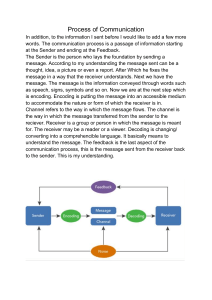
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY (MIL) Which of the pictures below illustrate media? These are the pictures which are related to media Learning Competencies The learners will be able to… describe how communication is affected by media and information (MIL11/12IMIL-IIIa-1); and Learning Objectives: a. Identify the elements of a communication process. b. Describe how media and information influence communication. • What the picture tells you about? the act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else Communication (http://www.merriam-webster.com) the process of sending and receiving messages through verbal and nonverbal means (Richard Nordquist, 2019) Two Types of Communication 1. Verbal Communication - refers to the form of communication in which message is transmitted verbally, communication is done by word of mouth and piece of writing. It is divided into two: Oral and Written Communication Two Types of Communication 2. Non-verbal Communication - the sending or receiving of wordless messages. - gesture, body language, posture or facial expression - all about the body language of the speaker The Communication Process The Communication Process 1. Source Communicator/Sender The source imagines, creates, and sends the message. This process of turning thoughts into communication is called Encoding. The Communication Process 2. Message The message is the stimulus or meaning produced by the source for the receiver or audience. Content of the communication process The Communication Process 3. Channel The channel is the way in which a message or messages travel between source and receiver. Verbal Written Non-verbal Words Text Body Language The Communication Process 4. Receiver The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the messages in ways both intended and unintended by the source. He/she listens, sees, touches, smells, and/or tastes to receive a message. The process or turning communication into thoughts is called Decoding. The Communication Process 5. Feedback When the receiver responds to the source intentionally or unintentionally, he/she is giving feedback. Feedback is composed of messages the receiver send back to the source. Reaction of the Receiver The Communication Process 6. Environment - is the atmosphere, physical and psychological, where an individual sends and receives messages - it can also include factors like formal dress that may indicate whether a discussion is open and caring or more professional and formal The Communication Process 7. Context - the context of the communication interaction involves the setting, scene, and expectations of the individuals involved. - a professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behabior among the participants The Communication Process 8. Interference or Noise - this is anything that blocks or changes the source’s intended meaning of the message Identify the following: Communicator/ Sender? Message? Medium/ Channel? Receiver? Effect? How media and information influence to communication? MEDIA INFORMATION provides a platform for allows people to connect people to shareMEDIA ideas and with others who might provides a platform forshare people thoughts similar interests to share ideas and thoughts How media and information influence to communication? Play a vital role in globalization MEDIA connected todifferent people around the world provides a platform for people Tools in sharingtoinformation, ideas, personal share ideas and thoughts messages Sources of information and entertainment REFERENCES Media and Information Literacy Curriculum Guide by DepEd Media and Information Literacy by Boots C. Liquigan, Diwa Learning Systems Inc. UNESCO Media and Information Literacy Curriculum for Teachers http://faculty.georgetown.edu/irvinem/CCTP748/Carey-summarycomm-culture.html http://juliemartin.org/juliemartin-audiencesreception.pdf http://communicationtheory.org/category/communicationmodels/page/2/