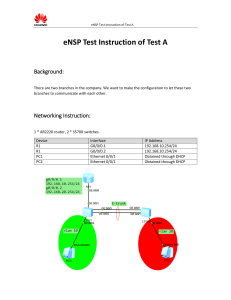
31277 SBA Modelling Instructions - PRACTICE Topology Addressing Table Device Name ISP South [ [ R1 Na m e ] [ [ R1 Na m e ]G 0 /0 North SWU Interface/Default Gateway Network address/prefix Lo1 111.111.111.111/32 S0/0/1 200.200.10.1/30 S0/0/0 200.200.10.2/30 G0/0 172.20.11.2/25 Lo1 172.20.2.1/32 G0/0 172.20.11.1/25 G0/1.10 172.20.10.1/26 G0/1.20 172.20.20.1/26 G0/1.50 172.20.50.1/28 VLAN 50 172.20.50.12/28 F0 / 0 Default Gateway 172.20.50.1 SWD VLAN 50 172.20.50.13/28 Default Gateway 172.20.50.1 NIC VLAN 50 172.20.50.10/28 Default Gateway 172.20.50.1 NIC VLAN 10 DHCP [ [ R3 Na m e ] PCU PC1 Page 1 of 4 Device Name PC3 Interface/Default Gateway Network address/prefix NIC VLAN 20 172.20.20.10/26 Default Gateway 172.20.20.1 Introduction You will be assessed on the following skills: Basic device configurations Configuration of static routing Configuration of OSPFv2 routing Customization of OSPF. Configuration of VLAN and Inter-VLAN routing Configuration of DHCP Configuration of dynamic NAT with PAT. Configuration of ACLs. Instructions Part 1: Configure the basics of the network Step 1: Basics. a. Configure device name (case sensitive). b. Configure IP addresses on the interfaces following the IP addressing table. Configure default gateway where needed. Enable interfaces where needed. Note: Some interfaces should be changed to obtain IP address from DHCP after implementing DHCP. Part 2: Configure VLAN and Inter-VLAN Routing Step 1: Configure VLANs on Switches a. Configure VLANs: VLAN 10, 20 and 50 b. Configure trunk link to allow eligible VLANs and with native VLAN 50. c. Assign access ports to VLAN 10, 20 and 50 according to the following table On SWU: VLAN Interface VLAN 50 F0/10 On SWD: VLAN Interface VLAN 10 F0/10 VLAN 20 F0/15 Step 2: Configure Inter-VLAN Routing on North a. Configure subinterfaces. b. Assign IP addresses to the subinterfaces according to the IP address table. c. Use the VLAN number as the subinterface ID. Part 3: Configure Static Routing to and from ISP Configure static routing between ISP and South with next hop IP address. Ensure ALL internal LAN addresses (including translated) are routed. Internal WAN addresses do not need to be routed in static routing. Note: your static routing may need to be revised after implementing NAT. Part 4: Configure OSPF Step 1: Activate OSPF. Use process ID 1 and area 0 for OSPF activation on routers: South and North. Activate OSPF using network statements and inverse masks on the routers. All internal networks (including LANs and WANs need to be advertised). Step 2: Customise OSPF operation. a. Automatically distribute the default route on South to all routers in the network. b. Configure OSPF so that routing updates are not sent into networks where OSPF updates are not required. Part 5: Configure NAT Step 1: Configure dynamic PAT. a. Create access list 1 to allow only all addresses in the internal networks. b. Create a NAT pool named PUBLIC_ACCESS. It should use address in the range of valid host address in 200.200.10.8/29. c. Configure NAT to dynamically use the addresses in the pool for all traffic entering and exiting the Internal network. Remember that it is likely that more than 6 hosts will be accessing traffic on the Internet. Verify that the translations are occurring. Part 6: Configure DHCP Step 1: Configure South as DHCP server a. Configure a DHCP address pool for North LAN VLAN10, with the pool 172.20.10.0/26, use pool name DHCPPOOL, exclude the first 9 valid host addresses, set PC1 as obtaining address from DHCP. b. Configure the DNS server address as 209.165.200.225 c. IP domain name ccna-lab.com Step 2: Configure DHCP relay agent a. Configure North be the DHCP relay agent. b. Configure DHCP relay agent to forward all DHCP requests to the DHCP server use the helper address 172.20.11.2. Part 7: Test Connectivity and troubleshoot Test connectivity and troubleshoot if needed. Your test may include but not limit to: • • • Internal devices should have end-to-end connectivity between each other. Internal PCs should have end-to-end connectivity to ISP Lo1. Internal addresses should get successfully translated. Part 8: Save configuration, save file and upload to Canvas a. Confirm your completion % in the activity. b. Save running config to startup config. c. Save the file in .pka file. Confirm to save your changes. Note: If you wish to double check your configuration is saved, after saving, close the file and re-open the file to see if your configuration and completion % is saved correctly. d. Upload the .pka file to Canvas. Marking criteria: Criteria Basics Routing Physical Interface status (up/up) IP addressing and DHCP NAT Switching Pts:63 4 14 3 30 4 8 In the pka activity, you will see a completion %, which is automatically calculated by points you got/total points. Your completion will be converted to max 30% of the total mark of the subject. For example, if your completion is 80% in the pka acticity, you will get 80% x 30% = 24% of the total mark of the subject.