file el arkam(DONE AND TOOK NOTES, HERE'S THE FILE IF YOU WANNA TAKE THE TEST AGAIN ON THE WEBSITE)
advertisement

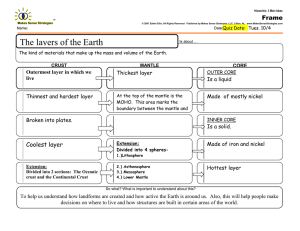
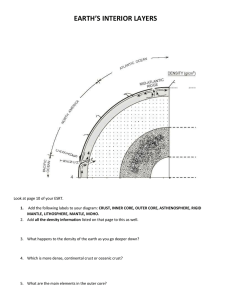
Multiple Choice Questions for Interior of the Earth - Chapter 17 Each chapter will include a few questions designed to test your knowledge of material covered in the chapter and in the Internet-based resources. Your answers are not being recorded. Try the following. 1. What is the approximate distance from the surface to the center of he Earth? 1,000 miles 4,000 miles 10,000 miles 40,000 miles 2. When sesimic waves pass across the boundary between two different materials, ___________. the waves refract the waves reflect the waves change in velocity all of the above 3. Which region in the Earth is about 85% iron? A B C D 4. Which region in the Earth molten? A B C D 5. In which region of the Earth is conduction the dominant heat transfer mechanism? A B C D 6. How long does it take a P-wave to travel through the Earth? 1 minute 5 minutes 10 minutes 20 minutes 7. Which of the following statements is false? the P-wave shadow zone is larger than the S-wave shadow zone. Seismic waves follow curved paths through the interior of the Earth P waves travel more slowly in the outer core than in the lower mantle Liquids do not transmit S waves 8. The S wave shadow zone is caused by the _________ . the crust-mantle boundary the outer core the lower mantle the inner core 9. The S-wave shadow zone extends from _____ to 180 o angular distance from the earthquake focus on one side and from ______ to 180o on the other. 45 degrees 75 degrees 105 degrees 145 degrees 10. The boundary between the mantle and the core lies at a depth of approximately ________ . 300 kilometers 1000 kilometres 3000 kilometers 5000 kilometers 11. Continental crust can be up to ______ kilometers thick. 5 35 65 100 12. Where do P waves travel the fastest? upper mantle lower mantle outer core inner core 13. Which of the following statements about the Moho is false? seismic waves speed up as they pass across the Moho heading downward the Moho separates denser rocks below from less dense rocks above the Moho separates the crust from the mantle the Moho marks the top of a partially molten layer 14. After melting of a continental ice cap, the surface of the continent will tend to __________ . rise sink sink or rise depending on the thickness of the ice cap remain the same - ice does not weigh that much 15. If the Earth cooled only by conduction, heat from depths greater than ______ kilometers would not yet have reached the surface. 20 100 400 2000 16. The mechanical transfer of heat by vibration of atoms and molecules is called __________ . radiation conduction magnetism convection 17. What drives plate tectonics? thermal convection thermal conduction solar energy erosion 18. In a deep mine, temperatures increase at the rate of ________ . 3 degrees C per kilometer 30 degrees C per kilometer 300 degrees C per kilometer 1 degree C per kilometer 19. Where is the Earth's magnetic field generated? in the crust in the mantle in the outer core in the inner core 20. At what temperature do materials loose their permanent magnetism? 100 degrees C 250 degrees C 400 degrees C 550 degrees C 21. Which of the following statements is true? the Earth's magnetic poles are aligned with the Earth's rotation axis the Earth's magnetic poles are inclined approximately 11 degrees from the Earth's rotation axis the Earth's magnetic poles are inclined approximately 45 degrees from the Earth's rotation axis the Earth's magnetic poles are perpendicular to the Earth's rotation axis 22. The Earth's magnetic field reverses itself roughly every ________ . 50 years 5,000 years 500,000 years 50 million years 23. Permanent magnetism acquired by minerals in igneous rocks during crystallization is called __________ magnetization. depositional remnant paleoremnant magnetism silicate thermoremanent magnetism 24. Which of the following rock types would be most likely to record the magnetic field at the time the rock formed? an alluvial conglomerate a basaltic lava flow an evaporite deposit of halite a schist 25. Which one of the following lists most accurately describes oceanic crust? basaltic - density of 3.0 g/cm3 granitic - density of 3.0 g/cm3 quartz arenites - density of 2.6 g/cm3 basaltic - density of 2.6 g/cc 26. The Moho separates: the outer core from the inner core the lithosphere from the asthenosphere the asthenosphere from the Mesosphere the crust from the mantle 27. Which one of the following term associations is FALSE? asthenosphere --- plastic behavior lithosphere --- rigid solid outer core --- right solid continental crust --- rigid solid 28. To induce a positive Bouguer anomaly, a rock unit should have the following property: transmit only P waves be denser than the surrounding materials be less dense than the surrounding materials be magnetic 29. The lithosphere includes: crust and uppermost, rigid mantle outer core and inner core asthenosphere and mesosphere outer core and lower mantle 30. A cooling magnetic material _________ its magnetic character at its Curie temperature: gains looses neither of these happens 31. What region of the Earth takes up the greatest volume? the crust the outer core the inner core the mantle 32. Which of the following terms describes the mechanical behavior of a part of the Earth? the continental crust the oceanic crust the lithosphere the mantle 33. The continental crust consists mainly of _________. granitic rocks basaltic rocks ultramafic rocks gabbroic rocks 34. The oceanic crust consists mainly of _________. granitic rocks basaltic rocks ultramafic rocks gabbroic rocks 35. The mantle consists mainly of _________. granitic rocks basaltic rocks ultramafic rocks gabbroic rocks 36. The boundary between the Earth's crust and mantle was first discovered by __________. analyzing seismic waves deep continental drilling detailed geologic mapping paleomagnetic studies 37. How fast do P-waves travel through granite? 4 kilometers per second 6 kilometers per second 8 kilometers per second 10 kilometers per second 38. Which of the following statements is false? the crust-mantle boundary is called the Mohorovicic discontinuity the oceanic crust consists of basalt and gabbro the crust is less dense than the mantle P-waves travel faster in the crust than in the mantle 39. An ophiolite may not include a piece of____________. continental crust oceanic crust upper mantle the Moho 40. Which of the following regions consists primarily of olivine and pyroxene? continental crust oceanic crust upper mantle the core 41. Which of the following statements is false? the asthenosphere lies beneath the lithosphere the asthenosphere is stronger than the lithosphere the asthenosphere rises close to the surface beneath mid-ocean ridges the asthenosphere is partially molten 42. The lithosphere is approximately _________ kilometers thick 25 100 250 2900 43. Which of the following statements is true the lithosphere contains the crust the crust contains the lithosphere the lithosphere and crust are different terms for the same part of the Earth the lithosphere and crust are totally separate parts of the Earth 44. The sharp increase in velocity of S-waves at 400 and 670 kilometers depth in the mantle are probably caused by ___________. changes to more compact mineral structures changes in the composition of the mantle changes in the temperature of the mantle changes in the pressure of the mantle 45. What element makes up most of the Earth's core? silicon oxygen iron nickle 46. The boundary between the inner core and the outer core lies at a depth of ______ kilometers 700 2900 5100 6400 47. How thick a continental root would be produced by a 3 kilometer thick continental ice sheet? about 1 kilometers about 2 kilometers about 10 kilometers about 30 kilometers 48. Which of the following statements best describes the nature of the core-mantle boundary? the core-mantle boundary is smooth the core-mantle boundary is rough with a topography of about 5 kilometers the core-mantle boundary is rough with a topography of about 100 kilometers the core-mantle boundary is rough with a topography of about 400 kilometers 49. Which of the following statements regarding the inner core is true? P waves do not travel through the inner core Primary S waves (those generated at the focus of an event) travel through the inner core P waves travel through the inner core at a higher velocity than S waves travel through the inner core the inner core is thought to be a liquid Try These Fill Ins Return to the Physical Geology Home Page