The HS also ensures the cleaning, sanitation, and disinfection of comfort rooms, lavatories, and all assigned areas, and implements proper tools/supplies and equipment management. To ensure that infection prevention controls are in place, the GHMC Infection/Prevention Control Committee promulgates policies and guidelines to ensure the safety of GHMC employees, patients, and other relevant interested parties. Wastes are disposed of in accordance with the GHMC waste management standards set by the regulating bodies. The collection of segregated wastes is regularly done in various areas of the GHMC and dumped at the GHMC collection bin prior to the collection of the LGU General Services. 4. Information technology The IT Unit maintains the IT infrastructure, which includes the computers, network, and database systems, of the GHMC. It processes requests for troubleshooting through an effective system of monitoring of job requests and feedback mechanisms. The IT Unit also implements preventive maintenance activities for IT infrastructure like scheduled data back-up, hardware cleaning, software virus scanning, and the like. The GHMC ensures the safety and security of data and complies with the Data Privacy Act. 5. Security and disaster risk management The Security Personnel, externally provided but supervised by the General Services Division, maintains peace and order and enforces rules and regulations within the GHMC. Inspection upon entry to the GHMC, regular roving within the GHMC facilities, and reporting of incidents are some of the security activities being performed by the externally-provided Security Personnel. 29 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 9 Appropriate precautionary measures are also installed to prevent/mitigate the impact of natural and man-made disasters such as floods, earthquakes, climate change, and noise, among others. Disaster risk management plans are also prepared, implemented, and monitored by the Disaster Risk and Recovery Management Committee. NOTE 7.4 In some GHMCs, security and disaster risk management are two separate functions. The GHMC may customize this section accordingly. C. Financial Management The Finance Service is composed of Accounting, Budget, Cash Operations, and Billing and Claims Units, which facilitates accountability, continuously improves and refines financial plans, ensures the use of appropriate accounting standards for timely, complete, and accurate financial reporting, ensures prudent and effective use of financial resources and application of internal controls at all levels, and recommends measures to improve management of financial resources. The Finance Service also safeguards the assets of the organization through strict compliance with the National Government Accounting System and the Government Accounting and Auditing Manual. D. Logistics and Supplies Management The GHMC ensures that goods and services needed in hospital/medical center operations are managed effectively and efficiently. This includes the procurement of goods and services, supplies, and inventory management. 1. Procurement of goods and services The procurement of goods and services for the GHMC is in accordance with Republic Act No. 9184, and other regulatory and statutory requirements. All procurement activities shall be within the approved budget of the GHMC and shall be meticulously and judiciously planned. No procurement shall be undertaken unless it is in accordance with an approved Annual Procurement Plan (APP). The GHMC adopts competitive bidding as the general mode of procurement. Alternative methods such as negotiated procurement, shopping, and emergency procurement shall be resorted to only in highly exceptional cases and duly approved by the chief of GHMC. The Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) oversees and manages the procurement activities of the GHMC. The BAC and the Technical Working Group (TWG) evaluate and select suppliers or providers of the goods and services in accordance with the GHMC’s requirements. Criteria for selection, evaluation, and periodical re-evaluation of suppliers are established. The results of evaluations and necessary follow-up actions are recorded and maintained. The BAC Secretariat provides administrative support to the BAC and the TWG and keeps the records of the GHMC’s procurement activities. 30 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 6 of 9 2. Inventory and supplies management The GHMC ensures that all supplies, materials, equipment, and other resources in its care are accounted for and safeguarded against loss and wastage. The Supply Section is responsible for receiving, managing, monitoring, and issuing supplies, materials, equipment, and other resources to the end-users. To ensure that goods and services received are in accordance with specified requirements by the end-users, an Inspection Committee implements inspection and other activities necessary for verification of the purchased product/service in relation to the specified purchase requirements. The Supply Section also conducts regular inventories and updating of the stock card to ensure that supplies, materials, equipment, and other resources are readily available and provided to the end-users. Issuance of supplies, materials, equipment, and other resources are based on request from end-users. NOTE 7.5 The GHMC may mention its good practices in inventory and supply management. E. Management of Documented Information The GHMC’s QMS has established and consistently monitors controls of all essential documented information affecting the processes within the scope of its QMS to ensure their availability, suitability for use and their protection. 1. Control of documents The documented information that is maintained for the effective operations of the GHMC are referred to as documents. This includes documents that provide directions, guidance, and instruction by nature. Thus, examples of these include internal and external documents, such as Memorandum Orders, Special Orders, Plans, QMS Manual, Service/Operations Manuals, Standard Operating Procedures, Flowcharts, Guidelines, Registers/Matrices, issuances and Memorandum Circulars of oversight agencies, among others. All documents are created or updated by a process owner, reviewed and approved for adequacy by authorized personnel prior to use. Once the document is approved, the document is forwarded to the Document Custodian (DC), who is designated to manage the process of creation, review, distribution, use, and revision of GHMC’s QMS documents. A Local Document Custodian (LDC) is also designated to facilitate the same process within offices, departments or units. The DC/LDC maintains a Masterlist of Documents that serves as a directory of officially released documents indicating the current versions of all documents. 31 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 7 of 9 Documents are reviewed by the original author or another subject matter expert or GHMC management every three years or as necessary. The DC ensures reevaluation is conducted and that documents are updated, if required. The DC maintains a record of document reevaluations to identify when documents are due. If a document requires updating, the changes are made and a new version is issued. Controls for the effective distribution of documents apply to documents that are of internal and external origin. The DC/LDC maintains a Distribution List containing the offices/units that were provided hardcopy of the documents. The DC affixes a signature on hardcopy documents to identify the officially distributed documents. Any changes to documents that require interested parties’ review and approval are submitted accordingly, and not implemented until such approval is obtained. If document changes require Interested Parties’ approval prior to implementation, this is obtained in writing. When processes are changed, the appropriate documentation is updated. The DC or LDC maintains a compilation of hardcopy versions of documents. Any obsolete or superseded hardcopies are filed separately as obsolete document file to prevent the use of incorrect, invalid or obsolete information. Obsolete documents later follow the disposition controls as specified by the General Records Disposition Schedule of the GHMC. For external documents such as policies from oversight agencies, standards, or third party specifications, the DC obtains the latest version of the document and maintains it on the GHMC server (for electronic versions) or in compilation of controlled external documents (for hard copies). 2. Control of records The documented information needed to be retained by the GHMC is referred to as records. This includes evidences of implementation of processes conformity to requirements and of the effective operation of the GHMC’s QMS. Examples of these include accomplished forms, reports, obsolete documents, logbooks, and the like. Each office/department/unit of the GHMC has the responsibility of managing records. The Medical Records Section manages the patient records as well as implements the policies of National Archives of the Philippines (NAP) in the hospital/ medical center. The GHMC clearly defines its policies for the identification, storage, protection, retrieval, retention time, and disposition of documented information that are retained by the GHMC. Records are retained based on the GHMC’s approved Records Disposition Schedule in accordance with the NAP guidelines. 32 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 8 of 9 Storage methods are identified depending on the type of record. Softcopy records and data are stored in the server or computers. In all cases, the GHMC should make a backup of records stored in computers. Hardcopy records are stored in suitable cabinets to prevent damage or deterioration. Archived records are stored in-house as well as offsite, in a controlled environment to protects it from damage or deterioration. Records that are discarded after the retention period shall also follow the disposition methods prescribed by the NAP. Availability and issuance of records requested by interested parties are guided by the GHMC’s Manual on Freedom of Information as required by Executive Order No. 2 s. 2016 Freedom of Information Bill. Records are maintained legible, readily identifiable, and retrievable. Records of electronic medium are subject to periodic backups. The IT Unit is responsible for the backup stored in the server. All entries by hand, on hardcopy forms, are made using permanent ink. NOTE 7.6 If there is an existing policy issuance on control of documented information, the GHMC may cite the policy in this section and provide a brief description or a summary of the policy. Ensure that the contents of this section are in accordance with the said policy issuance. The GHMC may also consider developing a separate procedure for controlling documented information. 7.2 CONTROL OF MONITORING AND MEASURING RESOURCES The GHMC determines the monitoring and measuring resources such as the cardiac monitor, BP apparatus, among others, needed to provide evidence of conformity of service provided. To ensure valid, accurate, and reliable results, these monitoring and measuring resources are: • • • • • • periodically calibrated or verified against standards traceable to national or international standards and calibration records are periodically reviewed/maintained; adjusted or re-adjusted, as necessary; checked if batteries are replaced, as necessary; labeled and identified for the calibration status as standard quality control, such as equipment type or process to be validated, location, frequency, methods of verification, acceptance criteria, and corrective actions taken; safeguarded from unintentional adjustments; and, protected from damage and deterioration due to environmental conditions during handling, maintenance, and storage. 33 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 7. Management System Support Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 9 of 9 Also, when the results of calibration are found to be unsatisfactory or the instrument malfunctions, such equipment is tagged as “non-functional.” These are referred to the Engineering Unit through job request for appropriate action or to the supplier in case of tie-up agreements. Computer software used for monitoring and measurement are also assessed and periodically calibrated. Initial testing is also conducted prior to application. 7.3 MANAGEMENT OF ORGANIZATIONAL KNOWLEDGE The GHMC recognizes the importance of organizational knowledge as a resource for the GHMC to support its QMS processes to ensure conformity in the delivery of integrated and comprehensive quality health care services. This knowledge, which includes those that are gained through training, conferences, experiences (lessons learned), and the like, are documented and shared through minutes of meetings, re-echo sessions, and compilation of materials gained from activities attended, fora on sharing of best practices, and documented work procedures, standards, and manuals. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 34 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services NOTE 8.1 Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 11 The GHMC needs to look into the contents of this section carefully and make necessary revisions to remove those that are not practiced by the hospital/medical center and/or add practices. This section is also better supported by GHMC policies, manuals, procedure, work instructions, and other reference documents used as a guide in the performance of the users’ day-to-day tasks. 8.1 OPER ATIONAL PLANNING AND CONTROL The GHMC ensures that it formulates and establishes necessary processes and sub-processes to fulfill product and service requirements. Each office, department or unit prepares various documents, such as the OPCR/DPCR/IPCR, Work and Financial Plan, operations plans, service manuals, guidelines and procedures, schedule of duties and facilities, calendar of activities, training plans, and other related documents, including those externally-generated documents from oversight agencies, to ensure effective planning that is consistent with the goals and objectives of the GHMC and requirements of other processes in the provision of patient care services. 8.2 REQUIREMENT FOR PRODUCTS AND SERVICES A. Communication with Relevant Interested Parties The GHMC implements effective strategies in communicating with patients and relevant interested parties relating to the following: • • • service information through the Citizen’s Charter, Public Assistance and Complaints Desk, advocacies, posters, billboards, bulletin boards, signages, brochures, web presence, radio, etc.; queries through the hospital’s telephone, text and email hotlines; and, feedback and perception on hospital products and services through the Patient/Client Satisfaction Survey. B. Determination of Requirements The Medical, Nursing, and Hospital Operations and Patient Support Services Divisions determine the requirements for the patient care services, which include the following: • • • patient’s health information, such as health records and other information on their needs and expectations, as specified or implied; available services/activities or strategies before, during, and after treatment; requirements necessary for services such as the availability of medicines, medical supplies, instruments, facilities and equipment, and medical expertise on the specific service; 35 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services • • • Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 11 statutory and regulatory requirements and standards applicable to the services such as DOH policies, medical/clinical practice standards, and PhilHealth guidelines; medical information and internal GHMC requirements for a specific service such as doctor’s order, patient’s consent, and requests form; and additional requirements, as decided by the management. C. Review of Requirements The concerned medical personnel reviews the requirements related to the patient care services, together with additional requirements as determined, such as patient’s information, physician’s diagnosis, and prescriptions, requests for diagnostic tests, etc. This review is conducted prior to the provision of service to the patient, and follow up is recorded through the Patient Chart. D. Changes of Requirements The GHMC ensures that whenever service requirements are changed as a result of the review of such, the relevant documents, particularly those that are related to the provision of patient care services, are amended. The concerned persons are made aware of the changed requirements and the basis for such. This is recorded in the Patient Chart, and patient, including his/her significant others, is informed about it. The GHMC also ensures that all agreements such as patients’ consent are conveyed clearly to all concerned and are subject for review. This includes the release of health record information, patient’s payment agreements, and third-party arrangements. 8.3 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF CLINICAL PATHWAYS Clinical Pathways (CPW) are some of the main tools used to standardize and manage the health care processes in the GHMC. These are developed and implemented in the GHMC to reduce the variability in clinical practice and improve outcomes for a homogenous patient group. The GHMC develops CPWs that are aligned to its local socio-cultural and economic health care situation. A. Planning the Development of Clinical Pathways Series of orientation sessions and meetings on the establishment of the CPWs are conducted. These are also cascaded to the Medical, Nursing, and Support Services staff. The planning for the design and development of the CPWs include the determination of the following: • • • the design and development stages; the review, verification, and validation that are appropriate to each design and development stage; and, the responsibilities and authorities for design and development. 36 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 11 The process of development of a CPW considers why tasks and interventions are performed and by whom as it promotes greater awareness of the role of each professional involved in the patient care cycle. B. Inputs to the Clinical Pathways CPWs are developed based on the clinical practice guidelines of the specialty societies, WHO guidelines, DOH guidelines, consensus statements, and treatment protocols. Current practices in the GHMC are also reviewed and the most recent evidence is incorporated into the pathway. The design of the CPW also considers the local socio-cultural and economic health care situation in the community that GHMC serves. Existing similar clinical pathways used internationally or locally are also reviewed for additional inputs to the design and development of the GHMC’s CPW. C. Contents of the Clinical Pathways The Departments’ Clinical Pathway Committee prepares and develops reviews their respective CPWs. Elements of the GHMC clinical pathways include the following: • • • • • • • • • • processes and procedures timeframe checklist of history and physical examination checklist of specific signs and symptoms checklist of diagnostic tests checklist of medications checklist of non-drug treatment remarks/advice disposition references D. Control on the Design and Development of Clinical Pathways Reviews, verification, and validation activities are implemented to ensure that clinical pathways are evaluated based on the ability to achieve coordinated care and desired outcomes within an anticipated timeframe, and to identify problems in its design or potential problems during its implementation and propose necessary actions. The CPW is presented to the management and staff and to the Chief Medical Professional Specialist of the Department for review and verification. The review and verification undertaken should ensure that each clinical pathway: • meets the applicable Clinical Pathway Guidelines (CPG), and all locally and internationally accepted guidelines; 37 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services • • • Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 11 provides information on the drugs, supplies, equipment and other resources needed for its implementation; contains standards and expected outcomes; and Provides mechanisms for recording variations/deviations from planned care/activities and continuous feedback via variance tracing and analysis. Approved CPWs are communicated to concerned professionals for implementation. Treatment for the specific diseases covered by clinical pathways is then based on these guidelines. An induction period of a minimum of one quarter or one trial implementation is allowed to validate the CPWs. Variations/deviations from planned care/activities and continuous feedback via variance tracing and analysis are monitored and recorded. CPWs are reviewed/evaluated as the need arises. All the changes made as results of the actions taken are recorded for traceability and future reference. NOTE 8.2 There may be a need to allow a certain level of flexibility in the design and development of CPWs. CPWs are standardized but there may be a need to allow variations due to differences in patients’ response to the treatment. This should also be considered in customizing this section. 8.4 CONTROL OF EXTERNAL PROVIDERS The GHMC manages its relationship with its external providers, such as interns, medical consultants, medicine suppliers, waste disposal services, among others, to ensure that they conform to specified requirements. The requirements of the GHMC to these external providers are specified in the memorandum of understanding/agreement, contracts, terms of reference, among others. 8.5 PATIENT CARE SERVICES AND TREATMENT A. Control of Processes for Patient Care The GHMC plans and delivers the provision of patient care under controlled conditions, including the following, when necessary or applicable: • • • availability of medical information such as diagnostic/treatment plan, patient’s medical history, electronic medical records (e-MR), and other necessary information such as medical procedures, other treatment options, related risks, etc.; availability of service manuals, procedures and guidelines, medical standards and studies, and the like; availability and use of suitable medicines, medical supplies, equipment, and facilities; 38 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services • • • Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 11 availability and use of the monitoring and measuring devices; implementation of patient care service monitoring and measurement activities such as patient assessment and evaluation, vital signs monitoring and medication recording in-patient chart, and other treatment verification and validation activities; and, implementation of patient discharge/transfer plan and follow-up check-up. NOTE 8.3 The GHMC should comply with the Data Privacy Act (DPA). Thus, there is a need to highlight and mention in this section, as part of the controls, the different practices of the GHMC in implementing the DPA. The GHMC operational processes performed/implemented by the Medical and Nursing personnel of the concerned department or unit of the Medical and Nursing Divisions as well as concerned support units are guided by departmental manuals, clinical practice guidelines, CPWs, and other reference documents. B. Validation of Process for Patient Care The Medical Division, Nursing Division and concerned support units validate the critical steps of the process in the provision of patient care services. However, the effectiveness of treatments implemented or the expected results of the services provided may not be completely verified upon discharge of the patient from the hospital/medical center due to differences in patients’ response to the treatment. Process validation activities may include the following: • • • • • • • review and approval of the medical procedures by the chief of GHMC or chief medical specialist by affixing his/her signature on the Patient’s Chart; ensure the availability of the necessary supplies, instruments, equipment, and facilities for the procedure; designate specific competent personnel who have the necessary minimum training, qualification, and/or experience to perform the procedures as established by the WHO, DOH and GHMC procedures and guidelines; use of locally and internationally accepted clinical practice guidelines, WHO guidelines, DOH guidelines, treatment protocols, consensus statement, clinical pathways, and other medical procedures and methods; record the pertinent information in the patient’s chart to allow feedback based on the actual process results; correlate the results clinically by reassessing the condition of the patient prior to discharge, which is recorded in the patient’s chart; and, conduct of health education and counselling of the patient, family, relatives, significant others, or caregivers on medications’ effect during and after treatment and home care, as applicable. 39 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 6 of 11 C. Identification and Traceability The GHMC identifies the service provided by suitable means throughout the process of provision of patient care services. It identifies the status of the service with respect to monitoring and measurement requirements. The GHMC controls and records the unique identification of patients, and associated products and services through the following: 1. Patient identification • • • • • • • Attachment of patient wrist tag with information such as patient name and age. Attachment of bed tags with information such as patient name, age, date of admission, chief complaint, and name of attending physician. Patients directory to identify the service provided. Patient chart to provide traceability of service provided. Use of hospital/medical center number, complete name, age, and sex in the patient chart. Color-coded baby tags (blue for male and pink for female) are attached to the left leg of newborn patients with information such as baby’s name, the complete name of mother, and date and time of delivery. Cadavers are tagged properly with information such as patient name, age, and date and time of death. 2. Laboratory specimen and results • • • Specimens are provided with specimen tags with information such as patient name and type of specimen. X-ray films have identification markers which contain information such as patient name, age, date and time of the procedure, and film number. X-ray result contains information such as patient name, age, gender, date, ward, requesting physician, examination requested, and result. 3. Medicines and hospital/medical center food for in-patients • • • • Preparation of medicines is based on the patient’s prescription. Medicines are labeled before dispensing to the clients with information such as the patient’s name and ward. Patients’ medications dispensed from the pharmacy are double-checked by the nurses and logged into specific logbooks. Modified diets are provided with meal tags with information such as patient name, ward, and specified diet. 40 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services NOTE 8.4 Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 7 of 11 The GHMC may cite other practices that could reflect the different identification and traceability of patients, laboratory specimen and results, medicines, and hospital/medical center food, among others. D. Care of Property Belonging to Patients and External Providers The GHMC exercises the utmost care and confidentiality of the patient’s personal belongings and data as necessary for the treatment. Inadvertent use or mishandling of data and loss of personal properties, entrusted to the hospital/medical center by both the patients and external providers, are dealt with accordingly. 1. Patient personal effects • • • • All jewelry is removed and properly handed to the patient or immediate family, companion, guardian, or significant others. In case of trauma/emergency case where the patient is unconscious without a responsible companion, all personal belongings are removed by the ER personnel and properly logged and endorsed to the authorized custodians on duty. Dentures are removed if the patient will undergo surgery or possible intubation and handed to a responsible companion or guardian. Patients and their significant others are consistently reminded to be responsible for the protection of their personal belongings as the GHMC may not be liable for any damage and loss of their belongings. 2. Patient’s body, body parts, and foreign object lodged • • • • • When patients are treated, the significant others can observe and listen as applicable, except in critical conditions, such as surgery, intensive care, among others, and during the use of radiation for their safety. Foreign objects lodged in patients’ bodies such as bullets, knife, scissors, among others, when removed, are properly labeled and secured at the OR/ER stockroom for possible medico-legal use. Body parts, such as amputated part and removed cyst, are properly packed and the option is given to the patient or significant others to take them for proper disposal or the GHMC will take the responsibility of disposal. During the expiration of a patient, the cadaver is shown to the significant other and they are informed of the procedure for post-mortem care and discharge. Include infection control. 41 Name of GHMC Quality Management System Manual GHMC Logo Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 8 of 11 3. Patient data • • • • • Personal data and medical information contained in the patient chart are considered confidential. Access to the all GHMC information is restricted only to GHMC center personnel only. Medical Records Section is not allowed to use the health record, in any way, which will jeopardize the interest of the patient or of the GHMC. A court order is required for access to records for medico-legal purposes. The records may also be used to defend the GHMC against any legal proceedings. Volatile and flammable liquids are never placed inside the records room. 4. Medicines and medical supplies for in-patient • • Medicines and supplies given by the patient’s significant others at the nurse station are recorded in the logbook and signed by the receiving nurse. Only the GHMC is allowed to purchase dangerous drugs according to the existing Guidelines on Dangerous Drugs. Prescriptions provided to the patient are duly approved by the doctor in-charge. The Pharmacy can only dispense the medicine to patients with their approved prescription. 5. Properties of external providers • Effective handling and maintenance, which are usually explicitly mentioned in contracts or memorandum of agreement/understanding with the external providers, is strictly implemented. NOTE 8.5 The GHMC may customize the different practices in caring for the properties of the patients, other relevant interested parties, and external providers. E. Proper Handling and Protection of Patients and Related Products The GHMC preserves the conformity of the service with the patient’s requirements through the use of the Automated Inventory System and/or the GHMC Information Systems. This covers the determination of required patient support services, planning, processing, delivery of service, and monitoring. 1. Handling of patients The medical doctors and nursing personnel ensure that the services provided match the treatment plan prepared for the patient within the given timeframe, as discussed during the initial consultation. All medical personnel should have undergone the General Clinical Practice (GCP) training. All medical procedures follow the guidelines set by medical societies. 42 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 9 of 11 The patients reserve the right to refuse a medical procedure. In cases where patients prefer a certain procedure to be undertaken, this shall be accommodated in developing the treatment plan. On completion of the treatment, the patient is given a summary of the service rendered. Safe and appropriate care in handling and transporting patients from one area to another is performed by trained personnel only. Appropriate wheelchairs and stretchers are provided. The medical Doctor and nursing personnel regularly monitor and check the patients’ response to the treatment and record the necessary information in the patients’ medical records. Appropriate home care instruction and medication to the patient and his/her significant others or caregivers before discharge. The GHMC may be sued by the patient if there any deviation in the medical procedure conducted. Post-mortem care of the cadaver is done appropriately and then brought to the morgue. It will stay there for a minimum of two hours before release, with proper documentation, depending on the circumstances surrounding the post-mortem. 2. Storage and preservation of medicines and supplies The Central Supplies Room and the Pharmacy practices close monitoring of expiration dates of medicines and supplies. “First expiration, first out,” “first in, first out,” and adherence to cold chain management is observed. Near expiry medicines are separated in a specified area labeled as “near expiry” and are disposed of in accordance with FDA and DENR policies. The pharmacist then informs the suppliers of the status and processes the return of such medicines to the suppliers in accordance with the terms of reference, as specified in the bidding process. The Pathology and Laboratory, and Radiology Department preserves and controls reagents through temperature monitoring, proper storage, and conduct of monthly inventory. Unprocessed/ unexposed x-ray films are kept in a required room temperature of 27 degrees Celsius and stocked vertically; while processed/exposed x-ray films are placed in an envelope categorized and filed by patient number. Solutions (developer and fixer) are also kept in a controlled room temperature. The Property and Supply Management Unit stores medical supplies in a stock room preferably accessible to concerned parties. The room should have proper ventilation, adequate space, open shelves, ample lighting, and necessary security. Stocks are stored and classified according to demand (i.e., fast or slow-moving), size, weight, shape, and perishability. Regular monitoring as to condition and quality of stocks is conducted to ensure quality and availability at all times. Supplies are labeled with the name and corresponding expiry dates. Only authorized personnel are allowed in the stockroom 43 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 10 of 11 The Nutrition and Dietetics properly preserves the food served to patients by controlling time throughout the process of preparation and distribution of meals. Storage of food products is also handled through monitoring of expiry dates upon receipt and prior to use and practice of “first in, first out” policy. During food preparation, time spent in room temperature is minimized and the boiling period is observed and guaranteed until the desired tenderness is achieved. The holding period of cooked food prior to distribution does not exceed two hours. 3. Infection control The Infection Control Committee promotes policies which prevent health care associated infection among patients, health care workers, and other persons involved in the care of the patient. It provides policies and guidelines on surveillance, isolation precautions, hand hygiene, use of protective equipment, microbiology services, housekeeping, patient care environment, waste collection and handling, toxic waste disposal, care of cadavers, and rational use of antimicrobials. Activities to enhance infection control awareness such as Anti-Microbial Stewardship Program are also regularly done by the Committee. NOTE 8.6 The GHMC should ensure that proper controls are established to ensure proper handling of patients, laboratory specimen and results, medicines and supplies as well as to prevent infections in the hospital/medical center. The GHMC may cite guidelines/policies on proper handling of patients, their properties, medicines, and supplies, among others. Ensure that the write-up in this section is in line with the existing guidelines/policies. F. Post-Patient Care Activities The GHMC’s patient care services do not end when the patient is discharged from the hospital/ medical center. Continued care and treatment are ensured through the following: • • • • • issuance of home care and treatment instructions by the doctor; nurse briefing and orientation; follow-up check-ups and continued laboratory testing, as advised and scheduled, whenever necessary; referral to other hospitals/medical centers, as necessary, through the service delivery network; and, facilitation of home visitations for critical cases. 44 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 8. Provision of Patient Care Services Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 11 of 11 For released products, the GHMC provides the following post-delivery activities: • • • return policy for medicines and other medical products that are defective/expired; correction and reprinting of erroneous laboratory results; and, customer feedback on items purchased and services received. NOTE 8.7 The GHMC may customize the different practices in caring for the properties of the patients, other relevant interested parties, and external providers. G. Control of Nonconforming Outputs The GHMC recognizes that nonconformity may occur within any phase of the provision of patient care services. Such nonconformities could come from unmet targets, complaints from patients and other interested parties, sentinel reports, audit reports, among others. The GHMC ensures that appropriate mechanisms are established to identify, control, and prevent unintended use or delivery of nonconforming products and services. Mechanisms are compiled in Annex C - Incident Report by the hospital/medical center personnel in cases of nonconformity. When nonconformities are corrected, they are reviewed in accordance with applicable documented procedures/standards. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 45 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 9. Performance Evaluation Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 5 9.1 MONITORING, MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS The GHMC effectively measures its performance through the duly approved monitoring and evaluation system. The data collected from the monitoring, evaluation, and analyses are used for the continual improvement of the policies/guidelines, systems, and procedures of the GHMC. The GHMC identifies specific and customized tools to be used in the monitoring and evaluation of processes that will determine the achievement of planned results. If these are not achieved, correction and corrective action are determined and implemented, as necessary. The following tools are some tools utilized in monitoring and measuring performance: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • GHMC Scorecard Office/Division/Department/Individual Performance Commitment Review Operational Plan Project Procurement Management Plan/Annual Procurement Plan Equipment Calibration Status and Report Work and Financial Plan GHMC Statistical Report Infection Control Committee Report Division Accomplishment Report Patient Safety Report GHMC Epidemiologic and Surveillance Report Financial Statement Report Inventory of Supplies Departmental Medical Audit Nursing Service Audit Monitoring of Nonconformity of Laboratory Examinations Customer Satisfaction Survey Report PHIC Mandatory Report 24 hours Floor Census (Daily Census-MD’s) - Daily Census is accomplished by the Nursing Service Reports on the performance of external providers. The GHMC analyzes data gathered from monitoring and evaluation activities as bases for the improvement of the QMS. The data include, but is not limited to, internal and external stakeholders’ feedback, process monitoring reports, internal quality audit reports, management reports, and product and service nonconformity reports. As applicable, graphs, trend analysis, among others, are the tools used for data analysis. 46 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 9. Performance Evaluation Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 5 9.2 STAKEHOLDERS’ FEEDBACK MANAGEMENT Feedback from patients, together with their significant others, are crucial to the GHMC. The hospital/ medical center’s products and services are directed to them. Thus, their perception of the quality of these products and services are highly valued by the GHMC. Stakeholders’ feedback is obtained through available mechanisms such as the stakeholders’ satisfaction survey, public assistance and complaints desk, suggestion box, comments through a phone call, text messages, e-mail, and letters, which are being monitored by responsible units. The Integrity Management Committee or the Customer Service Committee collects data, using available feedback mechanisms, tabulates and analyzes them for reporting to the ExeCom. The reports are submitted to the ExeCom and concerned units or departments for action. Thereafter, the Integrity Management Committee or the Customer Service Committee reports status of actions taken on the results of the Customer Satisfaction Survey during the Management Review. Complaints are considered nonconformity. As complaints are received, the responsible units issue a Corrective Action Request (CAR, see Annex C) form to the concerned office, department, or unit for proper action. The issuing unit monitors the accomplishment of the CAR and the implementation of the correction and corrective actions to ensure that all complaints are properly attended to and addressed. When this happens the complaints are forwarded to the IQA for issuance of an CAR form to the concerned office, department, or unit for proper action. NOTE 9.1 The GHMC may add other reports used to monitor, measure, and evaluate the performance of its QMS. Other evaluation activities, as practiced by the GHMC, may also be enumerated or further described in this section. NOTE 9.2 Depending on the nature of nonconformities, some complaints are not registered in the CAR, especially those arising from emergency situations. These are immediately acted upon by the customer/service office concerned. NOTE 9.3 CARs are issued when there are customer complaints depending on the frequency and nature of the complaint. 9.3 INTERNAL QUALITY AUDIT The GHMC conducts a semi-annual Internal Quality Audit (IQA) to evaluate the processes’ conformity with the requirements of ISO 9001 and the requirements of the GHMC, and determine the effectiveness of its QMS. 47 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 9. Performance Evaluation Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 3 of 5 A. Managing the IQA An IQA Committee is established to manage IQA activities. Likewise, a pool of competent auditors coming from different offices, departments, and units are mobilized to compose the IQA Team. They are identified and trained to ensure that they are capable of conducting and carrying out the audit. In the selection and assignment of IQA Teams, objectivity and impartiality of the audit process is considered. Thus, auditors do not audit the processes within their respective offices, department, or unit. B. Planning and Conducting the Audit An Audit Program is established to arrange the audits for the entire GHMC. An Audit Plan is communicated to the GHMC containing the audit criteria and scope for the conduct of the IQA. An audit is initiated through the opening meeting with the Head of the office, department, or unit. Audit methods include direct observation of the processes, interviews with relevant persons, and examination of documented information. C. Reporting the Audit Results After the IQA is completed, a closing meeting conducted to report the results of the audit to the Heads of the offices, departments, and units and clarify the audit findings. Once the findings are clarified, the auditors issue the audit report to the auditee. Based on the results, appropriate correction and corrective actions may be necessary. A nonconformity finding, recorded in the CAR form, requires corrective action. Response time is established to correct nonconformities and to take corrective actions to ensure that these are effectively implemented in a timely manner. The identification of potential weaknesses or opportunities for improvement in the QMS adds value to the conduct of IQA. As this is part of the report, it can provide the heads of offices, departments, and units with the information to decide whether it is appropriate to initiate action for improvement. The results of the IQA are used as inputs to Management Review. D. Monitoring, Verification, and Closing of Actions Taken on Audit Findings The IQA Committee also monitors all the CARs issued as a result of the IQA. Timely implementation of correction and corrective actions are ensured to mitigate consequences. Verification of the implementation may be done through a follow-up audit or during the next audit cycle. This verification may also include evaluation of the effectiveness of the actions taken, i.e., prevention of recurrence of nonconformity, an improvement on the performance, and the like. Upon verification of the effectiveness of action taken, the IQA Committee shall close the nonconformity. Otherwise, it recommends another audit verification until the evidence that such action taken to address the nonconformity is proven effective. 48 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 9. Performance Evaluation Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 4 of 5 9.4 MANAGEMENT REVIEW The ExeCom reviews the QMS at least twice a year to adopt measures for its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. The review includes assessing the performance of the QMS and the adequacy of resources as well as determining opportunities to improve performance and the need for changes to the QMS, especially in the quality policy and quality objectives. A. Initiating the Management Review In coordination with the chief of GHMC, the QMS Leader and Secretariat prepare the agenda and template of presentation or report. The agenda is submitted to the Chief of GHMC for approval and issuance of a Notice of Meeting. The Secretariat/Office of the Chief of GHMC distributes the Notice of Meeting, the approved agenda, and other templates needed to all concerned at least five working days before the date of the Management Review. If possible, the Secretariat consolidates the reports prior to the conduct of the Management Review. B. Agenda for the Management Review The Management Review covers the following inputs: • • • • • • • • • • • • status of actions from previous management reviews or ExeCom meetings; changes in external and internal issues that are relevant to the QMS; customer satisfaction and feedback from relevant interested parties; extent to which quality objectives have been met; process performance and conformity of products and services; monitoring and measurement results; nonconformities and corrective actions; audit results; performance of external providers; adequacy of resources; effectiveness of actions taken to address risks and opportunities; and opportunities for improvement. C. Conducting the Management Review The chief of the GHMC presides the Management Review. It starts with the confirmation of the quorum and agenda. The QMS Leader shall ensure that all the required agenda inputs are discussed; actions, decisions, and recommendations are made to ensure the continual improvement of the QMS; and resources are allocated to ensure implementation of actions. 49 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 9. Performance Evaluation Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 5 of 5 D. Documenting the Management Review The Secretariat ensures that findings, outputs, and action plans are properly documented and filed. Specifically, the Secretariat records and documents proceedings such as decisions/actions regarding the improvement of the QMS and products/services related to customer requirements, and decisions/ actions regarding resource needs, among others. The Secretariat prepares the minutes of the meeting and distributes the draft to all attendees for review and inputs on the status of immediate action items. The Chief of GHMC approves the minutes of the meeting in the next management review. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 50 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 10. Improvement Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 1 of 2 10.1 IMPROVEMENT OF THE GHMC Continual improvement of the GHMC is the main objective of the QMS. As such, various inputs are considered for continual improvement such as the quality policy, performance targets, audit findings, analysis of performance data, corrective actions, and management reviews. The GHMC ensures that improvement actions are implemented through small-step improvement activities within existing processes and services such as benchmarking activities, implementation of new projects and programs, introduction of new processes and services, and use of new technologies and innovations in the medical field. These improvement activities may result in changes in the policies and procedures, work instructions, recalibration of performance targets, and reassessment of risks and opportunities needed to implement the selected solution. 10.2 CORRECTIVE ACTION The GHMC takes necessary actions to address nonconformities detected during operations as a result of IQA and management reviews and as gathered from stakeholders’ feedback. All nonconformities are recorded in the CAR form which is issued to the concerned office, department, or unit for proper response and action, within ten working days, to ensure proper monitoring. Upon receipt of the CAR, the division/department/section/unit heads identify concerned personnel who need to be involved in the corrective action. Coordination with the other concerned division/ department/section/unit is done as the nonconformity may affect them. When the need for corrective action is established, the concerned division/department/section/unit conducts root cause analysis to identify root causes and eliminate them, thus, preventing the recurrence of the nonconformity. Methods for identifying the root causes of the nonconformities include the five whys method, cause and effect diagram, and the like. From the root causes identified, appropriate corrective actions are determined and planned for proper implementation. The corrective action plan includes the activities, resources, responsibilities, and timelines needed to implement the selected solution. Corrective actions are collectively reviewed during the Management Review. Depending on the nature of the solution and the associated nonconformity, monitoring, and review continue for at least six months after implementation, after which the corrective action is deemed completed. It is then that the division/department/section/unit reviews the effectiveness of any corrective action by confirming through objective evidence that the actions/corrections have been implemented or taken, and as a result, the nonconformities have not recurred or that the process performance has improved. 51 Name of GHMC GHMC Logo Quality Management System Manual Section 10. Improvement Revision No. 0 Effective Date Page No. 2 of 2 After the review of corrective actions, the GHMC considers whether there are risks or opportunities that have not been determined previously, or if the actions for risks and opportunities were not effectively addressed. Updates are made to the Risk and Opportunity Registers. Prepared by: Approved by: NAME QMS Leader NAME Chief of GHMC 52 GHMC Logo Name of GHMC Revision No. Quality Management System Manual Effective Date Annex A. List of Needs and Expectations of Relevant Stakeholders Page No. 0 1 of 2 External Stakeholders Stakeholders Needs and Expecation Patients and their Significant Others • • • • • • • • Better health condition Effective medical treatment services Courteous Hospital personnel Skilled medical staff Responsive services Equitable and Affordable services Accurate diagnosis Appropriate and functional facilities and equipment Community and Civil Society Organizations: • Local Government Unit • Civil Society Organizations • Non-Government Organizations • International Organizations • • • • • Environment-friendly processes Socially responsive systems Effective and needs-based health programs Accessible services Conformance to local and international standards Oversight Agencies: • DOH • DBM • CSC • COA • PhilHealth • • • Timely submission of reports Accurate reports Compliance to statutory and regulatory requirements Medical Professional Organizations • • Availability of data Cooperation on relevant activities/events Suppliers • • • Clear specifications Timely payment Timely feedback 53 GHMC Logo Name of GHMC Revision No. Quality Management System Manual Effective Date Annex A. List of Needs and Expectations of Relevant Stakeholders Page No. 0 2 of 2 Internal Stakeholders Stakeholders Hospital Employees Needs and Expecation • • • • • Hospital Management • • • Training and other professional development interventions Employee welfare and benefits Protection from health hazards Clear directions and policies Appropriate and adequate facilities and equipment Supportive and performing staff Accurate and timely submission of reports Relevant and accurate data to support management decision 54 The lack of budget to renovate the kitchen facilities Getting a competent consultant who can assist the Hospital in establishing QMS and securing ISO 9001:2015 certification R O O 2 The poor physical condition of the Hospital kitchen potentially contaminating the food prepared and distributed to the patients 3 Directive of the DOH for all DOH- retained hospitals to secure ISO 9001 certification potentially improving the processes and systems of the Hospital 4 Availability of cuttingedge medical equipment can help the Hospital provide better patient care services Engineering c. Facilitate the renovation of the hospital kitchen Medical Dept Heads NAME GHMC President NAME Department Head b. Submit proposals based on the Budget & DOST timelines Procurement Unit a. Assisgn a qualified team b. Forge MOU with industries Admin Officer Budget & Procurement Unit b. Realign budget from MOOE and procure contractor to renovate the Hospital kitchen a. Network with the industries and explore partnerships Engineering HRDO b. Conduct customer relations training for medical personnel a. Prepare the renovation plan OPD a. Do process streamlining and finalize the revision on the procedures of the OPD Responsible Dec. 15, 2019 Dec. 15, 2019 Dec. 15, 2019 Dec. 31, 2019 Nov. 30, 2019 Target Date L I R/O Rating Risk/ Opportunity Rating after Treatment Page No. Approved by: 15 High 20 High 25 High 15 High Treatment/ Opportunity Pursuit Action Plan Revision No. Prepared by: 3 4 5 3 R /O Rating (LxC) Annex B. Risk and Opportunity Register 5 5 5 5 Likelihood Consequence (C) (L) Quality Management System Manual Most equipment are old and below the international standard specification Procedures and manuals are established but need updating. The Planning Unit is scouting some consultant. The budget was proposed last year but it has been slashed by the DBM Procedures are being reviewed and target timelines in OPD are indicated in IPCR. On discourteous staff, the EXECOM has consistently reminded the Department Heads to emphasize to their staff the need to always be courteous to the patients and their significant others. Current Controls/ Situation GHMC Logo Acquisition of modern medical equipment for areas needing these The main risks are that patient waiting time in OPD is extremely long and the medical staff are discourteous R Risk/ Type Opportunity (R /O) Causes 1 Failure to address significant patient experience/ concerns potentially impacting the reputation of the Hospital Risk/ Opportunity Description Name of GHMC 0 Effective Date 1 of 1 55 Revision No. Name of GHMC Quality Management System Manual GHMC Logo 0 Effective Date Annex C. Corrective Action Request Page No. 1 of 1 Section 1 - Details of Nonconformity (To be accomplished by the Auditor/Initiator) References: Date Issued: (manuals, procedures, policies, ISO clauses, etc.) Auditor/ Initiator: CAR Number: Occurring in other offices? Provide details: Yes No Signature over printed name Details: (As a result of) Internal Quality Audit Nonconforming Outputs Complaints Non-Attainment of Targets Others (Pls. specify) Office: Issued to: (Office Head) Noted by: Signature over printed name Signature over printed name Description of Nonconformity: (Include criteria and evidence) Acknowledged by: Section 2 - Necessary Action (s) (To be accomplished by the Auditee/Process Owners) Correction: Target Completion Date: Root Cause Analysis: Analyzed by: Describe the necessary Corrective Action(s): Target Completion Date: Approved by: Section 3 - Verification of Implementation and Effectiveness (To be accomplished by the Inititator) Results of Action(s) Taken Remarks Verified by: Verification Date: Acknowledged by: Results of Action(s) Taken Next Verification Date: Verified by: Verification Date: Acknowledged by: Next Verification Date: Remarks 56 PRODUCTIVITY AND DEVELOPMENT CENTER Government Quality Management Program Office DAP Building, San Miguel Avenue, Ortigas Center, Pasig City www.dap.edu.ph | gqmpo@dap.edu.ph (02) 8631 09 21 loc. 171 or (02) 8631 21 37 DEVELOPMENT ACADEMY OF THE PHILIPPINES