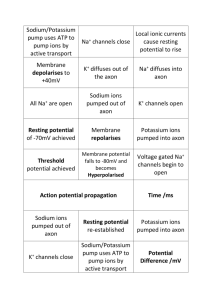
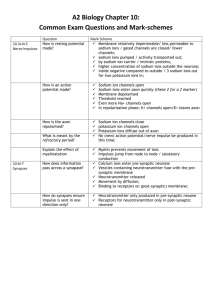
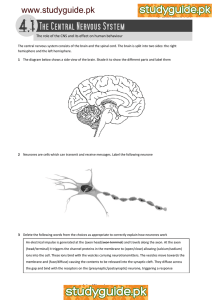
The neurone has a resting potential when it is not transmitting a nerve impulse The energy of the stimulus triggers some of the sodium voltage gated ion channels to open making the membrane more permeable to sodium ions. Sodium ions can therefore diffuse across the neuronal membrane into the axon The change in charge causes more sodium ion channels to open Potassium ions now diffuse out of the axon. This reduces the charge, resulting in the inside of the axon becoming more negative than the outside Initially, lots of potassium ions diffuse out of the axon resulting in the inside of the axon becoming more negative than in its resting state. This is known as hyperpolarisation. The voltage gated potassium channels now close. Sodium – Potassium pumps cause sodium ions to move out of the cell and potassium ions to move in. The axon returns to its resting potential When the potential difference reaches +40mV, the sodium ion channels close and the potassium channels open. This makes the membrane now impermeable to sodium ions and permeable to potassium ions. The neurone has a resting potential when it is not transmitting a nerve impulse The energy of the stimulus triggers some of the sodium voltage gated ion channels to open making the membrane more permeable to sodium ions. Sodium ions can therefore diffuse across the neuronal membrane into the axon The change in charge causes more sodium ion channels to open When the potential difference reaches +40mV, the sodium ion channels close and the potassium channels open. This makes the membrane now impermeable to sodium ions and permeable to potassium ions. Potassium ions now diffuse out of the axon. This reduces the charge, resulting in the inside of the axon becoming more negative than the outside Initially, lots of potassium ions diffuse out of the axon resulting in the inside of the axon becoming more negative than in its resting state. This is known as hyperpolarisation. The voltage gated potassium channels now close. Sodium – Potassium pumps cause sodium ions to move out of the cell and potassium ions to move in. The axon returns to its resting potential