Factors Affecting Reaction Rate: Temperature, Concentration, Catalysts
advertisement

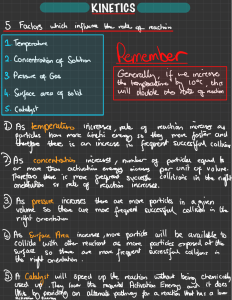
Factors effecting the rate of a reaction: Temperature (increase): - particles gain kinetic energy - particles collide more often and more frequently with energy more than activation energy - so more frequent successful collisions happen - rate of reaction is increased. Concentration of the reactant particles (increase): - there are more particles per unit area - collisions between particles happen more frequently - more successful collisions between reactant particles - rate of reaction is increased Note: particles do not gain energy when concentration is increased unlike in temperature Concentration of non-reactant particles (increase): - adding a non-reactant decreases the concentration (particles per unit area) of the reactant particles and they end up getting apart. - as particles increased, collisions between particles overall increases, but a successful collision is needed for the reaction to happen, which is a collision between reactant particles, now as their concentration has decreased, they collide less so even though collisions have increased, successful collisions have decreased - so this decreases rate of reaction Pressure of a gas reactant (increase): - increasing the pressure of a gas makes them collide more. - as collisions are more, the rate of successful collsions (collisions between reactant particles) increases as a result - the rate of reaction is increased. Surface area of solid reactant (increase): - more surface area means more exposure to the other reactant particles - as a result of higher exposure, there are more collisions between reactant particles - increasing the successful collisions - rate of reaction is increased Inorganic catalyst: - A catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction without being used up or altered itself - so rate of reaction increases, but the catalyst remains unsed and can be used for a new batch of the same reaction. Note: Inorganic catalysts, are not made from organic material, transition metals and their compounds usually act as inorganic catalysts. They are not temperature sensitive, however, some catalysts such as V2O5 [Vanadium (V) oxide] are inactive below a certain temperature. Organic catalyst (enzymes): - Organic catalysts, such as enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up the rate of reaction without being used up or altered themselves. - They are highly temperature and pH sensitive - They are inactive or less active at temperatures below their optimum temperature - They denature/get destroyed at high temperatures more than their optimum temperature - They are the most active at their optimum temperature, giving the highest rate of reaction at that temperature. Surface area of catalyst in a reaction with gas reactants (increase): - If the reactants in a reaction are gases, the catalyst's surface area can determine the rate of reaction too. - With greater surface area of catalyst, the gas reactants get more exposed to it. - with more exposure, more successful collisions (collisions between gas reactant particles) can be catalysed. - so rate of reaction increases By Rafay Saqib