Uploaded by
christianshakobepatinio
Business Combination: Acquisition Method Explained
advertisement

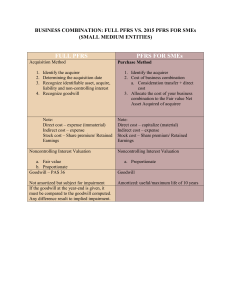
BUSINESS COMBINATION Method of Accounting for Business Combination Prepared by: Rowel Dela Cruz Marc Jomel Navarro BUSINESS A business consists of inputs and processes applied to those inputs that have the ability to contribute to the creation of outputs. 2 BUSINESS COMBINATION Is a transaction or event in which an acquirer obtains control of one or more businesses. Transactions sometimes referred to as 'true mergers' or 'mergers of equals' are also business combinations as that term is used in this PFRS. 3 Old Method Pooling of Interest Method Pooling method is pooling away By FASB Current Method Purchase Method Purchase method has been replaced or renamed. Acquisition Method Acquisition Method is the method that we currently using. 4 COMPARISON: Pooling Interest method • No revaluation to the fair market value under this method. But it is recorded at Book value. • No goodwill as a result of using this method. • No excess of cost over the book value exist, and no goodwill is recorded. • Revaluating process based on the Fair market value. • There is a Goodwill as a result of using this method. • Any excess of cost over the fair value of net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. ACQUISITION METHOD 5 ACQUISITION METHOD The acquisition method (called the 'purchase method' in the 2004 version of IFRS 3) is used for all business combinations. [IFRS 3.4] Steps in applying the acquisition method are: [IFRS 3.5] 1.Identification of the 'acquirer' 2. Determination of the 'acquisition date’ 3. Determine the consideration given by the acquirer. 4. Recognition and measurement of the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any noncontrolling interest (NCI, formerly called minority interest) in the acquiree 5. Recognition and measurement of goodwill or a gain from a bargain purchase 6 STEPS IN APPLYING THE ACQUISITION METHOD 1. IDENTIFY ACQUIRER Entity that transfer cash and other assets where the business combination is effective in this manner. The acquirer is usually the entity with the largest size of assets, revenues or profit. 2. DETERMINE ACQUISITION DATE An acquirer considers all the pertinent facts and circumstances when determining the acquisition date (the date on which it obtains control of the acquiree). 3. DETERMINE CONSIDERATION GIVEN Consideration given or price paid by the acquirer is assumed to be fair value of the acquiree as an entity. IFRS 3 requires these consideration to be measured at fair value on the acquisition date. Consideration can be cash, non-cash, bonds, ordinary share or preference share. 4. RECOGNITION AND MEASUREMENT OF IDENTIFIABLE ASSETS, LIABILITIES AND NCI Recognition principl. Identifiable assets acquired, liabilities assumed and non-controlling interest in the acquiree are recognized separately from Goodwill. Measurement principle. All assets acquire, liabilities assumed are measured at acquisition date fair value. 7 STEPS IN APPLYING THE ACQUISITION METHOD Consideration Paid Pxx Fair Value of the Net asset of Acquiree Goodwill (Gain on Bargain Purchase) (xx) xx/(xx) 4. RECOGNITION AND MEASUREMENT OF IDENTIFIABLE ASSETS, LIABILITIES AND NCI 2. DETERMINE ACQUISITION 3. DETERMINE CONSIDERATION DATE GIVEN 5. GOODWILL OR A GAIN FROM An acquirer considers all the A BARGAIN PURCHASE Consideration given or price Goodwill is measured as the difference pertinent facts and paid by the between: acquirer is circumstances when assumed to be fair value of the the aggregate of (i) the valuedetermining of consideration transferred (generally at fair value), (ii) the amount of any the acquisition acquiree as an entity. IFRS 3 non-controlling interest anddate (iii)(the in adate business combination in stages,tothe acquisition date fair on which it requiresachieved these consideration obtainsequity control of the be measured fair value on of the acquisition date value the acquirer previously-held interest in the acquiree,atand the net acquiree).and the liabilities theassumed(measured acquisition date. amounts of the identifiable assets acquired accordance with IFRS 3 ) Consideration can be cash, non-cash, bonds, ordinary share or preference share. 8 SAMPLE PROBLEM: The condensed Balance sheet of LYLIA Corporation as of December 31,2022 is shown below: BOOK VALUE FAIR VALUE P 200,000 P 225,000 Plant Assets 300,000 400,000 Total Assets P 500,000 Liabilities P 150,000 Current Assets Capital Stock,P10 par 50,000 Additional Paid in Capital 100,000 Retained Earnings 200,000 Total Equities P 500,000 On January 1, 2023, ATLAS Company paid P500,000 for the net asset of LYLIA Corporation. How much is the Goodwill as a result of the merger? 9 ANALYZING THE PROBLEM: BOOK VALUE FAIR VALUE P 200,000 P 225,000 Plant Assets 300,000 400,000 Total Assets P 500,000 Liabilities P 150,000 Current Assets Capital Stock,P10 par 50,000 Additional Paid in Capital 100,000 Retained Earnings 200,000 Total Equities STEPS: 1. Identification of the 'acquirer’ 2. Determination of the 'acquisition date’ 3.Determine the consideration given by the acquirer. 4. Recognition and measurement of the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest (NCI, formerly called minority interest) in the acquiree 5. Recognition and measurement of goodwill or a gain from a bargain purchase P 500,000 On January 1, 2023, ATLAS Company paid P500,000 for the net asset of LYLIA Corporation. How much is the Goodwill as a result of the merger? 10 COMPUTATION OF GOODWILL: Consideration Paid Pxx Fair Value of the Net asset of Acquiree Goodwill (Gain on Bargain Purchase) (xx) xx/(xx) Consideration Paid Fair Value of the Net Asset of the Acquiree Goodwill Fair Value of Assets – Fair Value of Liabilities 225,000 + 400,000 – 150,000 P500,000 ( 475,000) 25,000 11 Journalizing: Current Assets 225,000 Plant Assets 400,000 Goodwill 25,000 Liabilities Cash 150,000 500,000 12 THANK YOU FLORA@CONTOSO.COM Prepared by: Rowel Dela Cruz HTTP://WWW.CONTOSO.COM/ Marc Jomel Navarro