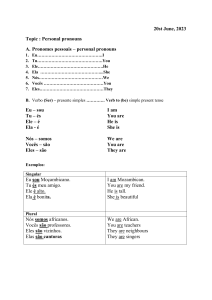
Carga Formal, Ligações, Ressonância e Isomeria em Química Orgânica
advertisement
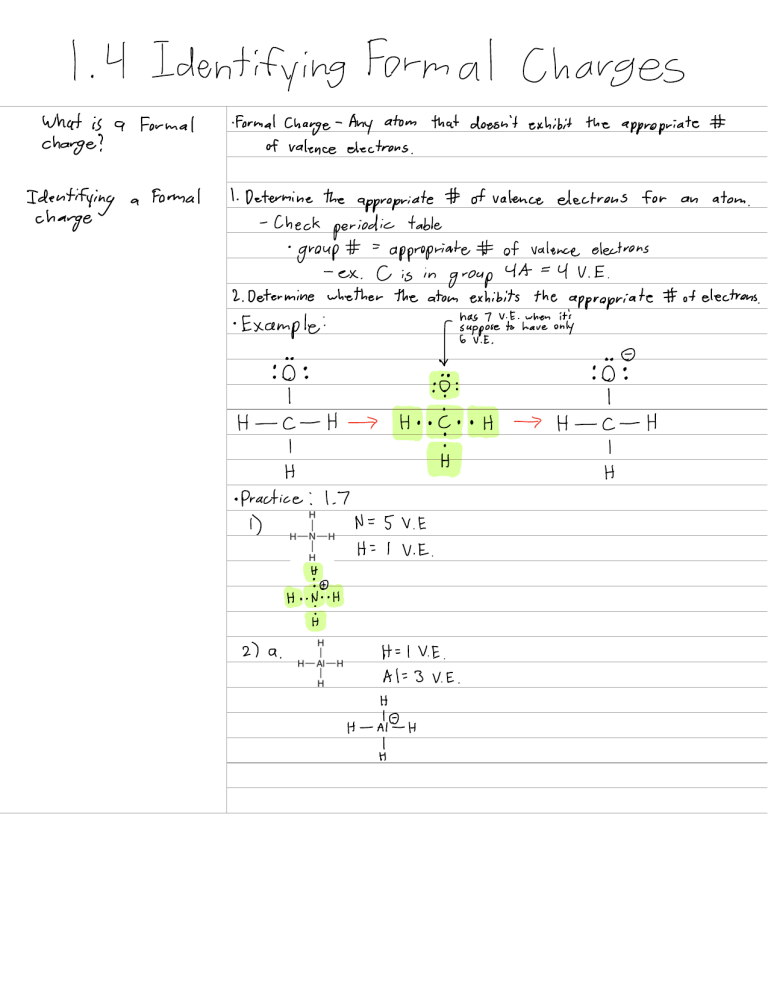
1 4 Identifying Formal Charges What is a Formal change Identifying charge a Formal FormalCharge Any atom thatdoesn'texhibit the appropriate of valenceelectrons 1 Determine the appropriate ofvalence electrons for Check periodic table the'itomistibits theapitipriate 2 DetermineEither Example ft O H I C I H H H c H Practice 1.7 1 D 5VE H I VE H t.lt it H I VE 2 a A 3 VE H H HEH atom of valence electrons appropriate group an eu iah oitIy p H H 1 C 1 H H ofelectron H lVE 0 6VE b d O H l VE 0 6V E 0 t I N 5 VE III e 4VE YEE E EYV E 9 0 h i C 6 E I IE to EYVE 0 6 E N 5V E Practice 1.8 a Bit H DEH it b NH H Celts P H É Yc Practice 1.9 H I VE Polar Covalent 1.5 Induction what are the 3 bond categories comesfrom the electronegativity values of theatom 1 Covalent 2 PolarCovalent sharing a bond g g Electronegativity Measure of electrons what is the difference in the electronegativity values of the 2 atoms Bonds the ability of an atom to attract Guidelines Covalentbond Ex If difference in electronegativity is PolarCovalent 0.5 Is If difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 1.7 Ex Induction the withdrawal of electrons toward the lesselectronegative atom symbol grggibal Ionic band If Ex difference in electronegativity is 3.5 1.7 09 5 ocating Partial Charges Identify all polar covalent bonds show any partial Resultingfrom Induction charges that result from inductive effects step 1 Identify all polarcovalent bonds is f ya Step 2 Determine the direction of each dipole Step 3 Indicate the location of partialcharges 2 1 Molecular Representations Different Representations Practice 2.1 Draw a Lewisstructure a for each of the H.CCHOCH.CHcH3 a H H L H Y E EEE H C H H b CHCH CHCH.CH OH tt I compound C CH CH Colt H ÉÉÉÉ I HH G H H H E Practice 2.2 Ecco a HOCH CH CH CHO I c go a É c CHzCOzCHzCHz Hiiiii e É É it Practice 2.3 Identify the to Esp of sp hybridized carbon atoms É3 H H y't't 2.2 Bond Line Structures what are therules to ravingbond line fractures Bond time structures Rules 1 Carbon atoms in a straight chain should be drawn in a zigzag format 2 When drawing doublebonds draw all bands as far as possible 3 Whendrawingsingle bonds the direction in which the bond are drawn is irrelevant 4 Allheteroatoms atomsotherthan C and H mustbe drawn andany H atoms attached to a heteroatom mustalso be drawn 5Never draw a C atom w more than 4 bands Carbons onlyhas 4 orbitals in its valence shell and therefore C atoms can form a maximum of 4 bonds Practice 2.2 Drawing Band Line Structures Step 1 Delete It atoms except for thoseconnected to heteroatoms step 2 Draw in zigzag format keeping triple bands linear Step 3 Delete carbon atoms Practice 2.4 b a Q c O g Practice a 2.5 fit CCCHs H H EH HH É Yd d É it I it it it it g g D CH CA CH CH i C i CH CHz COH cittjitis it d CH CHCH OH HI HH H E fH H E H o H Practice 2.6 CHCH CH É.IE It CHCH EtEt It it it it d it it z 2.3 Identifying Functional Groups what is a functional group group A characteristic group of atoms bonds Functional that possess a predictable chemical behavior R refers to the remainder of the compound usuallycarbon and hydrogen atoms 2.7 Introduction to Resonance hat is Resonance Resonance stabilization Resonance The approach that chemists use to deal w the inadequacy of bond line structures Drawmore than I bond line structure then mentally meld them together q ft Delocalization Stabilizing factor 2T electrons are spread out over 3C atoms of the allylicsystem Resonance Structure Resonance stabilization molecules andions are stabilized by the delocalization of electrons 2.8 Curved what are curved arrows Arrows Curved Arrows tools necessary to draw resonance structures properly They don'trepresent the motion ofelectrons where electrons the arecomingfrom shots where theelectrons shows therules for arrows for curved raving what are esonance structures are going Rules for drawing carved arrows 1 Avoid breaking a single bond 2 Neverexceed an for resonance structures octet for 2nd row elements The violation is difficult to see in bondline structures Not a violation if an a 2nd octet of electrons row element has less than Prentice 2.5 Identifying valid Resonance arrows Determine whether it violates either of the two rules for drawing curved arrows step1 it doesn'tbreak a single bond step 2 Ctonlyhas 3 bands not 4 Thecurved arrow will give the The arrow is correct Practice 2.12 a Catom a 4th bond 5.1 Overview of Isomerism what are isomers Isomers Compounds that are constructed from the same atoms same molecular formula differ in the connectivity of their atoms same molecular formula differ in theirconstitution different compounds w different physical properties same constitution differ in the spatialarrangement of theiratoms 5.1 Practice translepp side H this is not a stereoisomer Iistsg.ge E ble of this trans cis needs to attach to diff groups 5.2 Practice AM I YAY't H H since both double bonds are attached to the same group neither one is are stereoisomers 5.3 Practice I b gag trans stereoisomer chometyoups a stereoisomer gt TEFastereoisomer a stereoisomer stereoisomer 5.2 Intro to Stereoisomerism Chiral objects that aren't superimposable on their Molecular Chirality mirror images 1996 IUPAC re ommended that a tetrahedral carbon bearing 4 diff groups be called chirality center From now on we'll use chiralcenter ÉEF bond sooner No chiral center tow to locate chiral centers step Ignore sp and sp hybridized carbon atoms Remember Groups Hybridization Ipp Step2 Ignore Clt and Cfs groups P Step 3 Identify any carbon atoms bearing 4 different groups Enatiomers when compound is chiral it will have one nonsuperimposable mirror image called its a enantiomer The compound and its mirror image are said to be pair of enantiomers A chiral compound will have exactly ONE a enantiomers Drawing An Enantiomer There are 3 places 1 Behind 2 Next to 3 Beneath side side Behind beneath All produce the same answer 5.3 Designating Configuration Using the Cahn Ingold Prolog system ahn Ingold Prolog SystemStep 1 Assign priorities to each of the 4 groups attached to the chiral center based on atomic number Atom w priority Atom w highest atomic lowest atomic priority 4 step 2 I is assigned highest is assigned lowest Rotate molecule so that the 4th the page on a dash is directed behind Step 3 Then see if the l 2 3 sequence is clockwise or counterclockwise S counterclockwise R Clockwise Assigning Priorities to All 4 Groups