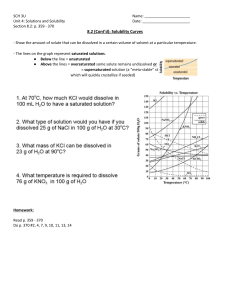
Chapter 2, Lesson 2: Factors Affecting Solubility In this lesson you must be familiar with the following terminologies and personages …. (please refer to your textbook pp. 63 – 95) Factors Affecting Solubility Solubility – the amount of a substance that dissolves in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature to produce a saturated solution. Saturated solution – a solution where no more solute appears to dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Unsaturated solution – a solution that contains less solute than a saturated solution. Supersaturated solution – a solution that contains a greater amount of solute than a saturated solution. Seeding – the process of inducing crystallization to occur by adding a crystal to a supersaturated solution. Nature of the solute and solvent – substances with similar intermolecular forces of attraction dissolve in each other and is usually expressed as “like dissolves like”. Temperature – the solubility of most molecular and ionic solids increases with the increase in temperature (endothermic). Pressure – pressure has almost no effect in the solubility of solids and liquids, but has a srong effect on the solubility of gases. William Henry found out Henry’s Law. The solubility of a gas in a liquid at a given temperature is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas over the solution. Colligative properties – properties that depend on the amount of dissolved solute (concentration) and not on the kind or chemical nature of the solute. Electrolyte solutions / nonelectrolyte solutions Vapor pressure reduction. Adding a nonvolatile solute to a pure solvent lowers the vapor pressure of the solution at any given temperature. It follows that a solution must be heated to a higher temperature than that of a pure solvent in order to boil. Francois Marie Raoult developed Raoult’s Law. The vapor pressure of a solution, PA, is equal to the mole fraction of the solvent, XA, times the vapor pressure of the pure solvent, PAO. Boiling point elevation Freezing point depression Osmotic pressure ****