High-Risk Pregnancy Assessment: Antenatal Tests & Risk Factors
advertisement

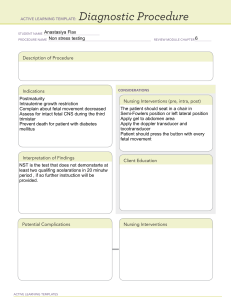
ASSESSMENT OF HIGHRISK PREGNANCY Chapter 10 Objectives ◦ Define the key terms relate to antenatal test ◦ Identify the purpose and indication for key antenatal tests ◦ Describe the procedure, interpretation, advantages, and risks of common antenatal tests ◦ Identify the nursing responsibilities related to key antenatal tests ◦ Identify patient teaching needs related to antenatal tests Assessment of Risk Factors (page 225) ◦ Biophysical Factors ◦ Psychosocial factors ◦ Sociodemographic factors ◦ Environmental factors Biophysical ◦Includes risks factors that originate within the mother/fetus which can affect the development ◦Genetic disorders ◦Nutritional ◦General health ◦Medical/obstetric related illness Psychosocial Risk ◦ Maternal behaviors and adverse lifestyles that have a negative effect on the health of mother and fetus ◦ Emotional distress ◦ Hx of depression ◦ Mental health problems ◦ Unhealthy interpersonal relationships (abuse) ◦ Smoking , caffeine, alcohol and drugs Sociodemographic Risks May place mother and fetus at risk Lack of prenatal care Age Low income Single marital status Residence Minority ethnic group Infections Anesthetic gases Radiation Environmental factors Therapeutic drugs Illicit drugs Cigarette smoke Stress Diet Antepartum testing Identify fetuses at risk for injury due to interrupted acute or chronic oxygenation, in order to prevent permanent injury or death Second goals is to identify appropriately oxygenated fetuses so that unnecessary intervention can be avoided Kick count, non-invasive and inexpensive Daily Fetal Movement Count Prescence of movement is normally and reassuring sign Decreased activity is noted in response to hypoxemia Different protocols • Once a day for 60 minutes • 2-3 times/day for 2 hours or until 10 movements • Count all fetal movements in a 12-hour period until 10 movements • Fewer than 3 movements/hour needs further evaluation • Assess nutrition and maternal position (lie on left) first Ultrasonography ◦ Considered the most valuable diagnostic tool in obstetrics. ◦ Ultrasound can be performed abdominally or transvaginally ◦ Levels of ultrasonography ◦ Standard: most frequently done in 2nd and 3rd trimesters to evaluate position/presentation, AFI, fetal growth ◦ Limited: to determine a specific piece of information re the pregnancy re AFI (amniotic fluid index) ◦ Specialized: done when anatomical or physiological abnormality is suspected ◦ Ultrasonography provides early diagnosis, that allows for plan of care to be in place ◦ Fetal heart activity, GA, fetal growth, fetal anatomy, genetic disorders, placental location ◦ Standard set of measurements are used ◦ Maximum embryo length of grownrump length ◦ Best done during first trimester ◦ After first trimester Biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference, abd circumference and femur length is used ◦ Growth id determined by both intrinsic growth potential and environmental factors Fetal Well-being ◦ Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) ◦ Oligohydramnios < 5cm ◦ Fetal renal disease ◦ Congenital abnormalities ◦ PPROM ◦ Polyhydramnios > 25 cm ◦ Gastrointestinal and CNS anomalies ◦ Twin-to-twin transfusion ◦ Placental abnormalities DOPPLER FLOW STUDIES ◦ Uses systolic/diastolic flow ratios and resistance indices to estimate blood flow in various arteries. ◦ Indicates fetal reserve and adaptation ◦ Absent or reversed flow are associated with growth restriction ◦ Doppler flow studies reduce perinatal mortality and unnecessary obstetric interventions Biophysical Profile (BPP) ◦ A noninvasive assessment of fetus based on acute and chronic marker so fetal disease ◦ Used in late 2nd and 3rd trimester for antepartum testing because its a reliable predictor of fetal well-being ◦ Recommended for woman with increased risk of problems ◦ Done after 32 weeks GA ◦ A low score may indicate further testing ◦ In some case, early or immediate delivery may be indicated ◦ Tables 10.2 + 10.3, page 231 and BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE (BPP) Amniocentesis ◦ Done >15 weeks gestation ◦ A needle is inserted transabdominally into uterus and amniotic fluid is withdrawn ◦ Indications include ◦ Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) ◦ prenatal diagnosis of genetic or congenital disorders (NTD’s) ◦ Assessment of fetal ling maturity (L/S ratio; presence of PG; LBC test) ◦ Risks/Complications ◦ Leaking of amniotic fluid ◦ Hemorrhage ◦ Infection ◦ Fetal death Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) ◦ Performed between 10-13 weeks ◦ Reflects the genetic make-up of the fetus ◦ Cannot be used for maternal serum maker ◦ Invasive ◦ Risks ◦ Chorioamnionitis ◦ PPROM ◦ Miscarriage Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) Screening tool for Neural Tube Defects (NTD) 85-92% o open NTD’s and most cases of anencephaly can be detected early Increased levels are detectable beginning week 7 GA NTD occurs in approximate in 1 in 1000 live births AFP screening should be done between 16-18 weeks gestation AFP is produced in the fetal gestrointestinal tract and liver AFP is usually part of the quad screen Multiple Marker/Coombs ◦ Screening to detect fetal chromosomal abnormalities, trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) ◦ 11-14 weeks GA ◦ Measures pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) and Human chorionic gonadotrophin (B-hCG) ◦ Trisomy 21 hCG and NT is higher: PAPP-A levels are lower ◦ Trisomy 13 and 18, hCG and PAPP-A lower ◦ Coombs ◦ Screening tool for Rh alloisoimmunization ◦ If values are high: increased risk for hydrops fetalis ◦ 1:8 to 1:32 is critical – significant risk Non-Stress Test (NST) ◦ NST interpretation is either reactive or nonreactive ◦ Acceleration of FHR and fetal movement indication adequate oxygenation and an intact CNS ◦ Reactive NST meets criteria of 2 accelerations of the FHR over 20 min ◦ If criteria not met test may be extended for further 20 min ◦ Nonreactive test will require further investigation ◦ Vibroacoustic Stimulation Oxytocin challenge (OCT) Identify jeopardized fetus that was stable at rest but showed evidence of compromise after stress. Uterine contraction decrease placenta perfusion Contraction Stress Test If the decrease is sufficient to produce hypoxia in the fetus, a deceleration in FHR results Done with nipple stimulation of Oxytocin-stimulated contractions Results are • • • • • •• • Negative Negative Positive Positive Equivocal-suspicious Equivocal-suspicious Equivocal Unsatisfactory • Equivocal • Unsatisfactory ◦ Negative- 3 contraction in 10 min with NO late decelerations CST ◦ Positive- repetitive persistent late deceleration occurring with more than half of the contractions ◦ Equivocal- FHR decelerations with hyperstimulation ◦ Unsatisfactory- fewer that 3 contractions in 10 min