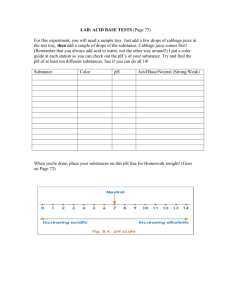
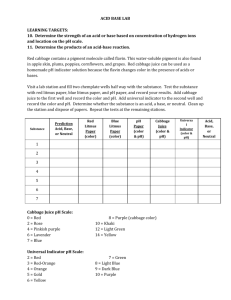
MEASURING pH Introduction The chemistry of a substance makes the substance either an acid or a base. Acids are compounds that are chemically bound with the hydrogen ion (H+). The hydrochloric acid (HCl) in your stomach is an example of an acid. Bases are compounds that contain a combination of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H), called the hydroxide ion (OH-). The common red/purple cabbage contains a substance called anthocyanin that you can use as an indicator. An indicator changes color when an acid or base is present. It indicates if the substance tested is an acid or a base based on a color change. In this lab you will use an anthocyanin solution to create a simple pH scale. What chemical properties do you think anthocyanin has that enables it to be used as an indicator? At neutral pH, anthocyanin is a deep purple-blue color. When an acid is added to it, it turns red or pink. When a base is added, it turns light blue or greenish-blue. The strength of an acid or base can be determined by the degree of color change observed in the anthocyanin indicator. Essential Question What are the properties of common household acids and bases? How can pH be used to determine what common household products are acids and which are bases? Materials Red/purple cabbage 250 mL beaker coffee filter strainer disposable pipettes test plate ziplock baggie small paper cups milk of magnesia lemon juice ammonia vinegar baking soda solution stock solutions for pH 4, 6, 8, 10 marking pencil Procedure (using red cabbage or red cabbage extract concentrate) Red Cabbage 1. Tear up 2 leaves of red cabbage and place these pieces into a zip-lock bag. 2. Add 100 ml of warm water and close the bag tightly. Use your hands to press the leaves inside the bag until the water turns a medium blue. This will be your indicator. 3. Filter the indicator through a coffee filter and discard the cabbage pieces. OR Red Cabbage Extract 1. Add 2 scoops powder to 100 ml distilled or tap water. 2. Stir with pipet. 3. Filter as needed. ASIM L2pH Acids, Bases, and pH student handout, revised 4/2016 Page 1 of 3 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Label four test plate wells according to the pH solution they will contain (4, 6, 8, 10). Dispense 5 drops of the pH solutions 4 through 10 into each of the labeled wells. IMPORTANT: USE A DIFFERENT PIPET FOR EACH pH SOLUTION. DO NOT CROSS CONTAMINATE THE pH SOLUTIONS! Using a disposable dropper, add 3 drops of anthocyanin indicator solution (cabbage liquid) into each well. (You may need to add more drops of indicator solution if weak.) You have now created a pH meter. Record the final color of each pH well on your lab data sheet. Your teacher will choose five (5) common substances for which you will measure the pH, using your pH meter as a guide. Dispense five (5) drops of each substance into 5 wells. Using the disposable pipette, add 3 drops of the anthocyanin indicator solution into each substance. Using the pH meter you created, infer the pH of each substance you tested. Record the color change in Table 1. Check the accuracy of your pH meter by using the pH tester or pH paper strips to test each substance. In Table 2, record the pH of each substance after testing the substances with the pH tester or paper indicator. ASIM L2pH Acids, Bases, and pH student handout, revised 4/2016 Page 2 of 3 Student Data Sheet Measuring pH Name:_____________________________ Date: _____________________________ Observations Table 1 Cabbage Juice pH pH 2 pH 4 pH 6 pH 8 pH 10 Color of Juice Table 2 Substance Approximate pH Based on Created Scale Actual pH Using pH Tester or Paper Ammonia Lemon Juice Soda Water Vinegar Milk of Magnesia Analysis 1. From the results of your tests, INFER which substance was the strongest acid. __________________________________ 2. Of the substances tested, INFER the strongest base.___________________________ 3. INFER the natural pH of a head of red/purple cabbage.____________ 4. A bush called the hydrangea has flowers that contain anthocyanin. A single plant may produce flowers that are pink, purple, or blue, depending on environmental conditions. HYPOTHESIZE what conditions may produce pink flowers. 5. Lye has a chemical formula NaOH. DEDUCE what kind of substance you would use to neutralize lye. _____________________ ASIM L2pH Acids, Bases, and pH student handout, revised 4/2016 Page 3 of 3