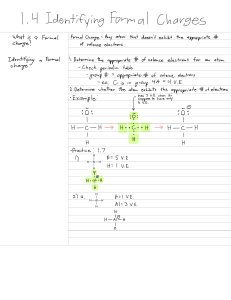
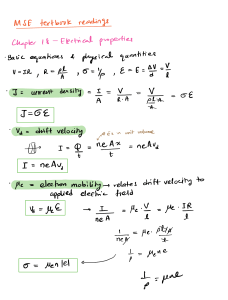
Ionic Compounds – Characteristics and Lewis Dot Structures Fill in the blanks below using words from the word bank. All words will not be used. WORD BANK: Negative Electrons Losing Positive Noble Gas Octet Rule Soft Anions Polyatomic Ions Electron Configuration Crystal Lattice Cations Transfer Malleable Empirical Formula Hard Gaining Metals Ions Sharing Nonmetals Brittle 1. An ionic bond is an attraction between oppositely charged _________________ that form due to a __________________ of electrons. r 2. Anions have a _____________ charge, while cations have a ________________ charge. v 3. An atom becomes an ion by losing or gaining _____________________. 4. The ___________________ states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of valence electrons. 5. When atoms form ions, their electron configuration will typically mimic that of a Noble _________________. god 6. ____________________ are covalently bonded atoms that have an overall electrical charge, allowing them to bond as one “unit.” 7. The ___________________________ is the simplest ratio of ions from which an ionic compound’s formula can be established. This is the smallest unit of an ionic compound. 8. The structure formed by an ionic compound is called a _____________________________. hard peak 9. Ionic compounds are __________ and ________________. 10. Calcium would become an ion by _________________ 2 electrons. Draw the full Lewis dot structure (from the formation all the way through to the product) for each of the following sets of atoms. Be sure to continue transferring electrons (and adding in atoms) until every cation has lost ALL of its valence electrons and every anion has a full outer shell. Ex: Mg and Cl 1. K and F R E CED É 2. Mg and I sign i I ng i 3. Be and S BETS I Be 4. Na and O Mayo Mce na C I've 5. Al and Br AT.BE Is B AEL Bi p 6. Ba and N Bar X Bays Bel BailD BET 7. K and O I Eto 8. Ca and P cig a can I cat ca Ba