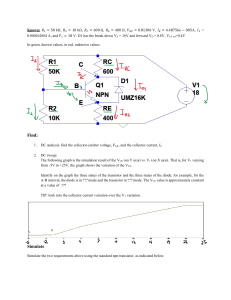
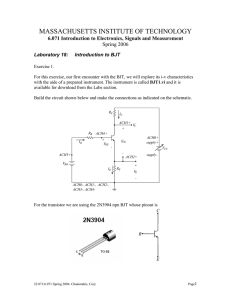
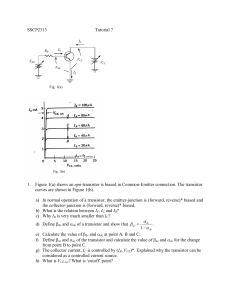
EMK11303 – ELECTRONICS 1 Tutorial 4 (Bipolar Junction Transistor – BJT) 1. Why is the base current in a transistor so much less than the collector current? 2. Figure 4.1 shows a base current of 50µA is applied to transistor and a voltage drop of 4V is dropped across RC. Determine: (a) αDC (b) βDC 2kΩ 100kΩ Figure 4.1 3. Assume that the transistor in Figure 4.1 is replaced with one a having a βDC of 150. Given that VCC = 10V and VBB 2.5V. Determine: (a) IB (b) IC (c) IE 4. The BJT circuit in Figure 4.2 has hFE = 200, determine (a) base current (b) base resistance Figure 4.2 5. For both circuits in Figure 4.3, determine: (a) VCE Prepared by : Dr Liew Hui Fang Page 1 EMK11303 – ELECTRONICS 1 (b) VBE (c) VCB (d) whether or not the transistors are saturated? RC 200 Ω RB 4 kΩ VCC 15V RB 30 kΩ βDC VBB 5V RC 400 Ω βDC VBB 4V 50 Figure 4.3 (a) VCC 10V 150 Figure 4.4 (b) 6. Based on Figure 4.4, determine the terminal voltages of transistor with respect to the ground and also determine VCE, VBE and VCB. VCC 10V VBB 5V RE 5 kΩ Figure 4.4 7. A 50mV signal is applied to the base of a properly biased transistor with r’e = 10 Ω and Rc = 600 Ω. Determine the signal voltage at collector. 8. Determine the value of collector resistor in an npn transistor amplifier with βDC = 250, VBB = 2.5V, VCC = 9V, VCE = 4V and RB = 100 kΩ. Prepared by : Dr Liew Hui Fang Page 2 EMK11303 – ELECTRONICS 1 9. Based on Figure 4.5, assume VCE(sat) = 0. Determine: (a) value of IC(sat) (b) value of IB necessary to produce saturation? (c) minimum value of VIN is necessary for saturation? 5V 10kΩ βDC 150 1 MΩ Figure 4.5 10. Based on Figure 4.6, assume VCE(sat) = 0. Determine: (a) value of RB required to ensure saturation when VIN = 5V (b) what must VIN be to cut off the transistor? 5V 1.2 kΩ βDC 50 Figure 4.6 Prepared by : Dr Liew Hui Fang Page 3